All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Human Health & Diseases for NEET Exam
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is- a)IgA
- b)IgE
- c)IgM
- d)IgG
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is
a)
IgA
b)
IgE
c)
IgM
d)
IgG

|
Yash answered |
IgG immunoglobin me sabse jyada 80% paye jate h . ye sbse chote imuno globin hote h kyuki enme paratopes kevel 2 hote h upr se ye monovalant hote h. chote size ke karan ye placenta ko cross kr jate h
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?
- a)Barbiturates - Tranquilliser
- b)Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) - Psychedelic (hallucinogen)
- c) Amphetamines - CNS stimulants
- d)Heroin - Depressant, slows down body functions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a drug and its category?
a)
Barbiturates - Tranquilliser
b)
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) - Psychedelic (hallucinogen)
c)
Amphetamines - CNS stimulants
d)
Heroin - Depressant, slows down body functions
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Heroin, commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine, which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver somniferum. Generally taken by snorting and injection, heroin is a depressant and slows down body functions.

Given below is the diagram of human lymphatic system, where A, B, C and D are lymphoid organs. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as A, B, C and D.
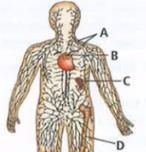
- a)T cells mature in B
- b)B and T cells undergo maturation in C
- c)B and T cells undergo proliferation and differentiation in A
- d)B cells mature in D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below is the diagram of human lymphatic system, where A, B, C and D are lymphoid organs. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as A, B, C and D.

a)
T cells mature in B
b)
B and T cells undergo maturation in C
c)
B and T cells undergo proliferation and differentiation in A
d)
B cells mature in D
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
'A'-lymph nodes, 'B'-Thymus, 'C'-spleen, 'D'-Bone marrow. Thymus and bone marrow are the primary lymphoid organs where maturation of T-cells and B-cells take place respectively. Lymph nodes and spleen are the secondary lymphoid organs where T-cells and B-cells undergo proliferation and differentiation.
Which of these glands is large at the time of birth but in adults, it reduces to a very small size?- a)Thyroid
- b)Adrenal
- c)Thymus
- d)Spleen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these glands is large at the time of birth but in adults, it reduces to a very small size?
a)
Thyroid
b)
Adrenal
c)
Thymus
d)
Spleen
|
|
Krithika Ahuja answered |
Thymus gland is the correct option as it is large at the time of birth but reduces to a very small size in adults.
Explanation:
Thymus gland is a specialized gland of the lymphatic system that plays an important role in the development of the immune system. It is located in the upper thorax, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. The thymus gland is large at the time of birth and continues to grow until puberty. After puberty, the thymus gland begins to shrink and is replaced by fatty tissue. By the age of 20, the thymus gland has reduced to about one-third of its maximum size, and by the age of 50, it has reduced to only a few grams of fatty tissue.
Why is Thymus gland large at the time of birth?
The thymus gland is very active during fetal development and plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. The thymus gland produces T-lymphocytes, which are immune cells that play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. The thymus gland is essential for the development of T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign substances in the body. The thymus gland is particularly important during fetal development because the fetus does not have a fully developed immune system and relies on the mother's immune system for protection.
Why does Thymus gland reduce in size in adults?
The thymus gland begins to shrink after puberty because the production of T-lymphocytes decreases with age. As a result, the thymus gland is no longer required to produce large numbers of T-lymphocytes, and its function gradually declines. The thymus gland is gradually replaced by fatty tissue, which is an irreversible process. However, the T-lymphocytes that are produced by the thymus gland during fetal development and childhood continue to circulate in the body and play a crucial role in the immune system throughout life.
Explanation:
Thymus gland is a specialized gland of the lymphatic system that plays an important role in the development of the immune system. It is located in the upper thorax, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. The thymus gland is large at the time of birth and continues to grow until puberty. After puberty, the thymus gland begins to shrink and is replaced by fatty tissue. By the age of 20, the thymus gland has reduced to about one-third of its maximum size, and by the age of 50, it has reduced to only a few grams of fatty tissue.
Why is Thymus gland large at the time of birth?
The thymus gland is very active during fetal development and plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. The thymus gland produces T-lymphocytes, which are immune cells that play a crucial role in fighting infections and diseases. The thymus gland is essential for the development of T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign substances in the body. The thymus gland is particularly important during fetal development because the fetus does not have a fully developed immune system and relies on the mother's immune system for protection.
Why does Thymus gland reduce in size in adults?
The thymus gland begins to shrink after puberty because the production of T-lymphocytes decreases with age. As a result, the thymus gland is no longer required to produce large numbers of T-lymphocytes, and its function gradually declines. The thymus gland is gradually replaced by fatty tissue, which is an irreversible process. However, the T-lymphocytes that are produced by the thymus gland during fetal development and childhood continue to circulate in the body and play a crucial role in the immune system throughout life.
Several genes called _____have been identified in normal cells which when activated will turn in to ___ , and under certain conditions, could lead to cancerous transformation of the cells.Complete the above paragraph by selecting correct sequence of words.- a)oncogenes, proto oncogenes
- b)cellular oncogenes, proto oncogenes
- c)proto oncogenes, oncogenes
- d)cellular oncogenes, oncogenes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Several genes called _____have been identified in normal cells which when activated will turn in to ___ , and under certain conditions, could lead to cancerous transformation of the cells.
Complete the above paragraph by selecting correct sequence of words.
a)
oncogenes, proto oncogenes
b)
cellular oncogenes, proto oncogenes
c)
proto oncogenes, oncogenes
d)
cellular oncogenes, oncogenes
|
|
Prisha Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes in cells that regulate cell growth and division. However, if these genes are mutated or activated, they can become oncogenes, which promote uncontrolled cell growth and division, leading to the development of cancer. Several proto-oncogenes have been identified in normal cells, and when activated, they can turn into oncogenes, potentially leading to the transformation of the cells into cancer cells.
The correct sequence of words to complete the paragraph is "proto-oncogenes, oncogenes." The other options presented include "oncogenes, proto-oncogenes," "cellular oncogenes, proto-oncogenes," and "cellular oncogenes, oncogenes," but none of these accurately reflect the relationship between proto-oncogenes and oncogenes.
In summary, proto-oncogenes are normal genes that can become oncogenes if they are mutated or activated. Several proto-oncogenes have been identified in normal cells, and when activated, they can turn into oncogenes, which can lead to the development of cancer.
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes in cells that regulate cell growth and division. However, if these genes are mutated or activated, they can become oncogenes, which promote uncontrolled cell growth and division, leading to the development of cancer. Several proto-oncogenes have been identified in normal cells, and when activated, they can turn into oncogenes, potentially leading to the transformation of the cells into cancer cells.
The correct sequence of words to complete the paragraph is "proto-oncogenes, oncogenes." The other options presented include "oncogenes, proto-oncogenes," "cellular oncogenes, proto-oncogenes," and "cellular oncogenes, oncogenes," but none of these accurately reflect the relationship between proto-oncogenes and oncogenes.
In summary, proto-oncogenes are normal genes that can become oncogenes if they are mutated or activated. Several proto-oncogenes have been identified in normal cells, and when activated, they can turn into oncogenes, which can lead to the development of cancer.
Which one of the following immune system components does not correctly match with its respective role?- a)Interferons - secreted by virus-infected cells and protect non-infected cells from further viral infection
- b)B- lymphocytes - produce antibodies in response to pathogens into blood to fight with them
- c)Macrophages - mucus secreting cells that trap microbes entering in the body
- d)IgA - present in colostrum in early days of lactation to protect infant from diseases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following immune system components does not correctly match with its respective role?
a)
Interferons - secreted by virus-infected cells and protect non-infected cells from further viral infection
b)
B- lymphocytes - produce antibodies in response to pathogens into blood to fight with them
c)
Macrophages - mucus secreting cells that trap microbes entering in the body
d)
IgA - present in colostrum in early days of lactation to protect infant from diseases
|
|
Ameya Majumdar answered |
Incorrect Immune System Component and Role Match
Explanation:
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. The immune system components and their respective roles are as follows:
a) Interferons - Secreted by virus-infected cells and protect non-infected cells from further viral infection. They stimulate the production of antiviral proteins that prevent the virus from replicating in healthy cells.
b) B-lymphocytes - Produce antibodies in response to pathogens into blood to fight with them. B-lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that recognizes and neutralizes specific pathogens by producing antibodies that bind to and destroy them.
c) Macrophages - Mucus-secreting cells that trap microbes entering in the body. This is an incorrect match as macrophages are actually white blood cells that engulf and digest foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses, in a process called phagocytosis.
d) IgA - Present in colostrum in early days of lactation to protect infant from diseases. IgA is an antibody that is found in secretions such as tears, saliva, and breast milk. It helps to prevent pathogens from entering the body through the mucous membranes.
In conclusion, the correct match of immune system components and their respective roles is important to understand the functioning of the immune system and to develop effective strategies to combat diseases.
Explanation:
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. The immune system components and their respective roles are as follows:
a) Interferons - Secreted by virus-infected cells and protect non-infected cells from further viral infection. They stimulate the production of antiviral proteins that prevent the virus from replicating in healthy cells.
b) B-lymphocytes - Produce antibodies in response to pathogens into blood to fight with them. B-lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that recognizes and neutralizes specific pathogens by producing antibodies that bind to and destroy them.
c) Macrophages - Mucus-secreting cells that trap microbes entering in the body. This is an incorrect match as macrophages are actually white blood cells that engulf and digest foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses, in a process called phagocytosis.
d) IgA - Present in colostrum in early days of lactation to protect infant from diseases. IgA is an antibody that is found in secretions such as tears, saliva, and breast milk. It helps to prevent pathogens from entering the body through the mucous membranes.
In conclusion, the correct match of immune system components and their respective roles is important to understand the functioning of the immune system and to develop effective strategies to combat diseases.
Which one of the following pairs of diseases is viral as well as transmitted by mosquitoes?- a)Encephalitis and sleeping sickness
- b)Yellow fever and sleeping sickness
- c)Elephantiasis and dengue
- d)Yellow fever and dengue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of diseases is viral as well as transmitted by mosquitoes?
a)
Encephalitis and sleeping sickness
b)
Yellow fever and sleeping sickness
c)
Elephantiasis and dengue
d)
Yellow fever and dengue
|
|
Rishabh Verma answered |
Yellow fever and dengue are the pair of diseases that are viral and transmitted by mosquitoes.
Yellow Fever:
- Yellow fever is a viral disease caused by the yellow fever virus.
- It is primarily transmitted by the bite of infected female mosquitoes, especially the Aedes aegypti species.
- The virus is endemic in tropical regions of Africa and Central and South America.
- Symptoms of yellow fever include fever, headache, muscle pain, jaundice, and bleeding.
- In severe cases, it can lead to organ failure and death.
- There is no specific treatment for yellow fever, but a vaccine is available for prevention.
Dengue:
- Dengue is a viral disease caused by the dengue virus.
- It is transmitted by the bite of infected female Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti.
- Dengue is common in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
- Symptoms of dengue include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and mild bleeding.
- In severe cases, it can lead to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
- There is no specific treatment for dengue, but supportive care can help manage symptoms.
Viral Diseases Transmitted by Mosquitoes:
- Mosquitoes are known to transmit several viral diseases, including yellow fever, dengue fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, and West Nile virus.
- These viruses are primarily transmitted when a mosquito bites an infected person and then bites another person, transmitting the virus through its saliva.
- Mosquito-borne viral diseases are more common in tropical and subtropical regions where mosquito populations are abundant.
- The Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti, are the main vectors for these viral diseases.
Conclusion:
- Among the given options, the pair of diseases that are both viral and transmitted by mosquitoes is yellow fever and dengue. Both diseases are caused by different viruses and are primarily transmitted by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes.
Yellow Fever:
- Yellow fever is a viral disease caused by the yellow fever virus.
- It is primarily transmitted by the bite of infected female mosquitoes, especially the Aedes aegypti species.
- The virus is endemic in tropical regions of Africa and Central and South America.
- Symptoms of yellow fever include fever, headache, muscle pain, jaundice, and bleeding.
- In severe cases, it can lead to organ failure and death.
- There is no specific treatment for yellow fever, but a vaccine is available for prevention.
Dengue:
- Dengue is a viral disease caused by the dengue virus.
- It is transmitted by the bite of infected female Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti.
- Dengue is common in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
- Symptoms of dengue include high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and mild bleeding.
- In severe cases, it can lead to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
- There is no specific treatment for dengue, but supportive care can help manage symptoms.
Viral Diseases Transmitted by Mosquitoes:
- Mosquitoes are known to transmit several viral diseases, including yellow fever, dengue fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, and West Nile virus.
- These viruses are primarily transmitted when a mosquito bites an infected person and then bites another person, transmitting the virus through its saliva.
- Mosquito-borne viral diseases are more common in tropical and subtropical regions where mosquito populations are abundant.
- The Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti, are the main vectors for these viral diseases.
Conclusion:
- Among the given options, the pair of diseases that are both viral and transmitted by mosquitoes is yellow fever and dengue. Both diseases are caused by different viruses and are primarily transmitted by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes.
The most abundant antibody produced against allergens is- a)lgE
- b)IgA
- c)IgC
- d)IgM
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant antibody produced against allergens is
a)
lgE
b)
IgA
c)
IgC
d)
IgM
|
|
Ankit Iyer answered |
lgE is the most abundant antibody produced against allergens
Allergens are substances that can trigger an allergic response in individuals who are sensitive or allergic to them. When allergens enter the body, they can bind to specific antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. IgE antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called B cells in response to exposure to allergens. These antibodies are particularly involved in allergic reactions.
Explanation:
There are five major classes of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig): IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. Each class of antibody has its own unique structure and function. Among these, IgE is the most abundant antibody produced against allergens.
Key Points:
- IgE is produced in response to allergen exposure.
- It plays a crucial role in allergic reactions by binding to allergens and triggering the release of chemicals such as histamine from mast cells and basophils.
- Histamine release leads to the typical symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as itching, swelling, redness, and increased mucus production.
- IgE antibodies are involved in allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever), asthma, and atopic dermatitis (eczema).
- The production of IgE antibodies is tightly regulated to prevent unnecessary allergic reactions.
- Individuals with allergies often have higher levels of IgE antibodies in their blood compared to non-allergic individuals.
Conclusion:
In summary, IgE is the most abundant antibody produced against allergens. It plays a key role in allergic reactions by binding to allergens and triggering the release of chemicals that cause allergy symptoms. Understanding the role of IgE antibodies in allergic reactions is important for the development of diagnostic tests and targeted treatments for allergies.
Allergens are substances that can trigger an allergic response in individuals who are sensitive or allergic to them. When allergens enter the body, they can bind to specific antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. IgE antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called B cells in response to exposure to allergens. These antibodies are particularly involved in allergic reactions.
Explanation:
There are five major classes of antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig): IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. Each class of antibody has its own unique structure and function. Among these, IgE is the most abundant antibody produced against allergens.
Key Points:
- IgE is produced in response to allergen exposure.
- It plays a crucial role in allergic reactions by binding to allergens and triggering the release of chemicals such as histamine from mast cells and basophils.
- Histamine release leads to the typical symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as itching, swelling, redness, and increased mucus production.
- IgE antibodies are involved in allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever), asthma, and atopic dermatitis (eczema).
- The production of IgE antibodies is tightly regulated to prevent unnecessary allergic reactions.
- Individuals with allergies often have higher levels of IgE antibodies in their blood compared to non-allergic individuals.
Conclusion:
In summary, IgE is the most abundant antibody produced against allergens. It plays a key role in allergic reactions by binding to allergens and triggering the release of chemicals that cause allergy symptoms. Understanding the role of IgE antibodies in allergic reactions is important for the development of diagnostic tests and targeted treatments for allergies.
Which of the following pairs contains an infectious and a non-infectious disease respectively?- a)Typhoid and AIDS
- b)AIDS and cancer
- c)Pneumonia and malaria
- d)Cancer and malaria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs contains an infectious and a non-infectious disease respectively?
a)
Typhoid and AIDS
b)
AIDS and cancer
c)
Pneumonia and malaria
d)
Cancer and malaria
|
|
Janani Bose answered |
Infectious and Non-infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are those that are caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. These diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through various modes of transmission such as direct contact, droplets, airborne, fecal-oral route, and vector-borne.
Non-infectious diseases are those that are not caused by pathogenic microorganisms. These diseases may have genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors as their causes. Some examples of non-infectious diseases include cancer, diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
Answer Explanation
The pair that contains an infectious and a non-infectious disease respectively is option 'B', which is AIDS and cancer.
- AIDS is an infectious disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, blood transfusions, and vertical transmission from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
- Cancer, on the other hand, is a non-infectious disease that is caused by uncontrolled growth and division of abnormal cells in the body. It can be caused by genetic mutations, exposure to environmental factors such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet radiation, and lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of physical activity.
Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as it contains one infectious disease (AIDS) and one non-infectious disease (cancer).
Infectious diseases are those that are caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. These diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through various modes of transmission such as direct contact, droplets, airborne, fecal-oral route, and vector-borne.
Non-infectious diseases are those that are not caused by pathogenic microorganisms. These diseases may have genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors as their causes. Some examples of non-infectious diseases include cancer, diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease.
Answer Explanation
The pair that contains an infectious and a non-infectious disease respectively is option 'B', which is AIDS and cancer.
- AIDS is an infectious disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, blood transfusions, and vertical transmission from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
- Cancer, on the other hand, is a non-infectious disease that is caused by uncontrolled growth and division of abnormal cells in the body. It can be caused by genetic mutations, exposure to environmental factors such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet radiation, and lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of physical activity.
Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as it contains one infectious disease (AIDS) and one non-infectious disease (cancer).
The antigen binding site of an antibody is present at- a)the constant region
- b)the C-terminal
- c)the variable region
- d)between constant and variable region
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The antigen binding site of an antibody is present at
a)
the constant region
b)
the C-terminal
c)
the variable region
d)
between constant and variable region
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Antibodies are made up of four polypeptide chains two heavy and two light chains. Light and heavy chains are subdivided into variable and constant regions. The variable portion is used for binding to antigen and a constant portion determines its adherence and diffusivity.
Which of the following is celebrated as 'World AIDS Day'?- a)31st March
- b)1st March
- c)1st December
- d)31st December
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is celebrated as 'World AIDS Day'?
a)
31st March
b)
1st March
c)
1st December
d)
31st December
|
|
Diya Banerjee answered |
World AIDS Day is celebrated on 1st December every year. It is an opportunity for people worldwide to unite in the fight against HIV, show support for people living with HIV, and remember those who have died from HIV/AIDS-related illnesses. The day also aims to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, reduce stigma, and encourage people to get tested and seek treatment.
The History of World AIDS Day
- World AIDS Day was first observed in 1988, making 2021 the 33rd anniversary of the event.
- The day was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) to raise awareness about the global AIDS epidemic and to encourage progress in HIV/AIDS prevention, treatment, and care.
- Since its inception, World AIDS Day has been recognized by governments, non-governmental organizations, and individuals around the world.
Why is World AIDS Day Important?
- HIV/AIDS remains one of the most significant public health challenges globally.
- Approximately 38 million people worldwide are living with HIV, and 690,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2019.
- Despite significant progress in HIV prevention, treatment, and care, many people still face barriers to accessing these services.
- World AIDS Day provides an opportunity to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, reduce stigma, and encourage people to get tested and seek treatment.
How is World AIDS Day Celebrated?
- World AIDS Day is marked by events and activities worldwide, including candlelight vigils, marches, conferences, and awareness-raising campaigns.
- The theme for World AIDS Day 2021 is "End inequalities, end AIDS."
- The theme highlights the need to address social and economic inequalities that contribute to the HIV epidemic, such as poverty, discrimination, and gender inequality.
- The day also provides an opportunity to showcase progress in the global response to HIV/AIDS and to renew commitments to ending the epidemic.
In conclusion, World AIDS Day is an important global event that aims to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, reduce stigma, and encourage people to get tested and seek treatment. By working together, we can end the HIV epidemic and ensure that everyone living with HIV has access to the care and support they need.
The History of World AIDS Day
- World AIDS Day was first observed in 1988, making 2021 the 33rd anniversary of the event.
- The day was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) to raise awareness about the global AIDS epidemic and to encourage progress in HIV/AIDS prevention, treatment, and care.
- Since its inception, World AIDS Day has been recognized by governments, non-governmental organizations, and individuals around the world.
Why is World AIDS Day Important?
- HIV/AIDS remains one of the most significant public health challenges globally.
- Approximately 38 million people worldwide are living with HIV, and 690,000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2019.
- Despite significant progress in HIV prevention, treatment, and care, many people still face barriers to accessing these services.
- World AIDS Day provides an opportunity to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, reduce stigma, and encourage people to get tested and seek treatment.
How is World AIDS Day Celebrated?
- World AIDS Day is marked by events and activities worldwide, including candlelight vigils, marches, conferences, and awareness-raising campaigns.
- The theme for World AIDS Day 2021 is "End inequalities, end AIDS."
- The theme highlights the need to address social and economic inequalities that contribute to the HIV epidemic, such as poverty, discrimination, and gender inequality.
- The day also provides an opportunity to showcase progress in the global response to HIV/AIDS and to renew commitments to ending the epidemic.
In conclusion, World AIDS Day is an important global event that aims to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS, reduce stigma, and encourage people to get tested and seek treatment. By working together, we can end the HIV epidemic and ensure that everyone living with HIV has access to the care and support they need.
Charas and ganja are the drugs which affect- a)respiratory system
- b)cardiovascular system
- c)digestive system
- d)nervous system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Charas and ganja are the drugs which affect
a)
respiratory system
b)
cardiovascular system
c)
digestive system
d)
nervous system
|
|
Swara Datta answered |
The correct answer is option 'B' - ganja and charas affect the cardiovascular system.
Ganja and charas, commonly known as marijuana or cannabis, are drugs derived from the Cannabis plant. These drugs have psychoactive properties and can cause various effects on the body, including those on the cardiovascular system.
Here is a detailed explanation of how ganja and charas affect the cardiovascular system:
1. Vasodilation:
- Both ganja and charas contain cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which can cause vasodilation.
- Vasodilation refers to the widening of blood vessels, leading to an increase in their diameter.
- When blood vessels dilate, it reduces peripheral resistance and allows for increased blood flow.
- This effect can cause a decrease in blood pressure.
2. Tachycardia:
- Another effect of ganja and charas on the cardiovascular system is an increase in heart rate, known as tachycardia.
- THC activates the sympathetic nervous system, which increases the release of norepinephrine and epinephrine, leading to an increased heart rate.
- Tachycardia can put additional stress on the heart and may have adverse effects, especially in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
3. Increased risk of heart attack:
- The combination of vasodilation and tachycardia can increase the risk of a heart attack, particularly in susceptible individuals.
- When blood vessels dilate, it can lead to a decrease in coronary blood flow, which may be insufficient to meet the increased oxygen demand due to tachycardia.
- This can result in myocardial ischemia, where the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen, potentially leading to a heart attack.
4. Blood clotting:
- Ganja and charas can also affect blood clotting.
- THC has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, which is the process of platelets clumping together to form a blood clot.
- This effect may increase the risk of bleeding in individuals taking anticoagulant medications or those with bleeding disorders.
In summary, ganja and charas affect the cardiovascular system primarily through vasodilation, tachycardia, increased risk of heart attack, and alterations in blood clotting. It is important to note that these effects may vary depending on the dosage, frequency of use, and individual susceptibility.
Ganja and charas, commonly known as marijuana or cannabis, are drugs derived from the Cannabis plant. These drugs have psychoactive properties and can cause various effects on the body, including those on the cardiovascular system.
Here is a detailed explanation of how ganja and charas affect the cardiovascular system:
1. Vasodilation:
- Both ganja and charas contain cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which can cause vasodilation.
- Vasodilation refers to the widening of blood vessels, leading to an increase in their diameter.
- When blood vessels dilate, it reduces peripheral resistance and allows for increased blood flow.
- This effect can cause a decrease in blood pressure.
2. Tachycardia:
- Another effect of ganja and charas on the cardiovascular system is an increase in heart rate, known as tachycardia.
- THC activates the sympathetic nervous system, which increases the release of norepinephrine and epinephrine, leading to an increased heart rate.
- Tachycardia can put additional stress on the heart and may have adverse effects, especially in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
3. Increased risk of heart attack:
- The combination of vasodilation and tachycardia can increase the risk of a heart attack, particularly in susceptible individuals.
- When blood vessels dilate, it can lead to a decrease in coronary blood flow, which may be insufficient to meet the increased oxygen demand due to tachycardia.
- This can result in myocardial ischemia, where the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen, potentially leading to a heart attack.
4. Blood clotting:
- Ganja and charas can also affect blood clotting.
- THC has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, which is the process of platelets clumping together to form a blood clot.
- This effect may increase the risk of bleeding in individuals taking anticoagulant medications or those with bleeding disorders.
In summary, ganja and charas affect the cardiovascular system primarily through vasodilation, tachycardia, increased risk of heart attack, and alterations in blood clotting. It is important to note that these effects may vary depending on the dosage, frequency of use, and individual susceptibility.
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)Acquired immunity is pathogen specific.
- b)Macrophages can phagocytose and destroy microbes.
- c)Hallucinogenic chemicals obtained from leaves, resins and inflorescence of plant Cannabis sativa are called as cannabis sativa are called as cannabinoids.
- d)Opioid is a medicine used to help patients to cope with mental illnesses.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
Acquired immunity is pathogen specific.
b)
Macrophages can phagocytose and destroy microbes.
c)
Hallucinogenic chemicals obtained from leaves, resins and inflorescence of plant Cannabis sativa are called as cannabis sativa are called as cannabinoids.
d)
Opioid is a medicine used to help patients to cope with mental illnesses.
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Opioids act as analgesics which relieve pain by acting on the CNS.
Marijuana is extracted from- a)dried leaves and flowers of her
- b)ergot fungus
- c)roots of hemp plant
- d)cocoa plant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Marijuana is extracted from
a)
dried leaves and flowers of her
b)
ergot fungus
c)
roots of hemp plant
d)
cocoa plant
|
|
Lekshmi Tiwari answered |
Marijuana Extraction
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a psychoactive drug that is derived from the Cannabis plant. It is primarily extracted from the dried leaves and flowers of the herb. Let's explore this in more detail:
1. Cannabis Plant
- Cannabis is a flowering plant that belongs to the Cannabaceae family.
- It has three primary species: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis.
2. Marijuana Extraction Process
- Marijuana extraction involves separating the desired compounds, such as cannabinoids and terpenes, from the plant material.
- The most common method of extraction is through the use of solvents like ethanol, butane, or CO2.
- The dried leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant contain the highest concentration of these desired compounds.
3. Dried Leaves and Flowers
- The leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant are rich in cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
- THC is the primary psychoactive compound responsible for the "high" experienced when consuming marijuana.
- CBD, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and has various potential therapeutic benefits.
4. Other Plant Parts
- While the leaves and flowers are the main sources of marijuana, other parts of the cannabis plant can also contain cannabinoids, although in lower concentrations.
- For example, the stems and seeds may contain some cannabinoids, but they are less potent compared to the leaves and flowers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, marijuana is primarily extracted from the dried leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant. These plant parts contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. The extraction process involves separating these desired compounds from the plant material using solvents. While other parts of the plant, such as stems and seeds, may also contain cannabinoids, they are not commonly used for marijuana extraction due to their lower potency.
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a psychoactive drug that is derived from the Cannabis plant. It is primarily extracted from the dried leaves and flowers of the herb. Let's explore this in more detail:
1. Cannabis Plant
- Cannabis is a flowering plant that belongs to the Cannabaceae family.
- It has three primary species: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis.
2. Marijuana Extraction Process
- Marijuana extraction involves separating the desired compounds, such as cannabinoids and terpenes, from the plant material.
- The most common method of extraction is through the use of solvents like ethanol, butane, or CO2.
- The dried leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant contain the highest concentration of these desired compounds.
3. Dried Leaves and Flowers
- The leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant are rich in cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
- THC is the primary psychoactive compound responsible for the "high" experienced when consuming marijuana.
- CBD, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and has various potential therapeutic benefits.
4. Other Plant Parts
- While the leaves and flowers are the main sources of marijuana, other parts of the cannabis plant can also contain cannabinoids, although in lower concentrations.
- For example, the stems and seeds may contain some cannabinoids, but they are less potent compared to the leaves and flowers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, marijuana is primarily extracted from the dried leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant. These plant parts contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. The extraction process involves separating these desired compounds from the plant material using solvents. While other parts of the plant, such as stems and seeds, may also contain cannabinoids, they are not commonly used for marijuana extraction due to their lower potency.
Which of the following pairs correctly matches a disease and a pathogen causing it?- a)Typhoid - Salmonella typhi
- b)Pneumonia - Haemophilus pneumoniae
- c)Malaria - Ascaris lumbricoides
- d)Ringworm - Entamoeba histolytica
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs correctly matches a disease and a pathogen causing it?
a)
Typhoid - Salmonella typhi
b)
Pneumonia - Haemophilus pneumoniae
c)
Malaria - Ascaris lumbricoides
d)
Ringworm - Entamoeba histolytica
|
|
Tarun Verma answered |
Disease and Pathogen Pairing
Typhoid - Salmonella typhi
Explanation:
Typhoid is a bacterial infection that is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. This bacterium is commonly found in contaminated food and water, especially in areas with poor sanitation. The symptoms of typhoid include fever, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Pneumonia - Haemophilus pneumoniae
Explanation:
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by many different types of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. One of the common pathogens that cause pneumonia is Haemophilus pneumoniae. The symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
Malaria - Ascaris lumbricoides
Explanation:
Malaria is a parasitic disease that is transmitted by infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The parasite responsible for malaria is Plasmodium falciparum, which infects red blood cells and causes fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. Ascaris lumbricoides, on the other hand, is a type of roundworm that infects the intestines.
Ringworm - Entamoeba histolytica
Explanation:
Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin that can affect different parts of the body, such as the scalp, feet, and groin. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. Entamoeba histolytica, on the other hand, is a protozoan parasite that can cause amoebiasis, a disease that affects the intestines. It is not associated with ringworm.
Therefore, the correct pairing of a disease and its pathogen is Typhoid - Salmonella typhi.
Typhoid - Salmonella typhi
Explanation:
Typhoid is a bacterial infection that is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. This bacterium is commonly found in contaminated food and water, especially in areas with poor sanitation. The symptoms of typhoid include fever, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Pneumonia - Haemophilus pneumoniae
Explanation:
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by many different types of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. One of the common pathogens that cause pneumonia is Haemophilus pneumoniae. The symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
Malaria - Ascaris lumbricoides
Explanation:
Malaria is a parasitic disease that is transmitted by infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The parasite responsible for malaria is Plasmodium falciparum, which infects red blood cells and causes fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. Ascaris lumbricoides, on the other hand, is a type of roundworm that infects the intestines.
Ringworm - Entamoeba histolytica
Explanation:
Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin that can affect different parts of the body, such as the scalp, feet, and groin. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. Entamoeba histolytica, on the other hand, is a protozoan parasite that can cause amoebiasis, a disease that affects the intestines. It is not associated with ringworm.
Therefore, the correct pairing of a disease and its pathogen is Typhoid - Salmonella typhi.
A toxic substance, responsible for the chills and high fever recurring every three to four days in malarial fever, is- a)interferon
- b)haemozoin
- c)colostrum
- d)hirudin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A toxic substance, responsible for the chills and high fever recurring every three to four days in malarial fever, is
a)
interferon
b)
haemozoin
c)
colostrum
d)
hirudin
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In malaria, chills and shivers are caused by the release of toxic substance haemozoin into the blood at the time of RBCs rupture. It is generally followed by fever.
Amoebic dysentery (amoebiasis) is caused by- a)Entamoeba histolytica
- b)E. coli
- c)Streptococcus pneumoniae
- d)Trichophyton
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amoebic dysentery (amoebiasis) is caused by
a)
Entamoeba histolytica
b)
E. coli
c)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
d)
Trichophyton
|
|
Mansi Chakraborty answered |
Amoebic dysentery (amoebiasis) is caused by Entamoeba histolytica.
Amoebic dysentery, also known as amoebiasis, is a parasitic infection that affects the intestines. It is caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. This parasite is commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and contaminated water. It can also be transmitted through the consumption of food or water contaminated with the cysts of the parasite.
Mode of Transmission:
The primary mode of transmission of Entamoeba histolytica is through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. The parasite exists in two forms: a cyst and a trophozoite. The cyst is the dormant stage of the parasite that can survive outside the body for a long time. When a person ingests the cyst, it passes through the stomach and reaches the intestines, where it transforms into the active trophozoite form. The trophozoites then multiply and invade the intestinal lining, causing inflammation and destruction.
Pathogenesis:
Once the trophozoites invade the intestinal lining, they can cause a range of symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to severe dysentery. The trophozoites feed on the intestinal cells, causing ulceration and tissue destruction. They can also penetrate the intestinal wall and enter the bloodstream, leading to extra-intestinal manifestations such as liver abscesses.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of amoebic dysentery include:
- Diarrhea (often bloody)
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of amoebic dysentery involves the detection of the parasite in stool samples. Microscopic examination of the stool can reveal the presence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites or cysts. In some cases, a blood test may be performed to detect antibodies against the parasite.
Treatment and Prevention:
Amoebic dysentery can be treated with specific anti-parasitic medications that target Entamoeba histolytica. These medications can help eliminate the parasite from the intestines and alleviate the symptoms. It is also important to maintain good personal hygiene and avoid consuming food or water from unreliable sources to prevent the transmission of the infection.
In conclusion, amoebic dysentery is caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. It is transmitted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water and can cause a range of gastrointestinal symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage the infection effectively.
Amoebic dysentery, also known as amoebiasis, is a parasitic infection that affects the intestines. It is caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. This parasite is commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and contaminated water. It can also be transmitted through the consumption of food or water contaminated with the cysts of the parasite.
Mode of Transmission:
The primary mode of transmission of Entamoeba histolytica is through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. The parasite exists in two forms: a cyst and a trophozoite. The cyst is the dormant stage of the parasite that can survive outside the body for a long time. When a person ingests the cyst, it passes through the stomach and reaches the intestines, where it transforms into the active trophozoite form. The trophozoites then multiply and invade the intestinal lining, causing inflammation and destruction.
Pathogenesis:
Once the trophozoites invade the intestinal lining, they can cause a range of symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to severe dysentery. The trophozoites feed on the intestinal cells, causing ulceration and tissue destruction. They can also penetrate the intestinal wall and enter the bloodstream, leading to extra-intestinal manifestations such as liver abscesses.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of amoebic dysentery include:
- Diarrhea (often bloody)
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of amoebic dysentery involves the detection of the parasite in stool samples. Microscopic examination of the stool can reveal the presence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites or cysts. In some cases, a blood test may be performed to detect antibodies against the parasite.
Treatment and Prevention:
Amoebic dysentery can be treated with specific anti-parasitic medications that target Entamoeba histolytica. These medications can help eliminate the parasite from the intestines and alleviate the symptoms. It is also important to maintain good personal hygiene and avoid consuming food or water from unreliable sources to prevent the transmission of the infection.
In conclusion, amoebic dysentery is caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. It is transmitted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water and can cause a range of gastrointestinal symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage the infection effectively.
Which one of the following diseases cannot be cured by taking antibiotics?- a)Plague
- b)Amoebiasis
- c)Leprosy
- d)Whooping cough
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following diseases cannot be cured by taking antibiotics?
a)
Plague
b)
Amoebiasis
c)
Leprosy
d)
Whooping cough
|
|
Neha Menon answered |
**Explanation:**
**Introduction:**
Antibiotics are medications that are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria. However, not all diseases are caused by bacteria, and therefore, not all diseases can be cured by antibiotics.
**Explanation:**
Out of the diseases listed in the options, amoebiasis is the one that cannot be cured by taking antibiotics. Here's why:
1. **Plague:** Plague is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. It can be treated with antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, or doxycycline. With prompt treatment, most people recover from the plague.
2. **Amoebiasis:** Amoebiasis is caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Antibiotics are not effective against parasites. The treatment for amoebiasis typically involves antiparasitic medications like metronidazole or tinidazole, which specifically target the parasite.
3. **Leprosy:** Leprosy is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It is treated with a combination of antibiotics such as dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine. Leprosy treatment usually requires long-term antibiotic therapy to completely eliminate the bacteria.
4. **Whooping cough:** Whooping cough, or pertussis, is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Antibiotics such as azithromycin or erythromycin can be used to treat whooping cough, especially in the early stages of the infection.
Therefore, the correct answer is **(b) Amoebiasis**, as it is caused by a parasite and requires antiparasitic medications rather than antibiotics for treatment.
**Introduction:**
Antibiotics are medications that are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria. However, not all diseases are caused by bacteria, and therefore, not all diseases can be cured by antibiotics.
**Explanation:**
Out of the diseases listed in the options, amoebiasis is the one that cannot be cured by taking antibiotics. Here's why:
1. **Plague:** Plague is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. It can be treated with antibiotics such as streptomycin, gentamicin, or doxycycline. With prompt treatment, most people recover from the plague.
2. **Amoebiasis:** Amoebiasis is caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Antibiotics are not effective against parasites. The treatment for amoebiasis typically involves antiparasitic medications like metronidazole or tinidazole, which specifically target the parasite.
3. **Leprosy:** Leprosy is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It is treated with a combination of antibiotics such as dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine. Leprosy treatment usually requires long-term antibiotic therapy to completely eliminate the bacteria.
4. **Whooping cough:** Whooping cough, or pertussis, is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Antibiotics such as azithromycin or erythromycin can be used to treat whooping cough, especially in the early stages of the infection.
Therefore, the correct answer is **(b) Amoebiasis**, as it is caused by a parasite and requires antiparasitic medications rather than antibiotics for treatment.
Which of the following factors affect human health?
(i) Infections
(ii) Silent mutations
(iii) Life style
(iv) Genetic disorders
- a)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors affect human health?
(i) Infections
(ii) Silent mutations
(iii) Life style
(iv) Genetic disorders
(i) Infections
(ii) Silent mutations
(iii) Life style
(iv) Genetic disorders
a)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Rajeev Shah answered |
The correct answer is option 'C' (i), (iii) and (iv) - infections, lifestyle, and genetic disorders all affect human health.
(i) Infections: Infections are caused by various microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. These microorganisms can enter the body through various routes and cause diseases. Infections can range from mild illnesses such as the common cold to more severe diseases like pneumonia, tuberculosis, or HIV/AIDS. Infections can significantly impact human health by causing symptoms, weakening the immune system, and potentially leading to complications or even death.
(iii) Lifestyle: Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in determining an individual's health. Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse can have detrimental effects on human health. These habits can increase the risk of developing chronic diseases like obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancers. On the other hand, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management can promote overall well-being and reduce the risk of various diseases.
(iv) Genetic disorders: Genetic disorders are caused by abnormalities or mutations in an individual's genes. These disorders can be inherited from one or both parents or can occur as a result of spontaneous genetic mutations. Genetic disorders can affect various aspects of human health, including physical and mental development, metabolism, immune system function, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Examples of genetic disorders include Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease. These disorders can have varying degrees of severity and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and overall health.
In conclusion, infections, lifestyle choices, and genetic disorders are all factors that can affect human health. Understanding these factors and taking appropriate measures to prevent infections, adopt a healthy lifestyle, and manage genetic disorders can help promote better health outcomes.
(i) Infections: Infections are caused by various microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. These microorganisms can enter the body through various routes and cause diseases. Infections can range from mild illnesses such as the common cold to more severe diseases like pneumonia, tuberculosis, or HIV/AIDS. Infections can significantly impact human health by causing symptoms, weakening the immune system, and potentially leading to complications or even death.
(iii) Lifestyle: Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in determining an individual's health. Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse can have detrimental effects on human health. These habits can increase the risk of developing chronic diseases like obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancers. On the other hand, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management can promote overall well-being and reduce the risk of various diseases.
(iv) Genetic disorders: Genetic disorders are caused by abnormalities or mutations in an individual's genes. These disorders can be inherited from one or both parents or can occur as a result of spontaneous genetic mutations. Genetic disorders can affect various aspects of human health, including physical and mental development, metabolism, immune system function, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Examples of genetic disorders include Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease. These disorders can have varying degrees of severity and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and overall health.
In conclusion, infections, lifestyle choices, and genetic disorders are all factors that can affect human health. Understanding these factors and taking appropriate measures to prevent infections, adopt a healthy lifestyle, and manage genetic disorders can help promote better health outcomes.
Which of the following is not a function of the Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?- a)Provide nutrition to spermatogonia
- b)Secrete testosterone
- c)Support developing germ cells
- d)Secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a function of the Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
a)
Provide nutrition to spermatogonia
b)
Secrete testosterone
c)
Support developing germ cells
d)
Secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP)

|
Lead Academy answered |
Answer: Option B: Secrete testosterone
Solution: Sertoli cells provide nutrition to spermatogonia, support developing germ cells, and secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP), but they do not secrete testosterone. Testosterone is actually secreted by the Leydig cells (interstitial cells) located in the interstitial spaces between the seminiferous tubules. An additional fact about Sertoli cells is that they also play a key role in the blood-testis barrier, protecting germ cells from autoimmune attacks.
Solution: Sertoli cells provide nutrition to spermatogonia, support developing germ cells, and secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP), but they do not secrete testosterone. Testosterone is actually secreted by the Leydig cells (interstitial cells) located in the interstitial spaces between the seminiferous tubules. An additional fact about Sertoli cells is that they also play a key role in the blood-testis barrier, protecting germ cells from autoimmune attacks.
Which of the following statements regarding different barriers of innate immunity is not correct?- a)Acid present in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from the eyes prevent the growth of microorganisms and constitute physiological barriers of our body
- b)Mucous membrane lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts helps in trapping the microbes and constitute physiological barriers of our body
- c)Certain types of leucocytes such as polymorpho nuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) and lymphocytes such as natural killer cells, constitute cellular barriers of our body
- d)Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection and constitute cytokine barriers of our body
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding different barriers of innate immunity is not correct?
a)
Acid present in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from the eyes prevent the growth of microorganisms and constitute physiological barriers of our body
b)
Mucous membrane lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts helps in trapping the microbes and constitute physiological barriers of our body
c)
Certain types of leucocytes such as polymorpho nuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) and lymphocytes such as natural killer cells, constitute cellular barriers of our body
d)
Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection and constitute cytokine barriers of our body
|
|
Palak Goyal answered |
Innate immunity is the first line of defense of our body against pathogens. It consists of physiological and cellular barriers that prevent the entry and growth of microorganisms in our body. These barriers are present in different parts of our body and work together to protect us from infections.
Physiological barriers:
Physiological barriers are the physical and chemical barriers present in our body that prevent the entry and growth of microorganisms. The following statements regarding different physiological barriers of innate immunity are correct:
a) Acid present in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from the eyes prevent the growth of microorganisms and constitute physiological barriers of our body.
- Acid in the stomach kills most of the microorganisms that enter our body through food or water.
- Saliva in the mouth contains enzymes and antibodies that prevent the growth of microorganisms in the oral cavity.
- Tears from the eyes contain lysozyme, an enzyme that can break down the cell wall of bacteria and prevent their growth.
b) Mucous membrane lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts helps in trapping the microbes and constitute physiological barriers of our body.
- This statement is not correct as the mucous membrane is not just a physical barrier but also a site of active immune defense. The mucous membrane contains specialized cells called epithelial cells that secrete mucus, which traps microorganisms and prevents their entry into the body. The mucous membrane also contains immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes that can recognize and destroy the invading microorganisms.
Cellular barriers:
Cellular barriers are the immune cells present in our body that can recognize and destroy the invading microorganisms. The following statements regarding different cellular barriers of innate immunity are correct:
c) Certain types of leucocytes such as polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) and lymphocytes such as natural killer cells, constitute cellular barriers of our body.
- Polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) are the most abundant type of white blood cells in our body. They can recognize and engulf bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte that can recognize and kill virus-infected and cancerous cells.
d) Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection and constitute cytokine barriers of our body.
- This statement is correct. Interferons are proteins produced by virus-infected cells that activate the immune cells and protect non-infected cells from viral infection. Interferons can induce the expression of antiviral genes in the non-infected cells, which can prevent the replication of the virus.
In conclusion, statement b is not correct as the mucous membrane is not just a physical barrier but also a site of active immune defense.
Physiological barriers:
Physiological barriers are the physical and chemical barriers present in our body that prevent the entry and growth of microorganisms. The following statements regarding different physiological barriers of innate immunity are correct:
a) Acid present in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from the eyes prevent the growth of microorganisms and constitute physiological barriers of our body.
- Acid in the stomach kills most of the microorganisms that enter our body through food or water.
- Saliva in the mouth contains enzymes and antibodies that prevent the growth of microorganisms in the oral cavity.
- Tears from the eyes contain lysozyme, an enzyme that can break down the cell wall of bacteria and prevent their growth.
b) Mucous membrane lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts helps in trapping the microbes and constitute physiological barriers of our body.
- This statement is not correct as the mucous membrane is not just a physical barrier but also a site of active immune defense. The mucous membrane contains specialized cells called epithelial cells that secrete mucus, which traps microorganisms and prevents their entry into the body. The mucous membrane also contains immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes that can recognize and destroy the invading microorganisms.
Cellular barriers:
Cellular barriers are the immune cells present in our body that can recognize and destroy the invading microorganisms. The following statements regarding different cellular barriers of innate immunity are correct:
c) Certain types of leucocytes such as polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) and lymphocytes such as natural killer cells, constitute cellular barriers of our body.
- Polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMNL-neutrophils) are the most abundant type of white blood cells in our body. They can recognize and engulf bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte that can recognize and kill virus-infected and cancerous cells.
d) Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection and constitute cytokine barriers of our body.
- This statement is correct. Interferons are proteins produced by virus-infected cells that activate the immune cells and protect non-infected cells from viral infection. Interferons can induce the expression of antiviral genes in the non-infected cells, which can prevent the replication of the virus.
In conclusion, statement b is not correct as the mucous membrane is not just a physical barrier but also a site of active immune defense.
Which of the following cells actively participate during allergy?- a)B-lymphocytes
- b)Liver cells
- c)Mast cells
- d)Red blood cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cells actively participate during allergy?
a)
B-lymphocytes
b)
Liver cells
c)
Mast cells
d)
Red blood cells
|
|
Roshni Basak answered |
Allergy and Mast Cells
Allergy is an exaggerated immune response to harmless substances called allergens. These allergens can be anything from pollen to certain foods, medications, or animal dander. During an allergic response, mast cells play an active role in the inflammatory process.
Mast Cells
Mast cells are a type of white blood cell that resides in connective tissues throughout the body, particularly in areas that are exposed to the external environment such as the skin, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. They are involved in both innate and adaptive immunity.
Role of Mast Cells in Allergy
When an allergen enters the body of an allergic individual, it triggers an immune response. In the case of allergies, the immune system reacts to the allergen as if it were harmful. Mast cells have specific receptors on their surface that recognize and bind to allergens.
Release of Mediators
Upon allergen binding, mast cells release a variety of chemical mediators, including histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins. These mediators are responsible for the symptoms of allergies such as itching, redness, swelling, and increased mucus production.
Effects on Surrounding Tissues
Histamine, one of the primary mediators released by mast cells, causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable. This leads to increased blood flow to the affected area and the leakage of fluid and immune cells into the surrounding tissues. The resulting inflammation contributes to the characteristic symptoms of allergies.
Recruitment of Other Immune Cells
Mast cells also play a role in recruiting other immune cells to the site of the allergic reaction. They release chemotactic factors that attract eosinophils, basophils, and T-cells to the area. These immune cells further contribute to the inflammatory response.
Conclusion
In summary, mast cells actively participate during allergies by recognizing and binding to allergens, releasing chemical mediators that cause inflammation and allergic symptoms, and recruiting other immune cells to the site of the allergic reaction. Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - Mast cells.
Allergy is an exaggerated immune response to harmless substances called allergens. These allergens can be anything from pollen to certain foods, medications, or animal dander. During an allergic response, mast cells play an active role in the inflammatory process.
Mast Cells
Mast cells are a type of white blood cell that resides in connective tissues throughout the body, particularly in areas that are exposed to the external environment such as the skin, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. They are involved in both innate and adaptive immunity.
Role of Mast Cells in Allergy
When an allergen enters the body of an allergic individual, it triggers an immune response. In the case of allergies, the immune system reacts to the allergen as if it were harmful. Mast cells have specific receptors on their surface that recognize and bind to allergens.
Release of Mediators
Upon allergen binding, mast cells release a variety of chemical mediators, including histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins. These mediators are responsible for the symptoms of allergies such as itching, redness, swelling, and increased mucus production.
Effects on Surrounding Tissues
Histamine, one of the primary mediators released by mast cells, causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable. This leads to increased blood flow to the affected area and the leakage of fluid and immune cells into the surrounding tissues. The resulting inflammation contributes to the characteristic symptoms of allergies.
Recruitment of Other Immune Cells
Mast cells also play a role in recruiting other immune cells to the site of the allergic reaction. They release chemotactic factors that attract eosinophils, basophils, and T-cells to the area. These immune cells further contribute to the inflammatory response.
Conclusion
In summary, mast cells actively participate during allergies by recognizing and binding to allergens, releasing chemical mediators that cause inflammation and allergic symptoms, and recruiting other immune cells to the site of the allergic reaction. Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - Mast cells.
An auto-immune disease is- a)SCID
- b)rheumatoid athritis
- c)myasthenia gravis
- d)both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An auto-immune disease is
a)
SCID
b)
rheumatoid athritis
c)
myasthenia gravis
d)
both (b) and (c)
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
If the immune system fails to recognize 'self from non-self and starts destroying the body's own cells, this leads to some malfunctions, which are termed as autoimmune diseases. Both rheumatoid arthritis and myasthenia gravis are autoimmune diseases. In rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation of the synovial membrane in synovial joints occurs. When this membrane, which is the source of synovial fluid, becomes inflamed, it produces too much fluid. Thus, the joints swell and become extremely painful. Myasthenia gravis is a chronic disease marked by abnormal fatigability and weakness of selected muscles. The degree of fatigue is so extreme that these muscles are temporarily paralysed. In this disease, antibodies bind to cholinergic receptors on muscle cells, which impairs the ability of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to induce muscle contraction.
Following table summarises the differences between normal cells and cancerous cells. Pick up the wrong difference(s) and select the correct option.
- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(iii) only
- d)(ii) only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Following table summarises the differences between normal cells and cancerous cells. Pick up the wrong difference(s) and select the correct option.

a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(iii) only
d)
(ii) only
|
|
Megha Das answered |
Cancer is a dreadful disease and is also called a malignant neoplasm or the disease of uncontrolled proliferation of certain cells without differentiation. The term neoplasm is also used as a synonym for tumour. The cells of tumour cells can pass to new sites for forming a secondary tumour, in a process called metastasis. The following are the properties of cancer cells :
1. They do not need external extracellular growth factors.
2. They do not have control over the cell cycle.
3. They divide rapidly and form a solid mass of cells.
4. They do not exhibit the property of contact inhibition.
5. The nuclei of these cells are irregular, and granular.
6. They do not differentiate and keep dividing continuously.
7. There is no definite life span for a cancer cell.
Hope it helps you.... :)
1. They do not need external extracellular growth factors.
2. They do not have control over the cell cycle.
3. They divide rapidly and form a solid mass of cells.
4. They do not exhibit the property of contact inhibition.
5. The nuclei of these cells are irregular, and granular.
6. They do not differentiate and keep dividing continuously.
7. There is no definite life span for a cancer cell.
Hope it helps you.... :)
AIDS is characterized by- a)decrease in the number of Killer T-cell
- b)decrease in the number of suppressor T-cells
- c)decrease in the number of helper T-cells
- d)increase in the number of helper T-cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
AIDS is characterized by
a)
decrease in the number of Killer T-cell
b)
decrease in the number of suppressor T-cells
c)
decrease in the number of helper T-cells
d)
increase in the number of helper T-cells
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
AIDS is caused by HIV. When HIV enters into helper T-cells, it replicates and produces other viruses that kill the helper T-cells. Thus the number of T-cells decrease in the body of the infected person and the person starts suffering from various infections.
The abbreviation AIDS stands for- a)Acquired immuno disease syndrome
- b)Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome
- c)Acquired immunity determining syndrome
- d)Acquired immunity delay syndrome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The abbreviation AIDS stands for
a)
Acquired immuno disease syndrome
b)
Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome
c)
Acquired immunity determining syndrome
d)
Acquired immunity delay syndrome
|
|
Lekshmi Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
The correct abbreviation for AIDS is "Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome." Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
Acquired:
- AIDS is a condition that is acquired after birth, rather than being congenital or present at birth.
- It is not a genetic disorder or hereditary condition.
Immuno:
- "Immuno" refers to the immune system.
- The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from infectious diseases and other harmful invaders.
Deficiency:
- "Deficiency" means a lack or insufficiency of something.
- In the case of AIDS, it refers to a deficiency or impairment of the immune system.
Syndrome:
- A syndrome is a collection of symptoms and signs that occur together.
- AIDS is considered a syndrome because it is characterized by a variety of symptoms and signs that result from the immune system deficiency.
Overall:
- When combined, the abbreviation AIDS stands for "Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome."
- This term is used to describe a condition in which the immune system is severely compromised, leaving the individual susceptible to various opportunistic infections and diseases.
- AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which attacks and destroys immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells.
- Without proper treatment, AIDS can be life-threatening.
- It is important to note that AIDS is not a single disease but rather a stage of HIV infection where the immune system is significantly damaged.
The correct abbreviation for AIDS is "Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome." Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
Acquired:
- AIDS is a condition that is acquired after birth, rather than being congenital or present at birth.
- It is not a genetic disorder or hereditary condition.
Immuno:
- "Immuno" refers to the immune system.
- The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from infectious diseases and other harmful invaders.
Deficiency:
- "Deficiency" means a lack or insufficiency of something.
- In the case of AIDS, it refers to a deficiency or impairment of the immune system.
Syndrome:
- A syndrome is a collection of symptoms and signs that occur together.
- AIDS is considered a syndrome because it is characterized by a variety of symptoms and signs that result from the immune system deficiency.
Overall:
- When combined, the abbreviation AIDS stands for "Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome."
- This term is used to describe a condition in which the immune system is severely compromised, leaving the individual susceptible to various opportunistic infections and diseases.
- AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which attacks and destroys immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells.
- Without proper treatment, AIDS can be life-threatening.
- It is important to note that AIDS is not a single disease but rather a stage of HIV infection where the immune system is significantly damaged.
Typhoid fever in human beings is caused by- a)Plasmodium vivax
- b)Trichophyton
- c)Salmonella typhi
- d)Rhinoviruses
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Typhoid fever in human beings is caused by
a)
Plasmodium vivax
b)
Trichophyton
c)
Salmonella typhi
d)
Rhinoviruses

|
Muskan Sharma answered |
Typhoid fever in human being is caused by Salmonella typhi (bacteria).
Small intestine is infected.
Symptom--- high fever, weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache, loss of appetite.
Confirmed by Widal Test.
Small intestine is infected.
Symptom--- high fever, weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache, loss of appetite.
Confirmed by Widal Test.
The common cold is caused by- a)Rhino viruses
- b)Streptococcus pneumoniae
- c)Salmonella typhimurium
- d)Plasmodium vivax
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common cold is caused by
a)
Rhino viruses
b)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
c)
Salmonella typhimurium
d)
Plasmodium vivax
|
|
Lekshmi Tiwari answered |
The Common Cold: Causes and Explanation
The common cold, also known as an upper respiratory tract infection, is a viral illness that affects the nose and throat. It is a highly contagious condition and is usually harmless, although it can cause discomfort and inconvenience. The primary cause of the common cold is rhinoviruses, which are responsible for the majority of cold infections. Let's explore this answer in more detail:
Rhinoviruses
Rhinoviruses are a group of small, single-stranded RNA viruses that belong to the family Picornaviridae. They are the most common cause of the common cold, accounting for approximately 30-50% of all cold cases. Rhinoviruses are highly contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Transmission and Symptoms
When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing rhinoviruses are released into the air. These droplets can be inhaled by others, leading to the transmission of the virus. Additionally, rhinoviruses can survive on surfaces for several hours, increasing the risk of transmission through touch.
Once the rhinovirus enters the body, it attaches to the cells lining the nose and throat. This attachment triggers an immune response, leading to inflammation of the respiratory tract. The most common symptoms of a cold include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat, cough, mild headache, and fatigue. These symptoms typically appear 1-3 days after exposure to the virus and can last for 7-10 days.
Other Causes
While rhinoviruses are the primary cause of the common cold, it is important to note that other viruses can also contribute to cold-like symptoms. These include coronaviruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, and adenoviruses. However, rhinoviruses remain the most prevalent and significant cause of the common cold.
Conclusion
In summary, the common cold is mainly caused by rhinoviruses. These viruses are highly contagious and can be transmitted through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces. Understanding the cause of the common cold helps in implementing preventive measures, such as frequent handwashing, covering the mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, to reduce the spread of the virus.
The common cold, also known as an upper respiratory tract infection, is a viral illness that affects the nose and throat. It is a highly contagious condition and is usually harmless, although it can cause discomfort and inconvenience. The primary cause of the common cold is rhinoviruses, which are responsible for the majority of cold infections. Let's explore this answer in more detail:
Rhinoviruses
Rhinoviruses are a group of small, single-stranded RNA viruses that belong to the family Picornaviridae. They are the most common cause of the common cold, accounting for approximately 30-50% of all cold cases. Rhinoviruses are highly contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Transmission and Symptoms
When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny droplets containing rhinoviruses are released into the air. These droplets can be inhaled by others, leading to the transmission of the virus. Additionally, rhinoviruses can survive on surfaces for several hours, increasing the risk of transmission through touch.
Once the rhinovirus enters the body, it attaches to the cells lining the nose and throat. This attachment triggers an immune response, leading to inflammation of the respiratory tract. The most common symptoms of a cold include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat, cough, mild headache, and fatigue. These symptoms typically appear 1-3 days after exposure to the virus and can last for 7-10 days.
Other Causes
While rhinoviruses are the primary cause of the common cold, it is important to note that other viruses can also contribute to cold-like symptoms. These include coronaviruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, and adenoviruses. However, rhinoviruses remain the most prevalent and significant cause of the common cold.
Conclusion
In summary, the common cold is mainly caused by rhinoviruses. These viruses are highly contagious and can be transmitted through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces. Understanding the cause of the common cold helps in implementing preventive measures, such as frequent handwashing, covering the mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, to reduce the spread of the virus.
During the life cycle of Plasmodium, sexual reproduction takes place in which of the following hosts?- a)Human
- b)Female Anopheles mosquito
- c)Male Anopheles mosquito
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During the life cycle of Plasmodium, sexual reproduction takes place in which of the following hosts?
a)
Human
b)
Female Anopheles mosquito
c)
Male Anopheles mosquito
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Tanishq Choudhary answered |
Plasmodium is a protozoan parasite that causes malaria in humans. The life cycle of Plasmodium involves both asexual and sexual reproduction. The asexual reproduction takes place in the human host, while the sexual reproduction takes place in the female Anopheles mosquito.
Explanation:
The life cycle of Plasmodium involves the following stages:
1. Sporozoites: The sporozoites are the infective form of Plasmodium, which are injected into the human host by the female Anopheles mosquito while taking a blood meal.
2. Liver stage: The sporozoites enter the liver cells and multiply asexually to form merozoites.
3. Blood stage: The merozoites are released into the bloodstream and infect the red blood cells, where they multiply asexually and cause the symptoms of malaria.
4. Gametocytes: Some of the merozoites differentiate into male and female gametocytes, which are the sexual forms of Plasmodium.
5. Mosquito stage: When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected human, it ingests the gametocytes along with the blood.
6. Fertilization: The male gametocytes fertilize the female gametocytes in the mosquito's gut, forming zygotes.
7. Ookinete: The zygotes develop into motile ookinetes, which penetrate the gut wall and form oocysts.
8. Sporozoites: The oocysts release sporozoites into the mosquito's hemocoel, which migrate to the salivary glands.
9. Transmission: When the infected mosquito bites a human, it injects the sporozoites into the bloodstream, and the cycle repeats.
Therefore, the sexual reproduction of Plasmodium takes place in the female Anopheles mosquito, while the asexual reproduction takes place in the human host. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Explanation:
The life cycle of Plasmodium involves the following stages:
1. Sporozoites: The sporozoites are the infective form of Plasmodium, which are injected into the human host by the female Anopheles mosquito while taking a blood meal.
2. Liver stage: The sporozoites enter the liver cells and multiply asexually to form merozoites.
3. Blood stage: The merozoites are released into the bloodstream and infect the red blood cells, where they multiply asexually and cause the symptoms of malaria.
4. Gametocytes: Some of the merozoites differentiate into male and female gametocytes, which are the sexual forms of Plasmodium.
5. Mosquito stage: When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected human, it ingests the gametocytes along with the blood.
6. Fertilization: The male gametocytes fertilize the female gametocytes in the mosquito's gut, forming zygotes.
7. Ookinete: The zygotes develop into motile ookinetes, which penetrate the gut wall and form oocysts.
8. Sporozoites: The oocysts release sporozoites into the mosquito's hemocoel, which migrate to the salivary glands.
9. Transmission: When the infected mosquito bites a human, it injects the sporozoites into the bloodstream, and the cycle repeats.
Therefore, the sexual reproduction of Plasmodium takes place in the female Anopheles mosquito, while the asexual reproduction takes place in the human host. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Where will you look for the sporozoites of malarial parasite?- a)Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- b)Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
- c)Spleen of infected humans
- d)red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where will you look for the sporozoites of malarial parasite?
a)
Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
b)
Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
c)
Spleen of infected humans
d)
red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
|
|
Aarav Yadav answered |
Where will you look for the sporozoites of malarial parasite?
To find the sporozoites of the malarial parasite, we need to understand the life cycle of the parasite and its transmission to humans. Malaria is caused by the Plasmodium parasite and is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito. Let's examine the options given and explain why the correct answer is option 'A' - saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
a) Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- When an infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a human, it injects saliva into the human's bloodstream to prevent blood clotting. Along with saliva, it also injects sporozoites, which are the infective form of the malarial parasite.
- These sporozoites travel through the bloodstream and eventually reach the liver, where they invade liver cells and undergo asexual replication.
- From the liver, they are released back into the bloodstream as merozoites, which invade and multiply within red blood cells, causing symptoms of malaria.
b) Salivary glands of freshly molted female Anopheles mosquito
- This option is incorrect because the sporozoites are not found in the salivary glands of freshly molted female Anopheles mosquitoes. It is only when the mosquito becomes infected by feeding on an infected human that the sporozoites develop and reach the salivary glands.
c) Spleen of infected humans
- The spleen plays a role in the immune response against malaria, but it is not the site where sporozoites are found. Sporozoites are injected into the bloodstream by infected mosquitoes and primarily invade liver cells, not the spleen.
d) Red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
- While red blood cells are indeed the target of the malarial parasite during the blood stage of infection, sporozoites are not found within red blood cells. Sporozoites are injected into the bloodstream by infected mosquitoes and initially invade liver cells, not red blood cells.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' - the sporozoites of the malarial parasite are found in the saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. When these infected mosquitoes bite humans, they inject sporozoites along with saliva into the bloodstream, initiating the infection process.
To find the sporozoites of the malarial parasite, we need to understand the life cycle of the parasite and its transmission to humans. Malaria is caused by the Plasmodium parasite and is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito. Let's examine the options given and explain why the correct answer is option 'A' - saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
a) Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- When an infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a human, it injects saliva into the human's bloodstream to prevent blood clotting. Along with saliva, it also injects sporozoites, which are the infective form of the malarial parasite.
- These sporozoites travel through the bloodstream and eventually reach the liver, where they invade liver cells and undergo asexual replication.
- From the liver, they are released back into the bloodstream as merozoites, which invade and multiply within red blood cells, causing symptoms of malaria.
b) Salivary glands of freshly molted female Anopheles mosquito
- This option is incorrect because the sporozoites are not found in the salivary glands of freshly molted female Anopheles mosquitoes. It is only when the mosquito becomes infected by feeding on an infected human that the sporozoites develop and reach the salivary glands.
c) Spleen of infected humans
- The spleen plays a role in the immune response against malaria, but it is not the site where sporozoites are found. Sporozoites are injected into the bloodstream by infected mosquitoes and primarily invade liver cells, not the spleen.
d) Red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria
- While red blood cells are indeed the target of the malarial parasite during the blood stage of infection, sporozoites are not found within red blood cells. Sporozoites are injected into the bloodstream by infected mosquitoes and initially invade liver cells, not red blood cells.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A' - the sporozoites of the malarial parasite are found in the saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. When these infected mosquitoes bite humans, they inject sporozoites along with saliva into the bloodstream, initiating the infection process.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Pneumonia can be transmitted to a healthy person by inhaling the droplets released by an infected person and also by sharing utensils
- b)Pathogens causing pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae
- c)There is no vaccine yet available to prevent pneumonia
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Pneumonia can be transmitted to a healthy person by inhaling the droplets released by an infected person and also by sharing utensils
b)
Pathogens causing pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae
c)
There is no vaccine yet available to prevent pneumonia
d)
None of these
|
|
Palak Basu answered |
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets, which are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets contain the infectious agents, and if a healthy person inhales them, they can become infected with pneumonia.
Pathogens causing pneumonia:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: This bacterium is one of the most common causes of pneumonia. It can also cause other respiratory infections such as sinusitis and ear infections.
- Haemophilus influenzae: This bacterium is another common cause of pneumonia, especially in young children and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Transmission of pneumonia:
- Inhaling droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, they release respiratory droplets into the air. If a healthy person inhales these droplets, they can become infected with pneumonia.
- Sharing utensils: It is possible to transmit pneumonia by sharing utensils with an infected person, as the pathogens can be present on the utensils and can be transferred to a healthy person.
Vaccine for pneumonia:
- Incorrect statement: The statement that there is no vaccine available to prevent pneumonia is incorrect. Vaccines are available for certain pathogens that cause pneumonia, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines can help prevent pneumonia caused by these specific pathogens.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that there is no vaccine available to prevent pneumonia. In reality, vaccines are available for some of the common pathogens that cause pneumonia, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines play a crucial role in preventing pneumonia and reducing its burden on public health.
Pathogens causing pneumonia:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: This bacterium is one of the most common causes of pneumonia. It can also cause other respiratory infections such as sinusitis and ear infections.
- Haemophilus influenzae: This bacterium is another common cause of pneumonia, especially in young children and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Transmission of pneumonia:
- Inhaling droplets: When an infected person coughs or sneezes, they release respiratory droplets into the air. If a healthy person inhales these droplets, they can become infected with pneumonia.
- Sharing utensils: It is possible to transmit pneumonia by sharing utensils with an infected person, as the pathogens can be present on the utensils and can be transferred to a healthy person.
Vaccine for pneumonia:
- Incorrect statement: The statement that there is no vaccine available to prevent pneumonia is incorrect. Vaccines are available for certain pathogens that cause pneumonia, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines can help prevent pneumonia caused by these specific pathogens.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that there is no vaccine available to prevent pneumonia. In reality, vaccines are available for some of the common pathogens that cause pneumonia, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines play a crucial role in preventing pneumonia and reducing its burden on public health.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.Statement 1: Malignant tumors normally remain confined to their original location, do not spread to other body parts and cause less damage.
Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer etc.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Malignant tumors normally remain confined to their original location, do not spread to other body parts and cause less damage.
Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer etc.
Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer etc.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Rishika Mehta answered |
Incorrect Statements about Malignant Tumors and Sarcoma
Incorrect Statement 1: Malignant tumors normally remain confined to their original location, do not spread to other body parts and cause less damage.
Explanation: Malignant tumors are cancerous growths that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. They are harmful and can cause significant damage to the affected organs and tissues.
Incorrect Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer, etc.
Explanation: Sarcoma is a type of cancer that arises from the connective tissue such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat. Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as carcinoma, not sarcoma. Examples of carcinoma include breast cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, etc.
Correct Answer: D) Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
In summary, malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body, causing significant damage. Sarcoma is a type of cancer that arises from connective tissue, while carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands.
Incorrect Statement 1: Malignant tumors normally remain confined to their original location, do not spread to other body parts and cause less damage.
Explanation: Malignant tumors are cancerous growths that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. They are harmful and can cause significant damage to the affected organs and tissues.
Incorrect Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer, etc.
Explanation: Sarcoma is a type of cancer that arises from the connective tissue such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat. Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as carcinoma, not sarcoma. Examples of carcinoma include breast cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, etc.
Correct Answer: D) Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
In summary, malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body, causing significant damage. Sarcoma is a type of cancer that arises from connective tissue, while carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands.
Humoral immunity is associated with- a)T-cells
- b)B-cells
- c)Macrophages
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Humoral immunity is associated with
a)
T-cells
b)
B-cells
c)
Macrophages
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Lakshmi Bose answered |
Humoral immunity is associated with B-cells.
Introduction:
The immune system is responsible for defending the body against external pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The immune system has two major types of immunity, including humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by the production of antibodies by B-cells.
B-cells:
B-cells are a type of white blood cell that is responsible for producing antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that are produced by B-cells in response to the presence of foreign antigens. B-cells have receptors on their surface that can recognize specific antigens. Once a B-cell recognizes an antigen, it undergoes a process of activation, proliferation, and differentiation into antibody-secreting cells called plasma cells.
Antibodies:
Antibodies are proteins that are produced by B-cells in response to the presence of foreign antigens. Antibodies have a Y-shaped structure that consists of two heavy chains and two light chains. The tips of the Y-shaped structure contain antigen-binding sites that can recognize specific antigens. Once an antibody binds to an antigen, it can neutralize the antigen or mark it for destruction by other cells of the immune system.
Humoral immunity:
Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by the production of antibodies by B-cells. Humoral immunity is effective against extracellular pathogens such as bacteria and viruses that are circulating in the blood or lymphatic system. In humoral immunity, B-cells recognize foreign antigens and produce antibodies that can neutralize the antigens or mark them for destruction by other cells of the immune system.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, humoral immunity is associated with B-cells. B-cells are responsible for recognizing foreign antigens and producing antibodies in response to the antigens. Antibodies can neutralize or mark the antigens for destruction by other cells of the immune system. Humoral immunity is effective against extracellular pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Introduction:
The immune system is responsible for defending the body against external pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The immune system has two major types of immunity, including humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by the production of antibodies by B-cells.
B-cells:
B-cells are a type of white blood cell that is responsible for producing antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that are produced by B-cells in response to the presence of foreign antigens. B-cells have receptors on their surface that can recognize specific antigens. Once a B-cell recognizes an antigen, it undergoes a process of activation, proliferation, and differentiation into antibody-secreting cells called plasma cells.
Antibodies:
Antibodies are proteins that are produced by B-cells in response to the presence of foreign antigens. Antibodies have a Y-shaped structure that consists of two heavy chains and two light chains. The tips of the Y-shaped structure contain antigen-binding sites that can recognize specific antigens. Once an antibody binds to an antigen, it can neutralize the antigen or mark it for destruction by other cells of the immune system.
Humoral immunity:
Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that is mediated by the production of antibodies by B-cells. Humoral immunity is effective against extracellular pathogens such as bacteria and viruses that are circulating in the blood or lymphatic system. In humoral immunity, B-cells recognize foreign antigens and produce antibodies that can neutralize the antigens or mark them for destruction by other cells of the immune system.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, humoral immunity is associated with B-cells. B-cells are responsible for recognizing foreign antigens and producing antibodies in response to the antigens. Antibodies can neutralize or mark the antigens for destruction by other cells of the immune system. Humoral immunity is effective against extracellular pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Which form of pathogen is used in vaccination?- a)Activated and strong pathogenic antigens
- b)Inactivated and weakened pathogenic antigens
- c)Hyperactive and strong pathogen
- d)Preformed antibodies
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which form of pathogen is used in vaccination?
a)
Activated and strong pathogenic antigens
b)
Inactivated and weakened pathogenic antigens
c)
Hyperactive and strong pathogen
d)
Preformed antibodies
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The process of introduction of vaccine into an individual to provide protection against a disease is called vaccination. Vaccine is a preparation or extract of an inactivated/ attenuated (weakened) pathogen of a disease which on inoculation into a healthy person provides immunity by inducing antibodies production.
An antibody consists of- a)two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains
- b)two light peptide chains and one heavy peptide chain
- c)one light peptide chain and one heavy peptide chain
- d)one light peptide chain and two heavy peptide chains
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An antibody consists of
a)
two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains
b)
two light peptide chains and one heavy peptide chain
c)
one light peptide chain and one heavy peptide chain
d)
one light peptide chain and two heavy peptide chains
|
|
Lekshmi Tiwari answered |
Anatomy of an Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a Y-shaped protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of antigens. Antibodies play a critical role in the immune response by recognizing and binding to specific antigens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
Structure of an Antibody
An antibody consists of two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains, making a total of four chains. These chains are held together by disulfide bonds, creating a stable and functional structure. The light chains are shorter in length compared to the heavy chains.
Light Peptide Chains
- An antibody has two identical light peptide chains, also referred to as the L chains.
- Each light chain is composed of approximately 220-230 amino acids.
- Light chains are further divided into two regions: the variable region (VL) and the constant region (CL).
- The variable region contains antigen-binding sites that interact with specific antigens.
- The constant region determines the antibody's class or isotype.
Heavy Peptide Chains
- An antibody has two identical heavy peptide chains, also referred to as the H chains.
- Each heavy chain is longer than the light chain and consists of approximately 440-450 amino acids.
- Similar to light chains, heavy chains are divided into two regions: the variable region (VH) and the constant region (CH).
- The variable region contains antigen-binding sites that complement those of the light chains.
- The constant region determines the antibody's class or isotype.
Role of the Chains
- The heavy and light chains together form the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) of the antibody.
- The Fab region is responsible for recognizing and binding to specific antigens.
- The constant regions of the heavy chains form the antibody's crystallizable fragment (Fc), which interacts with various immune cells and molecules to initiate immune responses.
Summary
An antibody is composed of two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains. The light chains are shorter and consist of variable and constant regions, while the heavy chains are longer and also have variable and constant regions. Together, these chains form the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) and the crystallizable fragment (Fc), allowing antibodies to recognize and neutralize specific antigens.
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a Y-shaped protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of antigens. Antibodies play a critical role in the immune response by recognizing and binding to specific antigens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
Structure of an Antibody
An antibody consists of two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains, making a total of four chains. These chains are held together by disulfide bonds, creating a stable and functional structure. The light chains are shorter in length compared to the heavy chains.
Light Peptide Chains
- An antibody has two identical light peptide chains, also referred to as the L chains.
- Each light chain is composed of approximately 220-230 amino acids.
- Light chains are further divided into two regions: the variable region (VL) and the constant region (CL).
- The variable region contains antigen-binding sites that interact with specific antigens.
- The constant region determines the antibody's class or isotype.
Heavy Peptide Chains
- An antibody has two identical heavy peptide chains, also referred to as the H chains.
- Each heavy chain is longer than the light chain and consists of approximately 440-450 amino acids.
- Similar to light chains, heavy chains are divided into two regions: the variable region (VH) and the constant region (CH).
- The variable region contains antigen-binding sites that complement those of the light chains.
- The constant region determines the antibody's class or isotype.
Role of the Chains
- The heavy and light chains together form the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) of the antibody.
- The Fab region is responsible for recognizing and binding to specific antigens.
- The constant regions of the heavy chains form the antibody's crystallizable fragment (Fc), which interacts with various immune cells and molecules to initiate immune responses.
Summary
An antibody is composed of two light peptide chains and two heavy peptide chains. The light chains are shorter and consist of variable and constant regions, while the heavy chains are longer and also have variable and constant regions. Together, these chains form the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) and the crystallizable fragment (Fc), allowing antibodies to recognize and neutralize specific antigens.
Which one of the following statements is true?- a)Dysentery, plague and diphtheria are viral diseases
- b)HIV replicates in host cell with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme
- c)The disease ringworm disappears during summer and rainy season
- d)Common cold could be confirmed by Widal test
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is true?
a)
Dysentery, plague and diphtheria are viral diseases
b)
HIV replicates in host cell with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme
c)
The disease ringworm disappears during summer and rainy season
d)
Common cold could be confirmed by Widal test
|
|
Uday Jain answered |
Statement: HIV replicates in host cell with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Explanation:
HIV, which stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is the causative agent of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). It is a retrovirus that infects and replicates within host cells. The replication of HIV involves the use of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
What is reverse transcriptase?
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that aids in the synthesis of DNA from an RNA template. It catalyzes the reverse transcription process, where RNA is converted into DNA. HIV contains an RNA genome, and in order to replicate, it needs to convert its RNA into DNA.
Replication of HIV:
1. Attachment: HIV attaches itself to the surface of host cells, specifically CD4+ T cells and macrophages.
2. Fusion: The viral envelope fuses with the host cell membrane, allowing the entry of the viral core into the host cell.
3. Reverse Transcription: Once inside the host cell, the RNA genome of HIV is reverse transcribed into DNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme. This DNA is known as cDNA (complementary DNA).
4. Integration: The newly synthesized cDNA is transported into the host cell nucleus and integrated into the host cell DNA. This integrated viral DNA is called a provirus.
5. Transcription: The provirus is transcribed into viral RNA molecules, which serve as both genomic RNA for new virus particles and as mRNA for the synthesis of viral proteins.
6. Translation and Assembly: The viral RNA is translated into viral proteins, which are then assembled into new virus particles.
7. Budding and Release: The new virus particles bud off from the host cell, acquiring an envelope from the host cell membrane. These newly formed viruses can now infect other host cells and continue the cycle of replication.
Significance of reverse transcriptase:
Reverse transcriptase plays a critical role in the replication of HIV. It allows the virus to convert its RNA genome into DNA, which can then be integrated into the host cell DNA. This DNA integration makes HIV difficult to eradicate from the body and enables the virus to persist and cause long-term infection.
Therefore, option B is the correct statement as HIV replicates in host cells with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Explanation:
HIV, which stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is the causative agent of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). It is a retrovirus that infects and replicates within host cells. The replication of HIV involves the use of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
What is reverse transcriptase?
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that aids in the synthesis of DNA from an RNA template. It catalyzes the reverse transcription process, where RNA is converted into DNA. HIV contains an RNA genome, and in order to replicate, it needs to convert its RNA into DNA.
Replication of HIV:
1. Attachment: HIV attaches itself to the surface of host cells, specifically CD4+ T cells and macrophages.
2. Fusion: The viral envelope fuses with the host cell membrane, allowing the entry of the viral core into the host cell.
3. Reverse Transcription: Once inside the host cell, the RNA genome of HIV is reverse transcribed into DNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme. This DNA is known as cDNA (complementary DNA).
4. Integration: The newly synthesized cDNA is transported into the host cell nucleus and integrated into the host cell DNA. This integrated viral DNA is called a provirus.
5. Transcription: The provirus is transcribed into viral RNA molecules, which serve as both genomic RNA for new virus particles and as mRNA for the synthesis of viral proteins.
6. Translation and Assembly: The viral RNA is translated into viral proteins, which are then assembled into new virus particles.
7. Budding and Release: The new virus particles bud off from the host cell, acquiring an envelope from the host cell membrane. These newly formed viruses can now infect other host cells and continue the cycle of replication.
Significance of reverse transcriptase:
Reverse transcriptase plays a critical role in the replication of HIV. It allows the virus to convert its RNA genome into DNA, which can then be integrated into the host cell DNA. This DNA integration makes HIV difficult to eradicate from the body and enables the virus to persist and cause long-term infection.
Therefore, option B is the correct statement as HIV replicates in host cells with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Cocaine is commonly called as- a)smack
- b)coke
- c)crack
- d)both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cocaine is commonly called as
a)
smack
b)
coke
c)
crack
d)
both (b) and (c)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Cocaine, commonly called come or crack, is usually snorted, it has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sence of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosageof cocaine causes hallucinations.
Which type of immunity is acquired after birth?- a)Innate immunity
- b)Passive immunity
- c)Acquired immunity
- d)Cellular immunity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of immunity is acquired after birth?
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Passive immunity
c)
Acquired immunity
d)
Cellular immunity

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Answer: Option C.
Solution: Acquired immunity, also known as adaptive or specific immunity, is the type of immunity that an individual acquires after birth. This form of immunity is mediated by B and T lymphocytes and develops as a response to exposure to pathogens, vaccines, or through the transfer of antibodies from mother to child. Acquired immunity is characterized by its ability to remember previous exposures to pathogens and mount a stronger response upon subsequent exposures.
An intestinal parasite which causes blockage of the intestinal passage and whose eggs are excreted along with the faeces of infected person is____ .- a)Wuchereria bancrofti
- b)Ascaris
- c)Epidermophyton
- d)Microsporum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An intestinal parasite which causes blockage of the intestinal passage and whose eggs are excreted along with the faeces of infected person is____ .
a)
Wuchereria bancrofti
b)
Ascaris
c)
Epidermophyton
d)
Microsporum
|
|
Nishtha Dey answered |
Ascaris is an intestinal parasite that infects humans, causing a condition called ascariasis. It is a roundworm that lives in the small intestine and can grow up to 30 cm long. The female Ascaris worm can lay up to 200,000 eggs per day, which are excreted along with the infected person's faeces.
Symptoms of Ascaris infection include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, and malnutrition. In severe cases, the worms can cause blockage of the intestinal passage, leading to an emergency situation.
Ascaris is commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene, where people are more likely to come into contact with contaminated soil or food. The eggs of the worm can survive for many months in the environment, making it difficult to control the spread of the infection.
Treatment for ascariasis involves medication to kill the worms and alleviate symptoms. Prevention measures include improving sanitation and hygiene practices, such as washing hands before eating and after using the toilet, and avoiding contact with contaminated soil or food.
Symptoms of Ascaris infection include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, and malnutrition. In severe cases, the worms can cause blockage of the intestinal passage, leading to an emergency situation.
Ascaris is commonly found in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene, where people are more likely to come into contact with contaminated soil or food. The eggs of the worm can survive for many months in the environment, making it difficult to control the spread of the infection.
Treatment for ascariasis involves medication to kill the worms and alleviate symptoms. Prevention measures include improving sanitation and hygiene practices, such as washing hands before eating and after using the toilet, and avoiding contact with contaminated soil or food.
The pathogens responsible for causing elephantiasis are transmitted to a healthy person through:- a)Droplet
- b)Female mosquito vector
- c)Contaminated food and water
- d)Sexual contact
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pathogens responsible for causing elephantiasis are transmitted to a healthy person through:
a)
Droplet
b)
Female mosquito vector
c)
Contaminated food and water
d)
Sexual contact

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi), the filarial worms cause a slowly developing chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years, usually the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs and the disease is called elephantiasis or filariasis.
- The pathogens are transmitted to a healthy person through the bite by the female mosquito vectors.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Malarial parasite requires two hosts - humans and mosquitoes to complete its life cycle.
Statement 2: Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of liver cells during malarial infection.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement
- b)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Malarial parasite requires two hosts - humans and mosquitoes to complete its life cycle.
Statement 2: Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of liver cells during malarial infection.
Statement 1: Malarial parasite requires two hosts - humans and mosquitoes to complete its life cycle.
Statement 2: Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of liver cells during malarial infection.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement
b)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Malarial parasite requires two hosts- humans and mosquitoes to complete its life cycle. Mosquito acts as a primary host and human acts as a secondary host. Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of red blood cells.
Assertion (A): Cancer can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
Reason (R): Mutations in DNA can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, and these mutations can be inherited or induced by environmental exposures.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Cancer can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
Reason (R): Mutations in DNA can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, and these mutations can be inherited or induced by environmental exposures.
Reason (R): Mutations in DNA can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, and these mutations can be inherited or induced by environmental exposures.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Sneha Datta answered |
Explanation:
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Cancer:
- Cancer can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic factors include inherited mutations that increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Environmental factors such as exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke, UV radiation, and certain chemicals can also lead to mutations in DNA.
Mutations in DNA and Uncontrolled Cell Growth:
- Mutations in DNA can disrupt the normal control mechanisms of cell growth and division.
- These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, which is a hallmark of cancer.
- Mutations can be inherited from parents or acquired through exposure to environmental factors.
Relation between Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion that cancer can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors is supported by the reason that mutations in DNA can result in uncontrolled cell growth.
- The reason explains how both inherited genetic mutations and mutations induced by environmental exposures can contribute to the development of cancer.
Therefore, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. Thus, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Cancer:
- Cancer can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic factors include inherited mutations that increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Environmental factors such as exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke, UV radiation, and certain chemicals can also lead to mutations in DNA.
Mutations in DNA and Uncontrolled Cell Growth:
- Mutations in DNA can disrupt the normal control mechanisms of cell growth and division.
- These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, which is a hallmark of cancer.
- Mutations can be inherited from parents or acquired through exposure to environmental factors.
Relation between Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion that cancer can be caused by both genetic and environmental factors is supported by the reason that mutations in DNA can result in uncontrolled cell growth.
- The reason explains how both inherited genetic mutations and mutations induced by environmental exposures can contribute to the development of cancer.
Therefore, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. Thus, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Elephantiasis, a chronic inflammation that results in grossdeformities is caused by- a)Ascaris
- b)E coli
- c)Wuchereria
- d)Trichophyton
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Elephantiasis, a chronic inflammation that results in grossdeformities is caused by
a)
Ascaris
b)
E coli
c)
Wuchereria
d)
Trichophyton
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Elephantiasis or filariasis is caused by a number of worms. However, in India only two types of worms are responsible for this disease, Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi.This disease is transmitted by female Cu/exmosquitoes. Elephantiasis affects lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from codes given below.
- a)A−(iv), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(ii)
- b)A−(ii), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(iv)
- c)A−(iv), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(ii), E−(i)
- d)A−(ii), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(i), E−(iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from codes given below.

a)
A−(iv), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(ii)
b)
A−(ii), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(iv)
c)
A−(iv), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(ii), E−(i)
d)
A−(ii), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(i), E−(iv)

|
Stepway Academy answered |
B: A−(ii), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(iv)
C: A−(iv), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(ii), E−(i)
D: A−(ii), B−(v), C−(iii), D−(i), E−(iv)
Allergy: Linked to IgE, which is responsible for allergic reactions.
Helper T-cells: Linked to activation of B-cells, crucial for immune response.
AIDS virus: HIV is a single-stranded RNA virus.
X-rays: Known carcinogens that can cause cancer.
Treatment of cancer: Often involves immunotherapy.
The correct option is: A: A−(iv), B−(i), C−(v), D−(iii), E−(ii)
A metastatic cancerous tumour is termed 'sarcoma' if the disorder is in- a)fibroblasts
- b)circulatory system
- c)immune system
- d)epithelial cells
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A metastatic cancerous tumour is termed 'sarcoma' if the disorder is in
a)
fibroblasts
b)
circulatory system
c)
immune system
d)
epithelial cells
|
|
Shubham Kulkarni answered |
**Answer:**
A metastatic cancerous tumor is termed sarcoma if the disorder is in fibroblasts. Sarcomas are a type of cancer that develop from connective tissues, which include fibrous tissues such as bone, cartilage, and fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are a type of connective tissue cell that produces the extracellular matrix and collagen, which provides structural support to tissues and organs.
**Explanation:**
Sarcomas are a broad group of cancers that arise from different types of connective tissues. They are categorized based on the specific type of tissue from which they originate. Fibroblasts are a type of connective tissue cell that plays a crucial role in the maintenance and repair of tissues. They are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, which is a complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that provides structural support to tissues and organs.
When a cancerous tumor arises from fibroblasts or the connective tissue, it is termed sarcoma. These tumors can occur in various parts of the body, including bones, muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues. Sarcomas are relatively rare compared to other types of cancer, accounting for about 1% of all cancer cases.
Sarcomas can be further classified into different subtypes based on the specific type of tissue they arise from. Some common types of sarcoma include osteosarcoma (arising from bone tissue), chondrosarcoma (arising from cartilage), and fibrosarcoma (arising from fibrous tissue).
It is important to distinguish sarcomas from carcinomas, which are cancers that arise from epithelial cells. Epithelial cells are found in the linings of organs and tissues, such as the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Carcinomas are the most common type of cancer and account for the majority of cancer cases.
In summary, a metastatic cancerous tumor is termed sarcoma if the disorder is in fibroblasts or connective tissue. Sarcomas are a diverse group of cancers that arise from different types of connective tissues and can occur in various parts of the body.
A metastatic cancerous tumor is termed sarcoma if the disorder is in fibroblasts. Sarcomas are a type of cancer that develop from connective tissues, which include fibrous tissues such as bone, cartilage, and fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are a type of connective tissue cell that produces the extracellular matrix and collagen, which provides structural support to tissues and organs.
**Explanation:**
Sarcomas are a broad group of cancers that arise from different types of connective tissues. They are categorized based on the specific type of tissue from which they originate. Fibroblasts are a type of connective tissue cell that plays a crucial role in the maintenance and repair of tissues. They are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, which is a complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that provides structural support to tissues and organs.
When a cancerous tumor arises from fibroblasts or the connective tissue, it is termed sarcoma. These tumors can occur in various parts of the body, including bones, muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues. Sarcomas are relatively rare compared to other types of cancer, accounting for about 1% of all cancer cases.
Sarcomas can be further classified into different subtypes based on the specific type of tissue they arise from. Some common types of sarcoma include osteosarcoma (arising from bone tissue), chondrosarcoma (arising from cartilage), and fibrosarcoma (arising from fibrous tissue).
It is important to distinguish sarcomas from carcinomas, which are cancers that arise from epithelial cells. Epithelial cells are found in the linings of organs and tissues, such as the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Carcinomas are the most common type of cancer and account for the majority of cancer cases.
In summary, a metastatic cancerous tumor is termed sarcoma if the disorder is in fibroblasts or connective tissue. Sarcomas are a diverse group of cancers that arise from different types of connective tissues and can occur in various parts of the body.
Read the following statements regarding spleen and select the correct option.
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements regarding spleen and select the correct option.
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
|
|
Naveen Desai answered |
Spleen is an important organ of the lymphatic system that helps in filtering the blood and fighting against infections. Let's discuss the given statements and understand which ones are correct.
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
This statement is correct. Spleen contains lymphocytes and phagocytes which help in fighting against infections and foreign particles.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
This statement is incorrect. Although spleen does store some erythrocytes, it is not a primary reservoir of erythrocytes. Its main function is to filter the blood and remove old or damaged erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
This statement is incorrect. Spleen is not a primary lymphoid organ. Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus, where lymphocytes are produced and matured.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.
This statement is correct. Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms and removing them from the circulation.
Therefore, the correct option is (d) (i), (ii) and (iv).
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
This statement is correct. Spleen contains lymphocytes and phagocytes which help in fighting against infections and foreign particles.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
This statement is incorrect. Although spleen does store some erythrocytes, it is not a primary reservoir of erythrocytes. Its main function is to filter the blood and remove old or damaged erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
This statement is incorrect. Spleen is not a primary lymphoid organ. Primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus, where lymphocytes are produced and matured.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.
This statement is correct. Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms and removing them from the circulation.
Therefore, the correct option is (d) (i), (ii) and (iv).
Vaccine against polio viruses is an example of- a)auto-immunization
- b)passive immunization
- c)active immunization
- d)simple immunization
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vaccine against polio viruses is an example of
a)
auto-immunization
b)
passive immunization
c)
active immunization
d)
simple immunization
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
When a host is exposed to antigens, which may be in the form of living or dead microbes or other proteins, antibodies are produced in the host body. This type of immunity is called active immunity. Injecting the microbes deliberately during immunisation/vaccination induces active immunity e.g., polio vaccine
Read the given statements carefully.(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.Which of the above statements are correct?- a)(ii), (iv) and (v)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (v)
- d)(ii), (iii) and (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements carefully.
(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
(ii), (iv) and (v)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (v)
d)
(ii), (iii) and (v)
|
|
Muskaan Dasgupta answered |
The correct answer is option A: (ii), (iv), and (v).
Explanation:
(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
This statement is incorrect. Innate immunity is a non-specific type of defense mechanism that is present at birth. It provides the first line of defense against pathogens and is not specific to any particular pathogen. It includes physical barriers like the skin, mucous membranes, and chemical barriers like enzymes and antimicrobial peptides.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
This statement is true. Malignant malaria, also known as cerebral malaria, is a severe form of malaria caused by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. It is characterized by the invasion of the brain by the parasite and can lead to coma and death if not treated promptly.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
This statement is incorrect. The Widal test is not used to confirm malaria. It is a serological test used to diagnose typhoid fever caused by the Salmonella bacteria. Malaria is diagnosed through microscopic examination of blood smears or through rapid diagnostic tests that detect specific malaria antigens.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
This statement is true. Active immunity is acquired when the immune system is exposed to a pathogen or a vaccine and produces its own immune response. This process takes time as the immune system needs to recognize the pathogen, activate immune cells, and produce antibodies. It usually takes several days to weeks for the immune response to reach its full effectiveness.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as a physiological barrier for pathogens.
This statement is true. Saliva contains various components that act as a physiological barrier for pathogens. It contains enzymes like lysozyme and lactoferrin that can kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. It also contains antibodies and antimicrobial peptides that can neutralize or destroy pathogens. Additionally, saliva helps to wash away pathogens from the oral cavity, reducing the risk of infection.
Explanation:
(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
This statement is incorrect. Innate immunity is a non-specific type of defense mechanism that is present at birth. It provides the first line of defense against pathogens and is not specific to any particular pathogen. It includes physical barriers like the skin, mucous membranes, and chemical barriers like enzymes and antimicrobial peptides.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
This statement is true. Malignant malaria, also known as cerebral malaria, is a severe form of malaria caused by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. It is characterized by the invasion of the brain by the parasite and can lead to coma and death if not treated promptly.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
This statement is incorrect. The Widal test is not used to confirm malaria. It is a serological test used to diagnose typhoid fever caused by the Salmonella bacteria. Malaria is diagnosed through microscopic examination of blood smears or through rapid diagnostic tests that detect specific malaria antigens.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
This statement is true. Active immunity is acquired when the immune system is exposed to a pathogen or a vaccine and produces its own immune response. This process takes time as the immune system needs to recognize the pathogen, activate immune cells, and produce antibodies. It usually takes several days to weeks for the immune response to reach its full effectiveness.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as a physiological barrier for pathogens.
This statement is true. Saliva contains various components that act as a physiological barrier for pathogens. It contains enzymes like lysozyme and lactoferrin that can kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. It also contains antibodies and antimicrobial peptides that can neutralize or destroy pathogens. Additionally, saliva helps to wash away pathogens from the oral cavity, reducing the risk of infection.
The first line of defence in the immune system is provided by- a)skin and mucous membrane
- b)inflammatory response
- c)the complement system
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first line of defence in the immune system is provided by
a)
skin and mucous membrane
b)
inflammatory response
c)
the complement system
d)
none of these
|
|
Ananya Chauhan answered |
The first line of defence in the immune system is provided by the skin and mucous membranes.
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. The immune system has two main lines of defence: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The first line of defence is the innate immune system, which provides immediate, non-specific protection against pathogens.
The skin and mucous membranes are the first line of defence in the immune system because they act as physical barriers that prevent pathogens from entering the body.
Role of the skin:
The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a physical barrier between the internal organs and the external environment. It consists of multiple layers of cells that are tightly packed together, making it difficult for pathogens to penetrate. The outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis, is composed of dead skin cells that provide an additional layer of protection. The skin also produces sweat and sebum, which contain antimicrobial substances that can kill or inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Role of mucous membranes:
Mucous membranes are found in various parts of the body, including the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract. They are made up of a layer of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, a sticky substance that traps pathogens and prevents them from entering the body. Mucous membranes also contain specialized immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which can detect and eliminate pathogens.
The importance of the first line of defence:
The skin and mucous membranes play a crucial role in protecting the body from pathogens. By preventing pathogens from entering the body, they reduce the risk of infection and disease. However, if the first line of defence is breached and pathogens manage to enter the body, the second line of defence, which includes the inflammatory response and the complement system, is activated to eliminate the pathogens.
In conclusion, the skin and mucous membranes serve as the first line of defence in the immune system by acting as physical barriers and preventing pathogens from entering the body. They play a crucial role in protecting the body from infection and disease.
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. The immune system has two main lines of defence: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The first line of defence is the innate immune system, which provides immediate, non-specific protection against pathogens.
The skin and mucous membranes are the first line of defence in the immune system because they act as physical barriers that prevent pathogens from entering the body.
Role of the skin:
The skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a physical barrier between the internal organs and the external environment. It consists of multiple layers of cells that are tightly packed together, making it difficult for pathogens to penetrate. The outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis, is composed of dead skin cells that provide an additional layer of protection. The skin also produces sweat and sebum, which contain antimicrobial substances that can kill or inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Role of mucous membranes:
Mucous membranes are found in various parts of the body, including the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract. They are made up of a layer of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, a sticky substance that traps pathogens and prevents them from entering the body. Mucous membranes also contain specialized immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which can detect and eliminate pathogens.
The importance of the first line of defence:
The skin and mucous membranes play a crucial role in protecting the body from pathogens. By preventing pathogens from entering the body, they reduce the risk of infection and disease. However, if the first line of defence is breached and pathogens manage to enter the body, the second line of defence, which includes the inflammatory response and the complement system, is activated to eliminate the pathogens.
In conclusion, the skin and mucous membranes serve as the first line of defence in the immune system by acting as physical barriers and preventing pathogens from entering the body. They play a crucial role in protecting the body from infection and disease.
The human immuno deficiency virus is- a)an unenveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus
- b)an enveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus
- c)an enveloped, DNA genome containing retrovirus
- d)an enveloped, RNA genome containing rheovirus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The human immuno deficiency virus is
a)
an unenveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus
b)
an enveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus
c)
an enveloped, DNA genome containing retrovirus
d)
an enveloped, RNA genome containing rheovirus

|
Ameya Pillai answered |
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an enveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus.
Explanation:
HIV Structure:
- HIV is a type of retrovirus, which means it has a unique structure and replication process. It is composed of genetic material, proteins, and a lipid envelope.
- The genetic material of HIV is composed of RNA, not DNA. This RNA serves as the viral genome, containing all the necessary information for viral replication.
- The viral genome of HIV is surrounded by a protein coat called the capsid. This capsid is made up of proteins called capsid proteins.
- Surrounding the capsid is a lipid envelope, which is derived from the host cell membrane. The envelope contains viral glycoproteins that are essential for the virus to attach and enter host cells.
Retrovirus:
- Retroviruses are a family of RNA viruses that have the ability to convert their RNA genome into DNA using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase.
- This unique feature allows retroviruses to integrate their genetic material into the DNA of the host cell, becoming a permanent part of the host genome.
- HIV is a retrovirus, and it follows the typical replication cycle of retroviruses.
- Once HIV enters a host cell, it uses reverse transcriptase to convert its RNA genome into DNA. This viral DNA is then integrated into the host cell's DNA with the help of another viral enzyme called integrase.
- The integrated viral DNA, known as a provirus, can remain dormant within the host cell for an extended period.
- When conditions are favorable, the provirus can be transcribed and translated by the host cell machinery, producing new viral RNA and proteins.
- These new viral components are then assembled into new viral particles, which are released from the host cell and can infect other cells.
Enveloped Retrovirus:
- HIV is an enveloped retrovirus, meaning it has a lipid envelope derived from the host cell membrane.
- This envelope plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle as it allows HIV to enter and exit host cells.
- The envelope contains viral glycoproteins, such as gp120 and gp41, which mediate the attachment and fusion of the virus with the host cell membrane.
- The envelope also helps HIV evade the immune system by masking viral proteins and mimicking host cell components.
Conclusion:
In summary, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an enveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus. Its unique structure and replication cycle allow it to infect and hijack host cells, leading to the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Explanation:
HIV Structure:
- HIV is a type of retrovirus, which means it has a unique structure and replication process. It is composed of genetic material, proteins, and a lipid envelope.
- The genetic material of HIV is composed of RNA, not DNA. This RNA serves as the viral genome, containing all the necessary information for viral replication.
- The viral genome of HIV is surrounded by a protein coat called the capsid. This capsid is made up of proteins called capsid proteins.
- Surrounding the capsid is a lipid envelope, which is derived from the host cell membrane. The envelope contains viral glycoproteins that are essential for the virus to attach and enter host cells.
Retrovirus:
- Retroviruses are a family of RNA viruses that have the ability to convert their RNA genome into DNA using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase.
- This unique feature allows retroviruses to integrate their genetic material into the DNA of the host cell, becoming a permanent part of the host genome.
- HIV is a retrovirus, and it follows the typical replication cycle of retroviruses.
- Once HIV enters a host cell, it uses reverse transcriptase to convert its RNA genome into DNA. This viral DNA is then integrated into the host cell's DNA with the help of another viral enzyme called integrase.
- The integrated viral DNA, known as a provirus, can remain dormant within the host cell for an extended period.
- When conditions are favorable, the provirus can be transcribed and translated by the host cell machinery, producing new viral RNA and proteins.
- These new viral components are then assembled into new viral particles, which are released from the host cell and can infect other cells.
Enveloped Retrovirus:
- HIV is an enveloped retrovirus, meaning it has a lipid envelope derived from the host cell membrane.
- This envelope plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle as it allows HIV to enter and exit host cells.
- The envelope contains viral glycoproteins, such as gp120 and gp41, which mediate the attachment and fusion of the virus with the host cell membrane.
- The envelope also helps HIV evade the immune system by masking viral proteins and mimicking host cell components.
Conclusion:
In summary, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an enveloped, RNA genome containing retrovirus. Its unique structure and replication cycle allow it to infect and hijack host cells, leading to the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Health & Diseases - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Health & Diseases - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









