All Exams >
Class 10 >
6 Months Boards Preparation for Class 10 (CBSE) >
All Questions
All questions of Federalism for Class 10 Exam
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Belgium and Spain has ‘holding together’ federation.
Reason : A big country divides power between constituent states and national government.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Belgium and Spain has ‘holding together’ federation.
Reason : A big country divides power between constituent states and national government.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The power of a large country is divided between constituent states and national government. The central government is more powerful than the states.
The head of the municipal corporation is called______.
- a)Mayor
- b)MLAs
- c)Sarpanchs
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The head of the municipal corporation is called______.
a)
Mayor
b)
MLAs
c)
Sarpanchs
d)
none of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
A mayor is the head of the Municipal Corporation. He is elected by the members of the Municipal Corporation. He is known as the first citizen of the city.
Federations have been formed with the two kinds of- a)routes
- b)states
- c)people
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Federations have been formed with the two kinds of
a)
routes
b)
states
c)
people
d)
none of the above
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
First route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit this is known as coming together federation. The second route is where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national government this is holding together federation.
Which local govt works at district level ?- a)Panchayat samiti
- b)Village panchayat
- c)Zila Parishad
- d)None of the mention above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which local govt works at district level ?
a)
Panchayat samiti
b)
Village panchayat
c)
Zila Parishad
d)
None of the mention above
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Zilla Parishad is located at the apex of the Panchayat system at the district level. It consists of the Chairman of the Panchayat Samities as ex-officio Members, M.L.As, M.P.s of the area. Representatives of women, scheduled castes and tribes and backward class are co-opted as members.
What is the government at Block level called ?- a)Gram Sabha
- b)Gram Panchyat
- c)Panchayat Samiti
- d)Nayay Panchyat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the government at Block level called ?
a)
Gram Sabha
b)
Gram Panchyat
c)
Panchayat Samiti
d)
Nayay Panchyat
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
A Panchayat Samiti (block panchayat) is a local government body at the tehsil level. This body works for the villages of the tehsil that together are called a "development block". The Panchayat Samiti is the link between the Gram Panchayat and the district administration.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Zilla Parishad Chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad.
Reason : Mayor is the head of municipal corporation.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Zilla Parishad Chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad.
Reason : Mayor is the head of municipal corporation.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Panchayat samitis of a district together form the zilla parishad. Zilla Parishad chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad. Municipalities are set up in towns. Mayor is the head of municipal corporation. The reason does not however explain the assertion.
Which of the following statements is not correct about the federalism?- a)There are two or more levels of governments
- b)Different levels of govt, govern the same citizens but each level has its own jurisdiction in specific matters
- c)The jurisdiction of the respective levels or tiers of govt is specified in the constitution
- d)The fundamental provisions of the constitution can be unilaterally changed by the central govt
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about the federalism?
a)
There are two or more levels of governments
b)
Different levels of govt, govern the same citizens but each level has its own jurisdiction in specific matters
c)
The jurisdiction of the respective levels or tiers of govt is specified in the constitution
d)
The fundamental provisions of the constitution can be unilaterally changed by the central govt
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- There are two or more levels (or tiers) of government.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution. So the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government. The highest court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers.
By what name local govt at urban area called?A) Municipality B) Municipal corporation C) Panchayat samiti- a)Only A is true
- b)Only B is true
- c)Both B and C are true
- d)Both A and B are true
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
By what name local govt at urban area called?
A) Municipality B) Municipal corporation C) Panchayat samiti
a)
Only A is true
b)
Only B is true
c)
Both B and C are true
d)
Both A and B are true
|
|
Bhavana Sen answered |
The urban area don't have local governments they have muncipality to manage the city in hindi nagar palika.
Which of the following is not a feature of federalism?- a)There are two or more levels of government
- b)Different tiers of government govern the same citizens
- c)Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified
- d)The central government can order the state government
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a feature of federalism?
a)
There are two or more levels of government
b)
Different tiers of government govern the same citizens
c)
Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified
d)
The central government can order the state government
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. The state government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?- a)18
- b)20
- c)21
- d)22
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
a)
18
b)
20
c)
21
d)
22
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The 22 languages in the Eighth Schedule are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. Which non- Hindi speaking State demanded that the use of English should continue after 1965?- a)Hyderabad
- b)Chennai
- c)Tamil Nadu
- d)Kerala
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. Which non- Hindi speaking State demanded that the use of English should continue after 1965?
a)
Hyderabad
b)
Chennai
c)
Tamil Nadu
d)
Kerala
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
According to the Constitution, the use of English for the official purposes was to stop in 1965. However many non-Hindi speaking states demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu this movement took a militant form. The central government agreed to continue the use of English also with Hindi for official purposes.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.Q. Which of the following subjects comes under 'residuary' subjects?- a)Education
- b)Trade
- c)Banking
- d)Computer software
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Q. Which of the following subjects comes under 'residuary' subjects?
a)
Education
b)
Trade
c)
Banking
d)
Computer software
|
|
Anirudh Goyal answered |
Understanding Residuary Subjects
The term 'residuary subjects' refers to topics or areas of legislation that are not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution or fall outside the three main lists: the Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List. In India, the Union Government has the authority to legislate on these subjects.
Why Computer Software is a Residuary Subject
- The Constitution of India was enacted in 1950, long before the advent of advanced technologies such as computer software.
- As computer software did not exist at the time of the Constitution's framing, it does not fall under the predefined categories of subjects.
- Consequently, since it wasn't explicitly included in any of the lists, it is classified as a residuary subject, allowing the Union Government to create laws governing it.
Comparison with Other Subjects
- Education: This subject is covered under the Concurrent List, allowing both the Union and State Governments to legislate on educational matters.
- Trade: Trade is also included in the State List, meaning States have the authority to regulate trade within their territories.
- Banking: Banking falls under the Union List, empowering the central government to regulate banking institutions and their operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' (Computer software) because it is a subject that emerged after the Constitution was created and does not fit into the existing legislative categories outlined in the Constitution. This categorization allows the Union Government to legislate effectively on new and evolving subjects that arise over time.
The term 'residuary subjects' refers to topics or areas of legislation that are not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution or fall outside the three main lists: the Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List. In India, the Union Government has the authority to legislate on these subjects.
Why Computer Software is a Residuary Subject
- The Constitution of India was enacted in 1950, long before the advent of advanced technologies such as computer software.
- As computer software did not exist at the time of the Constitution's framing, it does not fall under the predefined categories of subjects.
- Consequently, since it wasn't explicitly included in any of the lists, it is classified as a residuary subject, allowing the Union Government to create laws governing it.
Comparison with Other Subjects
- Education: This subject is covered under the Concurrent List, allowing both the Union and State Governments to legislate on educational matters.
- Trade: Trade is also included in the State List, meaning States have the authority to regulate trade within their territories.
- Banking: Banking falls under the Union List, empowering the central government to regulate banking institutions and their operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' (Computer software) because it is a subject that emerged after the Constitution was created and does not fit into the existing legislative categories outlined in the Constitution. This categorization allows the Union Government to legislate effectively on new and evolving subjects that arise over time.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Central and state governments are separately answerable to the _______.- a)people
- b)none
- c)each other
- d)president
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Central and state governments are separately answerable to the _______.
a)
people
b)
none
c)
each other
d)
president
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
Under federal system, the Central government cannot order the State government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which ' it is not answerable to the Central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B: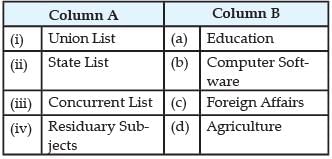
- a)(i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
- b)(i)-(a), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
- c)(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
- d)(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B:

a)
(i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
b)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
c)
(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
d)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
(i) Union List: Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. They are included in this list because we need a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country.
(ii) State List: In the Constitution, 'Agriculture' has been placed as Entry 14 in the State List along with several ancillary matters, while some agriculture-related items have been included in the Union List and the Concurrent List.
(iii) Concurrent list: The Indian constitution in its original enactment defined education as state subject. Under Article 42 of the constitution, an amendment was added in 1976 and education became a concurrent list subject which enables the central government to legislate it in the manner suited to it.
(iv) Residuary Subjects: Residuary Subjects are recognised as subjects that are not present in any of the lists stated in the constitution. The government of the Union has the powers to render law on Residuary Subjects. ,These subjects are e-commerce, Computer software and so on.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : India has a federal system.
Reason : Under a unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to central government.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : India has a federal system.
Reason : Under a unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to central government.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion because the federal and unitary systems of government are two different systems.
India has adopted a federal structure of government wherein powers and governance are divided between the centre, state, and local levels. The federal system allows for a responsive government that addresses the issues of their respective jurisdictions so that every stratum of society gets an equal opportunity to voice its opinions. On the other hand, there is a unitary system of government wherein the central government is supreme, and there is no distribution of powers among different levels of government.
India has adopted a federal structure of government wherein powers and governance are divided between the centre, state, and local levels. The federal system allows for a responsive government that addresses the issues of their respective jurisdictions so that every stratum of society gets an equal opportunity to voice its opinions. On the other hand, there is a unitary system of government wherein the central government is supreme, and there is no distribution of powers among different levels of government.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Usually, a federation has _________ levels of government.- a)three
- b)four
- c)two
- d)five
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Usually, a federation has _________ levels of government.
a)
three
b)
four
c)
two
d)
five
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.Q. How many languages are spoken in India?- a)More than 1200
- b)More than 1100
- c)More than 1400
- d)More than 1300
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Q. How many languages are spoken in India?
a)
More than 1200
b)
More than 1100
c)
More than 1400
d)
More than 1300
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Press Trust of India More than 19,500 languages or dialects are spoken in India as mother tongues, according to the latest analysis of a census released this week. There are 121 languages which are spoken by 10,000 or more people in India, which has a population of 121 crore, it said.
Find the incorrect option:Which of the following pair is incorrect?- a)State government – State List
- b)Central government – Union List
- c)Central and State – Concurrent List government List
- d)Local government – Residuary powers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the incorrect option:
Which of the following pair is incorrect?
a)
State government – State List
b)
Central government – Union List
c)
Central and State – Concurrent List government List
d)
Local government – Residuary powers
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The Incorrect option is (d): Local government – Residuary powers
Correct answer is: Union government – Residuary powers.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. What was the first and major test for democratic Politics in our country?- a)The creation of linguistic states
- b)The creation of the language policy
- c)The creation of new federal states
- d)The creation of new federal territories
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. What was the first and major test for democratic Politics in our country?
a)
The creation of linguistic states
b)
The creation of the language policy
c)
The creation of new federal states
d)
The creation of new federal territories
|
|
Sahana dasgupta answered |
Understanding the Major Test for Democratic Politics in India
The first and major test for democratic politics in India can be understood through the lens of the creation of linguistic states. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Background of Linguistic States
- After independence in 1947, India faced the challenge of uniting a diverse population with multiple languages and cultures.
- The demand for states to be formed on linguistic lines emerged as regional identities gained prominence.
Significance of Linguistic States
- The creation of linguistic states was crucial for addressing the aspirations of various linguistic communities.
- This approach helped in promoting local governance, enhancing administrative efficiency, and ensuring representation for different languages and cultures.
Political Implications
- The establishment of linguistic states marked a shift in political boundaries based on language, which was a bold move in a diverse nation like India.
- It showcased the democratic principle of accommodating diversity and gave a voice to regional aspirations.
Comparison with Language Policy
- While the language policy is important, it primarily deals with how languages are utilized in governance and administration.
- The creation of linguistic states was a foundational step that set the stage for subsequent policies, including language policy.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the creation of linguistic states stands out as the first and major test for democratic politics in India, as it directly addressed the complexities of a multilingual society and laid the groundwork for a more cohesive national framework.
The first and major test for democratic politics in India can be understood through the lens of the creation of linguistic states. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Background of Linguistic States
- After independence in 1947, India faced the challenge of uniting a diverse population with multiple languages and cultures.
- The demand for states to be formed on linguistic lines emerged as regional identities gained prominence.
Significance of Linguistic States
- The creation of linguistic states was crucial for addressing the aspirations of various linguistic communities.
- This approach helped in promoting local governance, enhancing administrative efficiency, and ensuring representation for different languages and cultures.
Political Implications
- The establishment of linguistic states marked a shift in political boundaries based on language, which was a bold move in a diverse nation like India.
- It showcased the democratic principle of accommodating diversity and gave a voice to regional aspirations.
Comparison with Language Policy
- While the language policy is important, it primarily deals with how languages are utilized in governance and administration.
- The creation of linguistic states was a foundational step that set the stage for subsequent policies, including language policy.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the creation of linguistic states stands out as the first and major test for democratic politics in India, as it directly addressed the complexities of a multilingual society and laid the groundwork for a more cohesive national framework.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Under which of the following systems, the central government can pass on orders to the provincial government?- a)Federal system
- b)Monarchy
- c)Unitary system
- d)Dictatorship
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Under which of the following systems, the central government can pass on orders to the provincial government?
a)
Federal system
b)
Monarchy
c)
Unitary system
d)
Dictatorship
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:Assertion : It is very simple to make the changes in the basic structure of the constitution.Reason : Both the houses have power to amend the constitution independently.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : It is very simple to make the changes in the basic structure of the constitution.
Reason : Both the houses have power to amend the constitution independently.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
It is difficult to make changes in the constitution in the federal system. Any change has to be first passed through both the houses of Parliament through atleast two-third majority. Then it has to be ratified by the legislatures of atleast half of the total states. Thus both reason and assertion are false.
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:It includes subjects of common interest to both the Union Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Union as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list.- a)Concurrent List
- b)Union List
- c)State List
- d)Government List
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
It includes subjects of common interest to both the Union Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Union as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list.
a)
Concurrent List
b)
Union List
c)
State List
d)
Government List
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
Concurrent List includes subjects of common interest to both the Union Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession. Both the Union as well as the State Governments can make laws on the subjects mentioned in this list. If their laws conflict with each other, the law made by the Union Government will prevail.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:Assertion : Coalition government is formed during dearth of coal in the country.Reason : It helps in overcoming coal crisis.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Coalition government is formed during dearth of coal in the country.
Reason : It helps in overcoming coal crisis.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
When no party is able to prove clear cut majority, several regional parties come together to form coalition government. It has no connection with scarcity of coal in the country.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.Q. Who has the power to legislate on 'residuary' subjects?- a)Union Government
- b)State government
- c)Community government
- d)Local government
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Q. Who has the power to legislate on 'residuary' subjects?
a)
Union Government
b)
State government
c)
Community government
d)
Local government
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
According to our constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on the residuary subjects. Trade is part of the union list and not a residuary subject. Computer software isn't part of any of the three lists mentioned in the constitution and hence is a residuary subject.
Assertion (A): Federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.Reason (R): In federalism, there are two levels of government, one for the entire country responsible for common national interests and others at the provincial or state level for day-to-day administration.- a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.
Reason (R): In federalism, there are two levels of government, one for the entire country responsible for common national interests and others at the provincial or state level for day-to-day administration.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
- Assertion (A) is correct. Federalism indeed involves the division of power between a central authority and constituent units like states or provinces, as mentioned in the provided text.
- Reason (R) is also correct. In a federal system, there are typically two levels of government: one at the national level responsible for national interests, and the other at the state or provincial level managing day-to-day administration, as outlined in the passage.
- The Reason (R) serves as a correct explanation for the Assertion (A) because it elaborates on how federalism works by specifying the dual levels of government and their respective roles, aligning with the definition of federalism provided in the Assertion.
Who is the chairperson of Municipal Corporation?- a)Block development officer
- b)Mayor
- c)Sarpanch
- d)Member of Lok Sabha
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the chairperson of Municipal Corporation?
a)
Block development officer
b)
Mayor
c)
Sarpanch
d)
Member of Lok Sabha
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
The Mayor is the head of the municipal corporation, but the role is largely ceremonial as executive powers are vested in the municipal commissioner. The office of the Mayor combines a functional role of chairing the Corporation meeting as well as ceremonial role associated with being the First Citizen of the city.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?- a)21 languages
- b)20 languages
- c)25 languages
- d)22 languages
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
a)
21 languages
b)
20 languages
c)
25 languages
d)
22 languages
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The 22 languages in the Eighth Schedule are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:Assertion : A major step towards decentralization was taken in 1992 by amending the constitution.Reason : Constitution was amended to make the third tier of democracy more powerful and effective.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : A major step towards decentralization was taken in 1992 by amending the constitution.
Reason : Constitution was amended to make the third tier of democracy more powerful and effective.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The constitution was amended in 1992 to make the third tier more powerful and effective. It includes steps like regular elections for local government bodies, reservation of seats for OBC, SC, ST and women and creation of State Election Commission. The reason thus justifies the assertion.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option :Assertion (A) : When power is taken away from Central and State governments and given to local government, it is called decentralization.Reason (R) : The basic idea behind decentralization is that there are a large number of problems and issues which are best settled at the local level.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
- d)(A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option :
Assertion (A) : When power is taken away from Central and State governments and given to local government, it is called decentralization.
Reason (R) : The basic idea behind decentralization is that there are a large number of problems and issues which are best settled at the local level.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
d)
(A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
- Both Assertion and Reason are Correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Here are the basic ideas & features of decentralization:
When power is taken away from central and state governments and given to local government, it is called decentralisation. - Decentralisation of powers:Decentralisation of powers is the sharing of powers among local self-governing bodies.
- Functioning of Government:It helps in proper functioning of government and through this, help by government can be reached to even remote parts of the country.
- Panchayat Raj system:On basis of decentralization three tier Panchayat Raj system has been introduced.
- Decentralization:The basic idea behind decentralization is that there are a large number of problems and issues which are best settled at the local level.
- Better knowledge of problems:People have better knowledge of problems in their localities. They also have better ideas on where to spend money and how to manage things more efficiently.
- Decision Making:Besides, at the local level it is possible for the people to directly participate in decision making. This helps to inculcate a habit of democratic participation.
- Local Government:Local government is the best way to realize one important principle of democracy, namely local self-government.
- So, Correct Answer is Option A
You can understand decentralization in India and key concepts of federalism by going through the doc:
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:Assertion : The subjects which are not included in Union List, State List and Concurrent List are considered as residuary subjects.Reason : The subjects included that came after constitution was made and thus could not be classified.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : The subjects which are not included in Union List, State List and Concurrent List are considered as residuary subjects.
Reason : The subjects included that came after constitution was made and thus could not be classified.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The subjects which are not included in Union List, State List and Concurrent List are considered as Residuary subjects. It includes the subjects such as computer software that came after constitution was made. Union Government has power to legislate on these ‘residuary’ subjects.
Assertion (A): The sharing of power between the Union Government and the State Governments is a key aspect of the Indian Constitution.Reason (R): Any change to the power-sharing arrangement between the Union Government and the State Governments requires a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament and ratification by legislatures of at least half of the total States.- a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The sharing of power between the Union Government and the State Governments is a key aspect of the Indian Constitution.
Reason (R): Any change to the power-sharing arrangement between the Union Government and the State Governments requires a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament and ratification by legislatures of at least half of the total States.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Nk Classes answered |
- Assertion (A) states the fundamental concept of power-sharing between the Union and State Governments, which is indeed a key aspect of the Indian Constitution.
- Reason (R) correctly explains that any alteration to this power-sharing arrangement necessitates a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament and approval by legislatures of at least half of the total States. This process highlights the careful and democratic approach required to modify the power distribution outlined in the Constitution.
- Therefore, both the Assertion and the Reason are true, and the Reason provides a correct explanation for the Assertion.
How does the relationship between the central government and state governments differ in federations compared to unitary systems?
- a)The central government in federations has no authority over state governments
- b)State governments in federations are subordinate to the central government
- c)The central government in unitary systems can not order state governments
- d)State governments in unitary systems have more autonomy than in federations
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer??
How does the relationship between the central government and state governments differ in federations compared to unitary systems?
a)
The central government in federations has no authority over state governments
b)
State governments in federations are subordinate to the central government
c)
The central government in unitary systems can not order state governments
d)
State governments in unitary systems have more autonomy than in federations
|
|
Kalyan singh answered |
The Nature of Federalism vs. Unitary Systems
In understanding the dynamics between central and state governments, it’s essential to differentiate between federations and unitary systems.
Federations: Distribution of Power
- In a federal system, power is divided between the central (national) government and state (regional) governments.
- Each level of government has its own sphere of authority, often enshrined in a constitution.
State Governments' Authority in Federations
- Option B correctly states that state governments in federations are subordinate to the central government. This means:
- The central government has the ultimate authority in areas defined by the constitution, including defense, foreign affairs, and immigration.
- State governments have their own powers but can be overridden or regulated by the central government.
- This relationship ensures a balance of power, where the central government can maintain national consistency while allowing states some autonomy.
Unitary Systems: Centralized Control
- In contrast, unitary systems concentrate power in a single central government.
- State or regional authorities exist but primarily serve to implement the directives of the central government.
Key Differences
- In unitary systems, the central government can easily direct state governments, often leading to less autonomy for regions.
- Federations encourage a degree of independence for states, yet they remain under the overarching authority of the central government.
In summary, while state governments in federations have a degree of independence, they remain subordinate to the central government, which is not the case in unitary systems where the central authority holds greater control.
In understanding the dynamics between central and state governments, it’s essential to differentiate between federations and unitary systems.
Federations: Distribution of Power
- In a federal system, power is divided between the central (national) government and state (regional) governments.
- Each level of government has its own sphere of authority, often enshrined in a constitution.
State Governments' Authority in Federations
- Option B correctly states that state governments in federations are subordinate to the central government. This means:
- The central government has the ultimate authority in areas defined by the constitution, including defense, foreign affairs, and immigration.
- State governments have their own powers but can be overridden or regulated by the central government.
- This relationship ensures a balance of power, where the central government can maintain national consistency while allowing states some autonomy.
Unitary Systems: Centralized Control
- In contrast, unitary systems concentrate power in a single central government.
- State or regional authorities exist but primarily serve to implement the directives of the central government.
Key Differences
- In unitary systems, the central government can easily direct state governments, often leading to less autonomy for regions.
- Federations encourage a degree of independence for states, yet they remain under the overarching authority of the central government.
In summary, while state governments in federations have a degree of independence, they remain subordinate to the central government, which is not the case in unitary systems where the central authority holds greater control.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. A candidate in an examination conducted for the central government positions has to opt for which language?- a)Hindi
- b)English
- c)Both Hindi and English
- d)Any of the 21 languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. A candidate in an examination conducted for the central government positions has to opt for which language?
a)
Hindi
b)
English
c)
Both Hindi and English
d)
Any of the 21 languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution
|
|
Nidhi nair answered |
Language Options for Central Government Examination Candidates
Candidates appearing for examinations conducted for Central Government positions have the option to choose any of the 21 languages recognized as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. This means that candidates can opt to take the examination in a language of their choice from the list of Scheduled Languages.
Explanation:
- The Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages, with Hindi being identified as the official language. However, candidates appearing for central government exams are not bound to choose Hindi as the medium of examination.
- Apart from Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognized as Scheduled Languages, and candidates have the flexibility to select any of these languages for taking the examination.
- This provision ensures that candidates from diverse linguistic backgrounds have the opportunity to take the exam in a language they are comfortable with, promoting inclusivity and equal opportunities for all candidates.
- The option to choose any of the Scheduled Languages for the examination reflects the government's commitment to respecting the linguistic diversity of the country and providing a level playing field for all candidates.
Candidates appearing for examinations conducted for Central Government positions have the option to choose any of the 21 languages recognized as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. This means that candidates can opt to take the examination in a language of their choice from the list of Scheduled Languages.
Explanation:
- The Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages, with Hindi being identified as the official language. However, candidates appearing for central government exams are not bound to choose Hindi as the medium of examination.
- Apart from Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognized as Scheduled Languages, and candidates have the flexibility to select any of these languages for taking the examination.
- This provision ensures that candidates from diverse linguistic backgrounds have the opportunity to take the exam in a language they are comfortable with, promoting inclusivity and equal opportunities for all candidates.
- The option to choose any of the Scheduled Languages for the examination reflects the government's commitment to respecting the linguistic diversity of the country and providing a level playing field for all candidates.
What is the primary basis for the distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments in India?- a)Geographical size
- b)Language diversity
- c)Administrative convenience
- d)Subject matter
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary basis for the distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments in India?
a)
Geographical size
b)
Language diversity
c)
Administrative convenience
d)
Subject matter

|
Nk Classes answered |
- The distribution of legislative powers in India between the Union Government and the State Governments is primarily based on the subject matter.
- This arrangement ensures that laws related to specific subjects are made by the appropriate level of government, creating a clear delineation of authority and responsibilities.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.Q. In terms of __________, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.- a)population
- b)languages
- c)forests
- d)religions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Q. In terms of __________, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
a)
population
b)
languages
c)
forests
d)
religions
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
India is a country with extreme diversity in geographical, religious, racial, linguistic and cultural bonding. In India, one can find a number of people living together sharing their culture and religion with love and enthusiasm. India is the most diverse land found anywhere else in the world. The diversity of India is unique. From language to different culture and religion, the country has been hailed as one of the most beautiful mixtures of various cultural identities.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:Assertion (A) : Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.Reason (R) : Usually, a federation has one level of government.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
- d)(A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A) : Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.
Reason (R) : Usually, a federation has one level of government.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
d)
(A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:Assertion : Third-tier of government is local government.Reason : It made democracy weak.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Third-tier of government is local government.
Reason : It made democracy weak.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The third tier of government is done through decentralisation. It helped in making democracy stronger by Bringing it to grass root level. Thus, the reason is false but assertion stands true.
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:It includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. They are included in this list because we need a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country.- a)State List
- b)Concurrent List
- c)Union List
- d)Enrolment List
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
It includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. They are included in this list because we need a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country.
a)
State List
b)
Concurrent List
c)
Union List
d)
Enrolment List
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. The Union Government alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the Union List.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.Q. Indians who are not permanent residents of ________ cannot buy land or house here.- a)Kerala
- b)Assam
- c)Jammu & Kashmir
- d)Bihar
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Q. Indians who are not permanent residents of ________ cannot buy land or house here.
a)
Kerala
b)
Assam
c)
Jammu & Kashmir
d)
Bihar
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.Q. Which of the following states has its own Constitution?- a)Uttar Pradesh
- b)Jammu & Kashmir
- c)Andhra Pradesh
- d)Kerala
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Q. Which of the following states has its own Constitution?
a)
Uttar Pradesh
b)
Jammu & Kashmir
c)
Andhra Pradesh
d)
Kerala
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
Jammu and Kashmir was the only Indian state which had its own Constitution. On 5 August 2019, the article of the Indian Constitution (article 370) which provided the state of Jammu and Kashmir this special status to have its own Constitution was repealed.
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B:
- a)(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(a)
- b)(i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
- c)(i)-(d), (ii)-(a), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
- d)(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B:

a)
(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(a)
b)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
c)
(i)-(d), (ii)-(a), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
d)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
(i) Union of India: The Union Cabinet headed by the prime minister is appointed by the President of India to assist the latter in the administration of the affairs of the executive.
(ii) State: Governors, all of whom are popularly elected, serve as the chief executive officers of the fifty states and five commonwealths and territories. As state managers, governors are responsible for implementing state laws and overseeing the operation of the state executive branch.
(iii) Municipal Corporation: The Mayor is the head of the municipal corporation, but in most states and territories of India the role is largely ceremonial as executive powers are vested in the Municipal Commissioner.
(iv) Gram Panchayat: A sarpanch or gram pradhan or mukya is a decision-maker, elected by the village-level constitutional body of local self-government called the Gram Sabha (village government) in India.
Chapter doubts & questions for Federalism - 6 Months Boards Preparation for Class 10 (CBSE) 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Federalism - 6 Months Boards Preparation for Class 10 (CBSE) in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Boards Preparation for Class 10 (CBSE)
344 videos|2427 docs|372 tests
|
Related Class 10 Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










