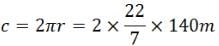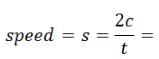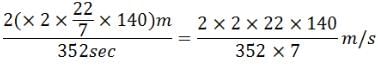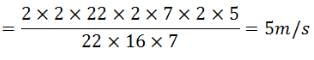All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Motion for Class 9 Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The equations of motion can be derived by using:
- A:
Distance – time graph
- B:
Velocity – time graph for non-uniform acceleration
- C:
Displacement time graph
- D:
Velocity – time graph for uniform acceleration
The answer is d.
The equations of motion can be derived by using:
Distance – time graph
Velocity – time graph for non-uniform acceleration
Displacement time graph
Velocity – time graph for uniform acceleration
|
|
Niharika Kapoor answered |
B)Velocity
c)Acceleration
d)Time
c)Acceleration
d)Time
A body starting at a point, say A, reaches, say B, ahead in a straight line and returns back to A. Then there is
- a)positive displacement
- b)negative displacement
- c)zero displacement
- d)cannot be said
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A body starting at a point, say A, reaches, say B, ahead in a straight line and returns back to A. Then there is
a)
positive displacement
b)
negative displacement
c)
zero displacement
d)
cannot be said

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
- Displacement is the straight line distance between the starting and ending points of an object's motion.
- In this scenario, the body starts at A, goes to B, and then returns to A. Even though the body travels a certain distance (twice the distance between A and B), it ends up back at its starting point (A).
- Since displacement considers the net change in position, and the body ends at the same point it started, the displacement is zero.
Topic in NCERT: Motion Along a Straight Line
Line in NCERT: "the final position coincides with the initial position, and therefore, the displacement is zero."
The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is
- a)always less than 1
- b)always equal to 1
- c)always more than 1
- d)equal to or less than 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is
a)
always less than 1
b)
always equal to 1
c)
always more than 1
d)
equal to or less than 1

|
Let's Tute answered |
- Displacement is the straightest shot (shortest distance) between start and end.
- Distance is the total path taken.
- Imagine going for a walk around a block - the displacement is the length of one side, while the distance is the entire walk.
- The numerical ratio of displacement to distance is calculated as displacement divided by distance.
- So the ratio:
- Can be 1 (straight path)
- Is less than 1 (curved path or going back and forth)
- Never more than 1
Therefore, the answer is D: equal to or less than 1.
Topic in NCERT: MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
Line in NCERT: "The magnitude of displacement (35 km) is not equal to the path length (85 km)."
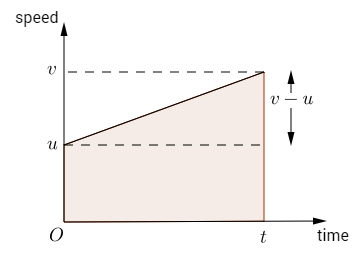
The displacement of the body in 5 seconds from the beginning of the motion is
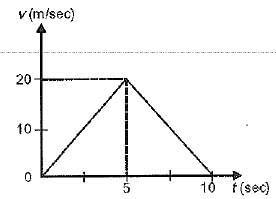
- a)12.5 m
- b)100 m
- c)87.5 m
- d)50 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The displacement of the body in 5 seconds from the beginning of the motion is


a)
12.5 m
b)
100 m
c)
87.5 m
d)
50 m

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Displacement = Area under the velocity- time graph the slope till 5 cm
the slope is a straight line and thus its area will be equal to the area of the triangle with height = 20 and base = 5
the slope is a straight line and thus its area will be equal to the area of the triangle with height = 20 and base = 5
Area of triangle = 1/2 x base x height
Area = 1/2 x 5 x 20 = 50 m.
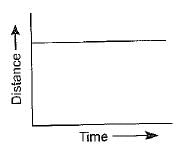
What is the slope of distance-time graph when object is at rest?- a)Decreases continuously
- b)Zero
- c)Increases continuously
- d)One
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the slope of distance-time graph when object is at rest?
a)
Decreases continuously
b)
Zero
c)
Increases continuously
d)
One

|
Preetam Pyare answered |
Since The Body is at Rest ,It clearly means that The Body hasn't covered any Distance here.So,Distance is equal to zero.So,There is no meaning of having any slope here.. So,The Slope=0 Becoz The Distance at anytime will represent same point in Distance-Time Graph at 0..So,(B)is d correct answer. .
A man is moving with 36 kmph. The time of reaction is 0.9 seconds. On seeing an obstacle in the path, he applies brakes and decelerates at 5 m/s2, the total distance covered before he stops is:- a)19 m
- b)17 m
- c)16 m
- d)18 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man is moving with 36 kmph. The time of reaction is 0.9 seconds. On seeing an obstacle in the path, he applies brakes and decelerates at 5 m/s2, the total distance covered before he stops is:
a)
19 m
b)
17 m
c)
16 m
d)
18 m
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Given :
u = 36 km/h = 36x (5/18) = 10 m/s
Time of reaction, t = 0.9 s
decelration, a = -5 m/s^2
v = 0 m/s
Let s1 be the distance covered by man when the object is seen by him
we have, u = s1/t
because s1 = u x t
= 10 x 0.9
= 9 m
when he applies brakes and decelerates at the rate of 5 m/s^2, the distance covered by him is s2
We have, v^2 = u^2 + 2as2
therefore 0 = u^2 - 2as2 ( therefore v=0 m/s)
therefore s2 = u^2/2a = 10^2/ (2 x 5)
therefore s2 =10 m
So, total distance covered s = s1 + s2 = 9 +10 =19 m
Hence 19 m distance covered by man before he stops.
An external influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest or uniform motion of body or its dimensions is called:- a)momentum
- b)force
- c)moment of force
- d)pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An external influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest or uniform motion of body or its dimensions is called:
a)
momentum
b)
force
c)
moment of force
d)
pressure
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The slope of the velocity-time graph determines the acceleration.
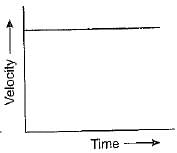
The speed-time graph for a particle moving at constant speed is a straight-line ________ to the time axis.- a)perpendicular
- b)parallel
- c)inclined
- d)aligned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed-time graph for a particle moving at constant speed is a straight-line ________ to the time axis.
a)
perpendicular
b)
parallel
c)
inclined
d)
aligned
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
The speed-time graph for a particle moving at constant speed is a straight-line parallel to the time axis.
The speedometer of a car measures
- a)average speed
- b)instantaneous speed
- c)acceleration
- d)none of the
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The speedometer of a car measures
a)
average speed
b)
instantaneous speed
c)
acceleration
d)
none of the

|
Let's Tute answered |
Speedometer Measurement
- Instantaneous Speed: The speedometer of a car measures the instantaneous speed at any given moment.
- It provides a real-time reading of how fast the car is moving at that particular moment.
- This measurement is important for drivers to ensure they are following speed limits and driving safely.
- It helps drivers make adjustments to their speed based on road conditions, traffic, and other factors.
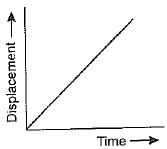
If the displacement-time graph of a particle is parallel to the time axis, the velocity of the particle is
- a)unity
- b)infinity
- c)zero
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the displacement-time graph of a particle is parallel to the time axis, the velocity of the particle is
a)
unity
b)
infinity
c)
zero
d)
none of these

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
- If the displacement-time graph of a particle is parallel to the time axis, this means that the displacement remains constant over time. In other words, there is no change in displacement as time progresses.
- Since velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement with respect to time, and there is no change in displacement, the velocity of the particle is zero.
Topic in NCERT: VELOCITY-TIME GRAPHS
Line in NCERT: "if the object moves at uniform velocity, the height of its velocity-time graph will not change with time."
Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure. Q. State the kind of motion that objects has, from A to B and from B to C.
Q. State the kind of motion that objects has, from A to B and from B to C.- a)Circular motion from A to B
- b)Uniform motion from A to B and non-uniform motion from B to C
- c)Cyclic motion
- d)Non uniform motion from A to B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following graph and choose the correct options to answer any four questions given below:
The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure.

Q. State the kind of motion that objects has, from A to B and from B to C.
a)
Circular motion from A to B
b)
Uniform motion from A to B and non-uniform motion from B to C
c)
Cyclic motion
d)
Non uniform motion from A to B

|
Aditi Bhosale answered |
In the graph, there is a straight line from point A to B and straight line in a velocity-time graph indicates uniform motion and point B to C has negative acceleration(Retardation) which is a non-uniform motion.
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion - Science Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Motion - Science Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 9
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|