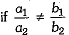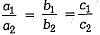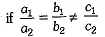CBSE Class 10 Maths Formulas PDF Download
Learning maths formulas in class 10 may seem like a daunting task, but it is actually a crucial step towards building a strong foundation in mathematics. These formulas are not only important for your current class, but they will also be useful in higher-level maths courses and in various industries and careers.
By understanding and memorizing these formulas, you will be able to solve problems more accurately and quickly, which will not only help you perform better in exams but also in real-world applications. Imagine being able to calculate complex measurements or financial transactions with ease, just by recalling a formula you learned in class!
Moreover, as you progress to higher education levels and professional careers, you will encounter more complex problems that build on these basic formulas. So, mastering them in class 10 is an essential step towards your future academic and professional success.
In this EduRev article, you will find all the essential formulas for class 10 Maths, covering all the important units including Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics and Probability, Mensuration, Coordinate Geometry, and Number Systems.
Important Formulas to Memorise for Class 10 Maths
Below, you will find a list of important formulas for class 10 Maths. While it may be tempting to simply memorize them, it's important to remember that the real value of these formulas lies in their application. By practicing these formulas through problem-solving, you will not only reinforce your understanding of them but also build a solid foundation for future studies.
Therefore, I urge you to not just memorize these formulas but also implement them in solving problems. This will help you to develop a better understanding of how these formulas work and how they can be applied in different scenarios. Additionally, practicing these formulas regularly will help to solidify them in your memory and make them easier to recall when needed.
Class 10 Algebra Formulas
In class 10, algebra typically involves solving linear and quadratic equations, simplifying expressions, and manipulating algebraic equations using various techniques such as factorization, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula.
Pair of Linear Equations in two Variables
The general form of a pair of linear equations in two variables x and y is
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0, and
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
where a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 are all real numbers and the coefficients of x and y cannot be zero simultaneously.
Conditions for Consistency/Inconsistency
Consistency/Inconsistency | Conditions |
Unique solution (consistent) | |
Infinite number of solutions (consistent) | |
No solution (inconsistent) |
To learn the methods for solving a system of two linear equations in two variables, it is recommended that you refer to the following resource. Important Definitions & Formulas: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Quadratic Equations
If ax2 + bx + c = 0 is a quadratic equation, then the value of x is given by the following formula: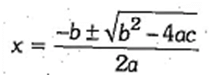
Just plug in the values of a, b and c, and do the calculations. The quantity in the square root is called the discriminant or D.
Nature of Roots
Based on the value of the discriminant, D=(b2 − 4ac), the roots of a quadratic equation can be of three types.
D=(b2 − 4ac) | Nature of Roots |
D>0 | two distinct real roots |
D=0 | two equal real roots |
D<0 | no real roots |
For acquiring the methods to solve quadratic equations, it is suggested that you access the following resource. Important Definitions & Formulas: Quadratic Equations
Algebraic Identities
- (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
- a2 – b2 = (a+b) (a-b)
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
- (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab (a + b)
- (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b)
- a³ + b³ = (a + b) (a² – ab + b²)
- a³- b³ = (a - b) (a²+ab+b²)
- a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
Arithmetic Progressions
General Form of an AP : a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d………………..
Where, ‘a’ is the first term and ‘d’ is the common difference.
Then,
nth term = a + (n-1) d
Sum of the first n terms in Arithmetic Progression;
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n-1)d]
You may access the detailed notes for arithmetic progression: Chapter Notes: Arithmetic Progressions
Class 10 Geometry Formulas
Class 10 Geometry consists of three chapters - Triangles, Circles, and Constructions - which are part of the fourth unit in the mathematics syllabus. In this unit, students learn about the properties of triangles and circles.
Triangles
Types of Triangles
On the basis of Sides:
Types | Description |
Scalene | A triangle with no sides equal |
Isosceles | A triangle with two sides equal |
Equilateral | A triangle with all sides equal |
On the basis of Angles:
Types | Description |
Acute angled | A triangle with all angles acute |
Right angled | A triangle with on angle a right angle |
Obtuse angled | A triangle with one angle an obtuse angle |
Similarity of Triangles
Two triangles are said to be similar, if
- Their corresponding angles are equal
- Their corresponding sides are in the same ratio
Criterias for Similarity of Triangles
Criteria | Description |
AA or AAA | If two angles of one triangle are equal to two corresponding angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar. |
SAS | If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are in the same ratio, then the two triangles are similar. |
SSS | If in two triangles, sides of one triangle are proportional (or are in the same ratio) to the sides of the other triangle, then the triangles are similar. |
Access the following resource on triangles for better understanding: Important Definitions & Formulas: Triangles
Circles
- Circumference of the circle = 2 π r
- Area of the circle = πr2
- Length of an arc of a sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × 2πr
- Area of the sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × πr
- Area of segment of a circle = Area of corresponding sector - area of corresponding triangle
- Where, r is the radius of circle
For more formulas on circles click the link below: Important Formulas: Circles
Class 10 Trigonometry Formulas
Trigonometry in class 10 involves the study of the relationships between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. Students learn about trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent, and how to apply them to find the unknown sides or angles of a triangle.
Trigonometry Formulas and Identities
For a right-angled triangle ABC:
Let opposite = a, Adjacent = b, Hypotenuse = c then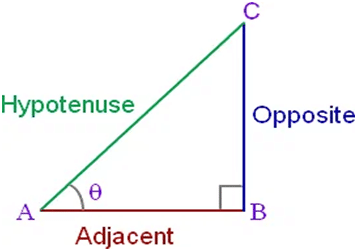
Let opposite = a, Adjacent = b, Hypotenuse = c then
Values of trigonometric functions for different values of angles:
Angle | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
Sinθ | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 |
Cosθ | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 |
Tanθ | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | Undefined |
Cotθ | Undefined | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 |
Secθ | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | Undefined |
Cosecθ | Undefined | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 |
Important Trigonometric Identities
(a) sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
(b) sec2θ = 1 + tan2θ
(c) cosec2θ = 1 + cot2θ
Co-Function Formula
- sin (90 - θ) = cos θ
- cos (90 - θ) = sin θ
- tan (90 - θ) = cot θ
- cosec (90 - θ) = sec θ
- sec (90 - θ) = cosec θ
- cot (90 - θ) = tan θ
- Important Definitions & Formulas: Introduction to Trigonometry
- Important Definitions & Formulas: Some Application of Trigonometry
 |
Download the notes
CBSE Class 10 Maths Formulas
|
Download as PDF |
Class 10 Statistics Formulas
Class 10th Statistics involves the collection, description, analysis, and inference of conclusions from quantitative data.
Mean:
The mean can be calculated by the following formulae :
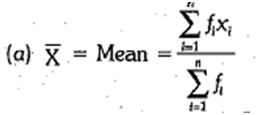

where A = assumed mean and di = xi - A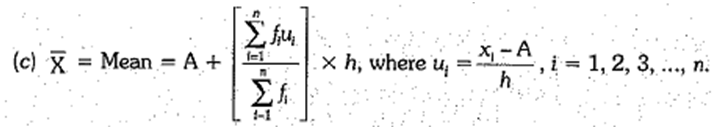
Median:
The median of a grouped frequency distribution can be calculated by: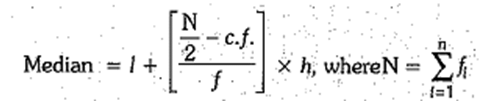
l = lower limit of median class
l = frequency of median class
h = width of median class
c.f. = cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class.
Mode:
The mode of a continuous frequency distribution may be computed by the following formulae: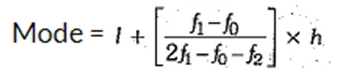
where
l = lower limit of the modal class.
f1 = frequency of modal class.
f2 = frequency of class succeeding the modal class.
fo = frequency of class preceding the modal class.
h = size of the class interval.
Mode = 3 Median - 2 Mean
You may also read: Important Definitions & Formulas: Statistics
Class 10 Mensuration Formulas
It is branch of mathematics which is concerned about the measurement of length ,area and Volume of plane and Solid figure
Surface, Areas and Volumes
Cube and Cuboid formulas
Type | Measurement |
Surface area of Cuboid of Length L, Breadth B and Height H | 2(LB + BH + HL) |
Longest Diagonal of the Cuboid | √(L2 + B2 + H2) |
Volume of a Cuboid | LBH |
Perimeter of Cuboid | |
Surface area of Cube of side L | 6L2 |
Diagonal of the Cube | L√3 |
Volume of Cube | L3 |
Sphere Formulas
Type | Measurement |
Diameter of sphere | 2r |
Surface area of sphere | 4 π r2 |
Volume of Sphere | 4/3 π r3 |
Cone Formulas
Type | Measurement |
Slant height of cone | l = √(r2 + h2) |
Curved surface area of cone | πrl |
Curved surface area of cone | πr (l + r) |
Volume of cone | ⅓ π r2 h |
Cylinder Formulas
Type | Measurement |
Curved surface area of Cylinder | 2 πrh |
Area of two circular bases | 2 πr2 |
Total surface area of Cylinder | 2 πrh + 2 πr2 |
Volume of Cylinder | π r2 h |
You may also read for detailed definition and formulas: Important Formulas: Surface Area & Volumes
Class 10 Coordinate Geometry Formulas
Coordinate Geometry is the study of Geometry with coordinate points. This branch of Mathematics is like a bridge between Algebra and Geometry.
- Distance Formula Between 2 Points P and Q in a 2D Plane

- Section Formula when the Line Segment joining points A(x1,y1) and B(x2,y2) separated Internally by a Point P(x,y)
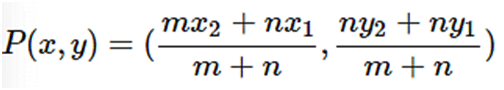
- Heron’s formula for area of the Triangle:
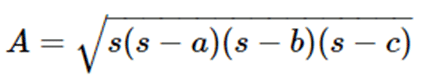
Where ‘s’ is the semi perimeter of the triangle and a, b and c are the sides of the triangle.
Semi perimeter of the triangle, s = (a + b + c)/2
Some other Important Formulas
Here are the formulas of some other important chapters of Class 10 Maths:
- Important Definitions & Formulas: Real Numbers
- Formulas : Polynomials
- Important Definitions & Formulas: Areas Related to Circles
- Important Definitions & Formulas: Probability
EduRev provides the exceptional courses and study material to score well in your Class 10 Board Exams:
Class 10 Preparation Material | |