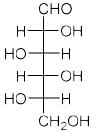
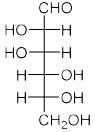
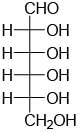
All Exams >
IIT JAM >
IIT JAM Past Year Papers and Model Test Paper (All Branches) >
All Questions
All questions of Chemistry - CY for IIT JAM Exam
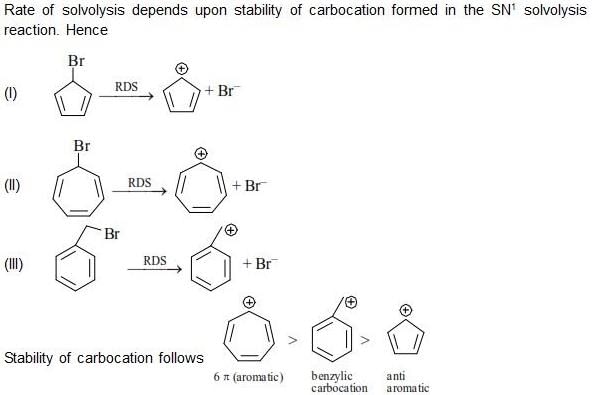
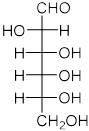
Which of these compounds is not aromatic in character?a)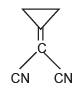 b)
b)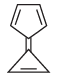 c)
c)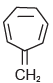 d)All of theseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
d)All of theseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Aditya Rajput answered |
Only B is correct answer due its a Quasi aromatic compond if break out the Pi bond generate polarity positve charge at cyclopropene ring and negative charge at cyclo pentadiene ring so both are aromatic in character an shows a very high dipole moment and less bond barrier energy
In the electronic structure of H2SO4, the total number of unshared electrons is ____.
Correct answer is '16'. Can you explain this answer?
In the electronic structure of H2SO4, the total number of unshared electrons is ____.

|
Mihir Singh answered |
Explanation:
The electronic structure of H2SO4 can be determined by considering the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule.
Valence Electrons:
Sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons (in the third shell), while Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons (in the second shell), and Hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron (in the first shell).
Covalent Bonding:
In H2SO4, each hydrogen atom shares its single valence electron with one of the oxygen atoms to form a covalent bond. Similarly, each oxygen atom shares two of its valence electrons with the sulfur atom to form two covalent bonds.
Shared Electrons:
Therefore, the total number of electrons shared in the covalent bonds in H2SO4 is:
2(H-H) + 2(O-S) + 4(O-H) = 2(2) + 2(2) + 4(2) = 16
Unshared Electrons:
In addition to the shared electrons, there are also unshared electrons present in the molecule. Each oxygen atom has two unshared pairs of valence electrons, for a total of 4 unshared pairs.
Total Unshared Electrons:
Therefore, the total number of unshared electrons in H2SO4 is:
4(O) = 4(2) = 8
Adding the number of shared and unshared electrons gives:
16 (shared electrons) + 8 (unshared electrons) = 24 (total electrons)
Therefore, the correct answer is 16.
The electronic structure of H2SO4 can be determined by considering the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule.
Valence Electrons:
Sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons (in the third shell), while Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons (in the second shell), and Hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron (in the first shell).
Covalent Bonding:
In H2SO4, each hydrogen atom shares its single valence electron with one of the oxygen atoms to form a covalent bond. Similarly, each oxygen atom shares two of its valence electrons with the sulfur atom to form two covalent bonds.
Shared Electrons:
Therefore, the total number of electrons shared in the covalent bonds in H2SO4 is:
2(H-H) + 2(O-S) + 4(O-H) = 2(2) + 2(2) + 4(2) = 16
Unshared Electrons:
In addition to the shared electrons, there are also unshared electrons present in the molecule. Each oxygen atom has two unshared pairs of valence electrons, for a total of 4 unshared pairs.
Total Unshared Electrons:
Therefore, the total number of unshared electrons in H2SO4 is:
4(O) = 4(2) = 8
Adding the number of shared and unshared electrons gives:
16 (shared electrons) + 8 (unshared electrons) = 24 (total electrons)
Therefore, the correct answer is 16.
If a Particle has linear momentum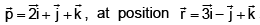 then its angular momentum is ________
then its angular momentum is ________- a)
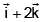
- b)
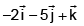
- c)
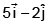
- d)
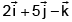
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a Particle has linear momentum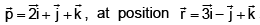 then its angular momentum is ________
then its angular momentum is ________
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Angular momentum
J = r × p
J = r × p
= (3i - j + k) × (2i + j + k)
= i(-1-1) +j(3-2) +k(3+2)
= -2i + j + 5k
Number of moles of ions produced by complete dissociation of one mole of Mohr ’s salt in water is- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of moles of ions produced by complete dissociation of one mole of Mohr ’s salt in water is
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
Tanishq Goyal answered |
Iron (II) ammonium sulfate (NH4)2Fe(SO4).6H2O ions produced by complete dissociation of Mohr salt
(NH4)2 Fe(SO4 )2 6H2O → 2NH+4 + Fe2+ + 2SO4-2
Total ions = 5 Correct option is (c)
(NH4)2 Fe(SO4 )2 6H2O → 2NH+4 + Fe2+ + 2SO4-2
Total ions = 5 Correct option is (c)
Which of the following is correct about ΔG ?- a)ΔG = ΔH - TDS
- b)At equilibrium ΔG° = 0
- c)At equilibrium ΔG° = -RT logk
- d)ΔG = ΔG° + RT logk
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct about ΔG ?
a)
ΔG = ΔH - TDS
b)
At equilibrium ΔG° = 0
c)
At equilibrium ΔG° = -RT logk
d)
ΔG = ΔG° + RT logk

|
Mukendra Singh answered |
I think in C option...if u take Log value then.....u can write as ∆Go= -2.303RT logK ...so C option is incorrect....u can write ∆Go=-RTlnk...
The ratio of the nearest neighbor atomic distances in body-centered cubic (bcc) and facecentered cubic (fcc) crystals with the same unit cell edge length is- a)
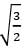
- b)
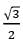
- c)
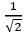
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of the nearest neighbor atomic distances in body-centered cubic (bcc) and facecentered cubic (fcc) crystals with the same unit cell edge length is
a)
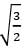
b)
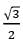
c)
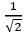
d)


|
Veda Institute answered |
- In BCC, the nearest atom from one corner is at the body center, at a distance of √(3a/2).
- In FCC, the nearest atom from one corner is at the face center at a distance of √(2a/2).
- The ratio would be √(3/2).
An electron is found in an orbital with one radial node and two angular nodes. Which orbital electron is it ?
a) 4db) 2dc) 3dd) 1sCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
b) 2d
c) 3d
d) 1s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aditya Deshmukh answered |
You will have observed that the total number of nodes is equal to the principal quantum number, n, minus one. In other words, the 1s has 0 nodes the 2s and the 2p orbitals each have 1 node the 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals each have 2 nodes the 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f orbitals each have 3 nodes and so on.
The diatomic molecule(s) that has(have) two π-type bonds is(are)
- a) B2
- b) C2
- c) N2
- d) O2
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The diatomic molecule(s) that has(have) two π-type bonds is(are)
a)
B2b)
C2c)
N2d)
O2

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Explanation:
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of two atoms of the same or different chemical elements. Each diatomic molecule has a characteristic bond type, which determines its chemical properties. There are three types of bonds that diatomic molecules can have: σ-type, π-type, and δ-type.
- σ-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the overlap of two atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis.
- π-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the sideways overlap of two atomic orbitals perpendicular to the internuclear axis.
- δ-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the overlap of two atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis, but with the electron density concentrated above and below the plane of the internuclear axis.
Based on the given options, we need to identify the diatomic molecule(s) that have two π-type bonds.
B2:
- Boron is an element that can form covalent bonds with itself to form a diatomic molecule (B2).
- The electronic configuration of boron is 1s2 2s2 2p1, which means that it has three valence electrons.
- In B2, each boron atom contributes one electron to form two π-type bonds between them.
- Therefore, B2 has two π-type bonds.
C2:
- Carbon is another element that can form covalent bonds with itself to form a diatomic molecule (C2).
- The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2, which means that it has four valence electrons.
- In C2, each carbon atom contributes two electrons to form two π-type bonds between them.
- Therefore, C2 has two π-type bonds.
N2 and O2:
- Nitrogen and oxygen are also elements that can form covalent bonds with themselves to form diatomic molecules (N2 and O2, respectively).
- The electronic configurations of nitrogen and oxygen are 1s2 2s2 2p3 and 1s2 2s2 2p4, respectively. This means that they have five and six valence electrons, respectively.
- In N2 and O2, each atom contributes three and two electrons, respectively, to form one π-type bond between them.
- Therefore, N2 and O2 have only one π-type bond each.
Conclusion:
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that the diatomic molecules that have two π-type bonds are B2 and C2.
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of two atoms of the same or different chemical elements. Each diatomic molecule has a characteristic bond type, which determines its chemical properties. There are three types of bonds that diatomic molecules can have: σ-type, π-type, and δ-type.
- σ-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the overlap of two atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis.
- π-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the sideways overlap of two atomic orbitals perpendicular to the internuclear axis.
- δ-type bond: A covalent bond formed by the overlap of two atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis, but with the electron density concentrated above and below the plane of the internuclear axis.
Based on the given options, we need to identify the diatomic molecule(s) that have two π-type bonds.
B2:
- Boron is an element that can form covalent bonds with itself to form a diatomic molecule (B2).
- The electronic configuration of boron is 1s2 2s2 2p1, which means that it has three valence electrons.
- In B2, each boron atom contributes one electron to form two π-type bonds between them.
- Therefore, B2 has two π-type bonds.
C2:
- Carbon is another element that can form covalent bonds with itself to form a diatomic molecule (C2).
- The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2, which means that it has four valence electrons.
- In C2, each carbon atom contributes two electrons to form two π-type bonds between them.
- Therefore, C2 has two π-type bonds.
N2 and O2:
- Nitrogen and oxygen are also elements that can form covalent bonds with themselves to form diatomic molecules (N2 and O2, respectively).
- The electronic configurations of nitrogen and oxygen are 1s2 2s2 2p3 and 1s2 2s2 2p4, respectively. This means that they have five and six valence electrons, respectively.
- In N2 and O2, each atom contributes three and two electrons, respectively, to form one π-type bond between them.
- Therefore, N2 and O2 have only one π-type bond each.
Conclusion:
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that the diatomic molecules that have two π-type bonds are B2 and C2.
The half-life of any zero-order reaction is:- a)independent of concentration
- b)Proportional to inverse of concentration
- c)proportional to concentration
- d)proportional to square to the concentration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The half-life of any zero-order reaction is:
a)
independent of concentration
b)
Proportional to inverse of concentration
c)
proportional to concentration
d)
proportional to square to the concentration

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
Zero-order reactions are typically found when a material that is required for the reaction to proceed, such as a surface or a catalyst, is saturated by the reactants. A reaction is zero-order if concentration data is plotted versus time and the result is a straight line.
The thermodynamic criterion for spontaneity of a process in a system under constantvolume and temperature and in the absence of any work other than expansion work (if any)is- a)change in entropy is positive
- b)change in enthalpy is negative
- c)change in Helmholtz free energy is negative
- d)change in Gibbs free energy is negative
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The thermodynamic criterion for spontaneity of a process in a system under constantvolume and temperature and in the absence of any work other than expansion work (if any)is
a)
change in entropy is positive
b)
change in enthalpy is negative
c)
change in Helmholtz free energy is negative
d)
change in Gibbs free energy is negative

|
Anshika Chavan answered |

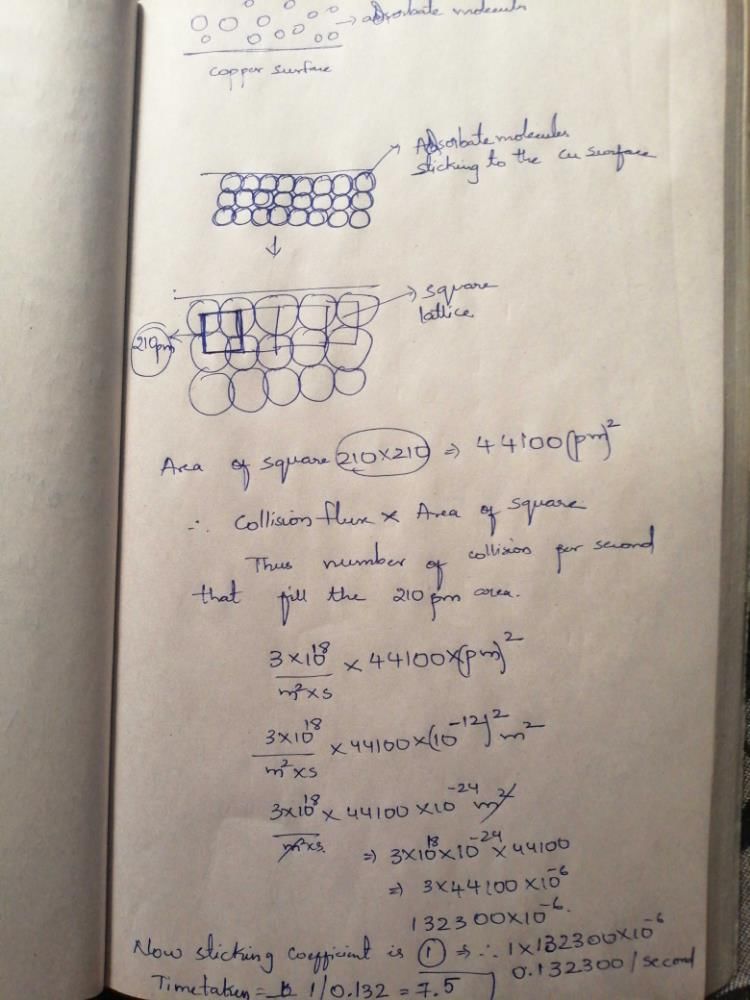
The collision flux of a monoatomic gas on copper surface is 3.0 x 1018 m–2 s–1. Note that copper surface forms a square lattice with lattice constant of 210 pm. If the sticking coefficient of the atom with copper is 1.0, the time taken by the gas to form a complete monolayer on the surface is __________ s. (Round off to one decimal place)
Correct answer is between '7.5,7.7'. Can you explain this answer?
The collision flux of a monoatomic gas on copper surface is 3.0 x 1018 m–2 s–1. Note that copper surface forms a square lattice with lattice constant of 210 pm. If the sticking coefficient of the atom with copper is 1.0, the time taken by the gas to form a complete monolayer on the surface is __________ s. (Round off to one decimal place)

|
Uday Kiran answered |
For a reaction of the type A + B → Products, the unit of the rate constant is mol L–1 s–1.The overall order of the reaction is- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For a reaction of the type A + B → Products, the unit of the rate constant is mol L–1 s–1.The overall order of the reaction is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
For zero-order reaction
Sum of exponents = 0
Unit of rate constant k = mol L-1s-1
The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is- a)0 ΔO
- b)2.0 ΔO – 2P
- c)0.4 ΔO – 2P
- d)2.0 ΔO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is
a)
0 ΔO
b)
2.0 ΔO – 2P
c)
0.4 ΔO – 2P
d)
2.0 ΔO

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) in [Mn(H2O)6]2+
CFSE is the energy that results from the interaction between the electrons of a transition metal ion and the ligands surrounding it. In the case of [Mn(H2O)6]2+, the ligands are water molecules.
The CFSE for [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is determined by calculating the energy difference between the two sets of d-orbitals in the Mn2+ ion, namely the lower energy t2g orbitals and the higher energy eg orbitals.
Calculation of CFSE
The CFSE for [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is given by the formula:
CFSE = -0.4 * n * ∆o
where n is the number of electrons in the d-orbitals and ∆o is the crystal field splitting energy.
For [Mn(H2O)6]2+, n = 5 (since there are five electrons in the d-orbitals) and ∆o is relatively small due to the weak ligand field of the water molecules. Therefore, the CFSE is close to zero.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A', i.e., the CFSE in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is zero. This is because the ligand field of the water molecules is weak, and the CFSE is small.
CFSE is the energy that results from the interaction between the electrons of a transition metal ion and the ligands surrounding it. In the case of [Mn(H2O)6]2+, the ligands are water molecules.
The CFSE for [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is determined by calculating the energy difference between the two sets of d-orbitals in the Mn2+ ion, namely the lower energy t2g orbitals and the higher energy eg orbitals.
Calculation of CFSE
The CFSE for [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is given by the formula:
CFSE = -0.4 * n * ∆o
where n is the number of electrons in the d-orbitals and ∆o is the crystal field splitting energy.
For [Mn(H2O)6]2+, n = 5 (since there are five electrons in the d-orbitals) and ∆o is relatively small due to the weak ligand field of the water molecules. Therefore, the CFSE is close to zero.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A', i.e., the CFSE in [Mn(H2O)6]2+ is zero. This is because the ligand field of the water molecules is weak, and the CFSE is small.
In the given reaction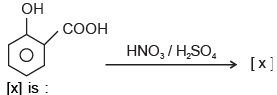
- a)2- hydroxy- 3- nitrobenzoic acid
- b)2- hydroxy- 2- nitrobenzoic acid
- c)2- hydroxy- 5- nitrobenzoic acid
- d)2, 4, 6- trinitrophenol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given reaction
a)
2- hydroxy- 3- nitrobenzoic acid
b)
2- hydroxy- 2- nitrobenzoic acid
c)
2- hydroxy- 5- nitrobenzoic acid
d)
2, 4, 6- trinitrophenol
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : A mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid introduces nitro group into benzene ring in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
When phenol is treated separately with a mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol ( also known as picric acid) is acid is obtained. Hydroxyl group is activating and ortho, para directing.
When nitrobenzene is treated separately with a mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid, m-dinitrobenzene is acid is obtained. Nitro group is deactivating and meta directing.
The number of vibrational mode(s) of a carbon dioxide molecule that can be detected usinginfrared spectroscopy is- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of vibrational mode(s) of a carbon dioxide molecule that can be detected usinginfrared spectroscopy is
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Mrinalini Singh answered |
CO2 molecule is linear so its vibrational degree of freedom is (3n-5)= (3*3-5)= 4 but 1 is symmetrical streching means IR inactive and 3 is (symmetrical +bending) means IR active so its correct ans is (3)
The tetrachloro complexes of Ni(II) and Pd(II) respectively, are (atomic numbers of Ni and Pd are 28 and 46 respectively)- a)diamagnetic and diamagnetic
- b)paramagnetic and paramagnetic
- c)diamagnetic and paramagnetic
- d)paramagnetic and diamagnetic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The tetrachloro complexes of Ni(II) and Pd(II) respectively, are (atomic numbers of Ni and Pd are 28 and 46 respectively)
a)
diamagnetic and diamagnetic
b)
paramagnetic and paramagnetic
c)
diamagnetic and paramagnetic
d)
paramagnetic and diamagnetic

|
Akshat Saini answered |
[NiCl4]2– Paramagnetic
Pairing occurs in case of Pd sine it has greater nuclear charge leading to quater interaction to the ligands.
Correct option is (d)
Correct option is (d)
The compound that contains the most acidic hydrogen is - a)H2C=CH2
- b)HC≡CH
- c)H2C=C=CH2
- d)H3C-CH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound that contains the most acidic hydrogen is
a)
H2C=CH2
b)
HC≡CH
c)
H2C=C=CH2
d)
H3C-CH3

|
Hrishikesh Verma answered |
L3c)HC≡CHd)H2O
d) H2O contains the most acidic hydrogen due to its ability to donate a proton (H+) in aqueous solutions, making it a strong acid. The other compounds listed do not have as strong of an acidic hydrogen.
d) H2O contains the most acidic hydrogen due to its ability to donate a proton (H+) in aqueous solutions, making it a strong acid. The other compounds listed do not have as strong of an acidic hydrogen.
The number of S- S bond(s) in tetrathionate ion is ___________.
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of S- S bond(s) in tetrathionate ion is ___________.

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Tetrathionate is one of the polythionates, a family of anions with the formula [Sn(SO3)2]2−. Its IUPAC name is (sulfonatodisulfanyl)sulfonate, the name of its corresponding acid is (sulfodisulfanyl)sulfonic acid.
The number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is:- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is:
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
The concept of degrees of freedom is an important one in thermodynamics. It refers to the number of independent variables that can be used to describe the state of a system. In the case of water and ice, the number of degrees of freedom is determined by the number of variables that are required to specify the state of the system.
Explanation:
- Degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent variables that can be used to describe the state of a system.
- In the case of water and ice, the number of degrees of freedom is determined by the number of variables that are required to specify the state of the system.
- When water and ice are in equilibrium, they exist in a state of coexistence where the temperature, pressure, and composition are constant.
- In this state, there is one independent variable that can be changed without changing the state of the system.
- This variable is the chemical potential of the water, which is the amount of energy that is required to add or remove a molecule of water from the system.
- Therefore, the number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is one.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is option 'B' because the number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is one.
Explanation:
- Degrees of freedom refer to the number of independent variables that can be used to describe the state of a system.
- In the case of water and ice, the number of degrees of freedom is determined by the number of variables that are required to specify the state of the system.
- When water and ice are in equilibrium, they exist in a state of coexistence where the temperature, pressure, and composition are constant.
- In this state, there is one independent variable that can be changed without changing the state of the system.
- This variable is the chemical potential of the water, which is the amount of energy that is required to add or remove a molecule of water from the system.
- Therefore, the number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is one.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is option 'B' because the number of degrees of freedom of liquid water in equilibrium with ice is one.
Correct trend in the bond order is:a) 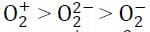 b)
b) 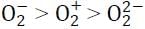 c)
c)  d)
d) 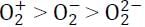 Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
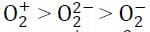
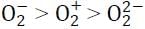

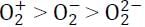
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Bond order for the following:
(i) O2− = 1.5
(ii) O2+ = 2.5
(iii) O22- = 1
(i) O2− = 1.5
(ii) O2+ = 2.5
(iii) O22- = 1
∴ The correct trend will be: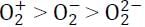
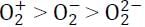
According to the kinetic theory of gases, the ratio of the root mean square velocity of molecular oxygen and molecular hydrogen at 300 K is- a)1: 1
- b)1: 2√2
- c)1: 4
- d)1: 16
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the kinetic theory of gases, the ratio of the root mean square velocity of molecular oxygen and molecular hydrogen at 300 K is
a)
1: 1
b)
1: 2√2
c)
1: 4
d)
1: 16
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Vrmsoxygen/Vrmshydrogen = √Mhydrogen/√Moxygen
∵ Vrms is inversely proportional to the molar mass
∵ Vrms is inversely proportional to the molar mass
Vrmsoxygen/Vrmshydrogen = √1/√16 = 1/4
The final products in the reaction of BF3 with water are- a)B(OH)3 and OF2
- b)H3BO3 and HBF4
- c)B2O3 and HBF4
- d)B2H6 and HF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The final products in the reaction of BF3 with water are
a)
B(OH)3 and OF2
b)
H3BO3 and HBF4
c)
B2O3 and HBF4
d)
B2H6 and HF
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Answer :
- b)H3BO3and HBF4
Boron trifluoride reacts with water to give
boric acid and fluoroboric acid.
The bond order of 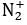 ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
Correct answer is '2.5'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond order of 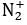 ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
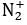 ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
ion is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)

|
Adarsh Shukla answered |
Being 13 electron system , have 9 bonding electrons and 4 non bonding electrons .
B.O = (Nb- Na)÷2
B.O = (9-4)÷ 2 = 2.5
A straight line having a slope of -ΔUo / R is obtained in a plot between :- a)In (Kp) versus T
- b)In (Kc) versus T
- c)In (Kp) versus 1/T
- d)In (Kc) versus 1/T
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight line having a slope of -ΔUo / R is obtained in a plot between :
a)
In (Kp) versus T
b)
In (Kc) versus T
c)
In (Kp) versus 1/T
d)
In (Kc) versus 1/T

|
Harshitha Sharma answered |
Explanation:
The slope of a straight line in a plot between two variables can provide important information about the relationship between those variables. In this case, we are given that the slope of the line is -Uo / R. Let's explore what this means for each of the given options.
Option A: In (Kp) versus T
- This option involves plotting the natural logarithm of the equilibrium constant for a reaction (Kp) against temperature (T).
- The slope of the line would be related to the activation energy of the reaction, not -Uo / R.
Option B: In (Kc) versus T
- This option is similar to Option A, but uses the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations (Kc).
- Again, the slope of the line would not be related to -Uo / R.
Option C: In (Kp) versus 1/T
- This option involves plotting the natural logarithm of Kp against the inverse of temperature.
- The slope of the line would be related to the enthalpy change of the reaction, not -Uo / R.
Option D: In (Kc) versus 1/T
- This option is similar to Option C, but uses Kc instead of Kp.
- The slope of the line would be related to -Uo / R, which is the ratio of the activation energy to the gas constant.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D, as it is the only option where the slope of the line is related to -Uo / R.
The slope of a straight line in a plot between two variables can provide important information about the relationship between those variables. In this case, we are given that the slope of the line is -Uo / R. Let's explore what this means for each of the given options.
Option A: In (Kp) versus T
- This option involves plotting the natural logarithm of the equilibrium constant for a reaction (Kp) against temperature (T).
- The slope of the line would be related to the activation energy of the reaction, not -Uo / R.
Option B: In (Kc) versus T
- This option is similar to Option A, but uses the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations (Kc).
- Again, the slope of the line would not be related to -Uo / R.
Option C: In (Kp) versus 1/T
- This option involves plotting the natural logarithm of Kp against the inverse of temperature.
- The slope of the line would be related to the enthalpy change of the reaction, not -Uo / R.
Option D: In (Kc) versus 1/T
- This option is similar to Option C, but uses Kc instead of Kp.
- The slope of the line would be related to -Uo / R, which is the ratio of the activation energy to the gas constant.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D, as it is the only option where the slope of the line is related to -Uo / R.
IR active molecule(s) is/are:- a)CO2
- b)CS2
- c)OCS
- d)N2
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
IR active molecule(s) is/are:
a)
CO2
b)
CS2
c)
OCS
d)
N2

|
Niharika Kulkarni answered |
IR active molecules are those that exhibit infrared absorption in the infrared spectroscopy technique. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibrations and rotations of molecules, and IR active molecules have certain molecular motions that can absorb infrared radiation.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A,B,C', which means that CO2, CS2, and OCS are IR active molecules. Let's understand why these molecules are IR active.
1. CO2 (Carbon Dioxide):
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
- Infrared spectroscopy measures the stretching and bending vibrations of molecules.
- CO2 has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- The symmetric stretching mode is IR active, which means it absorbs infrared radiation and produces a characteristic peak in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the symmetric stretching motion causes a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
2. CS2 (Carbon Disulfide):
- Carbon disulfide (CS2) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms.
- CS2 has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- Both the symmetric and asymmetric stretching modes are IR active, which means they absorb infrared radiation and produce characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the stretching motions cause a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
3. OCS (Carbonyl Sulfide):
- Carbonyl sulfide (OCS) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom, one oxygen atom, and one sulfur atom.
- OCS has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- Both the symmetric and asymmetric stretching modes are IR active, which means they absorb infrared radiation and produce characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the stretching motions cause a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
In conclusion, CO2, CS2, and OCS are IR active molecules because they have vibrational modes that cause a change in their dipole moments, leading to the absorption of infrared radiation.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A,B,C', which means that CO2, CS2, and OCS are IR active molecules. Let's understand why these molecules are IR active.
1. CO2 (Carbon Dioxide):
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
- Infrared spectroscopy measures the stretching and bending vibrations of molecules.
- CO2 has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- The symmetric stretching mode is IR active, which means it absorbs infrared radiation and produces a characteristic peak in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the symmetric stretching motion causes a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
2. CS2 (Carbon Disulfide):
- Carbon disulfide (CS2) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms.
- CS2 has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- Both the symmetric and asymmetric stretching modes are IR active, which means they absorb infrared radiation and produce characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the stretching motions cause a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
3. OCS (Carbonyl Sulfide):
- Carbonyl sulfide (OCS) is a linear molecule consisting of one carbon atom, one oxygen atom, and one sulfur atom.
- OCS has three vibrational modes: symmetric stretching, asymmetric stretching, and bending.
- Both the symmetric and asymmetric stretching modes are IR active, which means they absorb infrared radiation and produce characteristic peaks in the IR spectrum.
- This is because the stretching motions cause a change in the dipole moment of the molecule, resulting in the absorption of infrared radiation.
In conclusion, CO2, CS2, and OCS are IR active molecules because they have vibrational modes that cause a change in their dipole moments, leading to the absorption of infrared radiation.
The eigenvalue(s) of the matrix 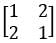 is/are
is/are- a)–1
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The eigenvalue(s) of the matrix 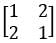 is/are
is/are
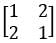 is/are
is/area)
–1
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Product of Eigenvalues = det A
Sum of Eigenvalues = trace A
Sum of Eigenvalues = trace A
Let a,b be the Eigenvalues of A.
Therefore,
a+b = 2
a.b = -3
On solving the two equations,
We get -1 and 3
Therefore,
a+b = 2
a.b = -3
On solving the two equations,
We get -1 and 3
The total number of pair of enantiomers possible with molecular formula C5H12O is ________.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of pair of enantiomers possible with molecular formula C5H12O is ________.

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same molecular formula and functional groups, but their spatial arrangement of atoms is different.
To determine the number of pairs of enantiomers possible with the molecular formula C5H12O, we need to first identify the number of chiral centers in the molecule. A chiral center is an atom that is bonded to four different groups. In C5H12O, there are two chiral centers, located at the second and third carbon atoms.
Next, we need to determine the number of possible stereoisomers for each chiral center. Each chiral center can have two possible configurations, designated as R and S. Therefore, there are a total of 2 x 2 = 4 possible stereoisomers for the molecule.
Therefore, the total number of pairs of enantiomers possible with molecular formula C5H12O is 4.
Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same molecular formula and functional groups, but their spatial arrangement of atoms is different.
To determine the number of pairs of enantiomers possible with the molecular formula C5H12O, we need to first identify the number of chiral centers in the molecule. A chiral center is an atom that is bonded to four different groups. In C5H12O, there are two chiral centers, located at the second and third carbon atoms.
Next, we need to determine the number of possible stereoisomers for each chiral center. Each chiral center can have two possible configurations, designated as R and S. Therefore, there are a total of 2 x 2 = 4 possible stereoisomers for the molecule.
Therefore, the total number of pairs of enantiomers possible with molecular formula C5H12O is 4.
The true statement(s) regarding the brown ring test carried out in the laboratory for the detection of NO3- is/are- a)Brown ring is due to the formation of the iron nitrosyl complex.
- b)Concentrated nitric acid is used for the test.
- c)The complex formed in the reaction is [Fe(CN)5NO]2-.
- d)The brown colored complex is paramagnetic in nature.
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The true statement(s) regarding the brown ring test carried out in the laboratory for the detection of NO3- is/are
a)
Brown ring is due to the formation of the iron nitrosyl complex.
b)
Concentrated nitric acid is used for the test.
c)
The complex formed in the reaction is [Fe(CN)5NO]2-.
d)
The brown colored complex is paramagnetic in nature.
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
- Complex formed is [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4.
- Concentrated Sulphuric acid is used.
- Brown ring is formed at the junction of two layers.
- Brown coloured complex is paramagnetic.
Silver crystallizes in face- centered cubic lattice. The lattice parameter of silver (in picometer) is ______.
[Given : Avogadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023 mol–1, molar mass of silver = 107.87 g mol–1 and density of crystal = 10.5 g cm–3]
Correct answer is '408.61'. Can you explain this answer?
Silver crystallizes in face- centered cubic lattice. The lattice parameter of silver (in picometer) is ______.
[Given : Avogadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023 mol–1, molar mass of silver = 107.87 g mol–1 and density of crystal = 10.5 g cm–3]
[Given : Avogadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023 mol–1, molar mass of silver = 107.87 g mol–1 and density of crystal = 10.5 g cm–3]
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
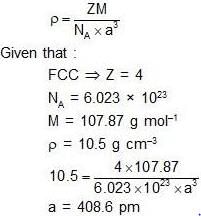
For a reaction, the rate constant at 25 °C is doubled when the temperature is raised to 45 °C. The activation energy (in kJ mol–1) of the reaction is _______ [Given: ln2 = 0.693]
Correct answer is '27'. Can you explain this answer?
For a reaction, the rate constant at 25 °C is doubled when the temperature is raised to 45 °C. The activation energy (in kJ mol–1) of the reaction is _______ [Given: ln2 = 0.693]

|
Shilpa Datta answered |
Solution:
Given data:
Temperature T1 = 25 °C = 298 K
Temperature T2 = 45 °C = 318 K
Rate constant k1 at temperature T1 = k
Rate constant k2 at temperature T2 = 2k
Activation energy Ea = ?
We know that the Arrhenius equation is given by:
k = A e^(-Ea/RT)
Where,
k = rate constant
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy
R = gas constant = 8.314 J mol^-1 K^-1
T = temperature in Kelvin
Doubling the rate constant k to 2k on increasing the temperature from T1 to T2 implies that the activation energy Ea is constant.
Therefore, we can write:
k1 = A e^(-Ea/RT1)
k2 = A e^(-Ea/RT2)
Dividing k2 by k1, we get:
k2/k1 = e^(Ea/R * (1/T1 - 1/T2))
Substituting the given values, we get:
2 = e^(Ea/8.314 * (1/298 - 1/318))
Taking natural logarithm on both sides, we get:
ln2 = Ea/8.314 * (1/298 - 1/318)
Solving for Ea, we get:
Ea = ln2 * 8.314 / (1/298 - 1/318)
Ea = 27.09 kJ mol^-1 (approx.)
Therefore, the activation energy of the reaction is 27 kJ mol^-1.
Given data:
Temperature T1 = 25 °C = 298 K
Temperature T2 = 45 °C = 318 K
Rate constant k1 at temperature T1 = k
Rate constant k2 at temperature T2 = 2k
Activation energy Ea = ?
We know that the Arrhenius equation is given by:
k = A e^(-Ea/RT)
Where,
k = rate constant
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy
R = gas constant = 8.314 J mol^-1 K^-1
T = temperature in Kelvin
Doubling the rate constant k to 2k on increasing the temperature from T1 to T2 implies that the activation energy Ea is constant.
Therefore, we can write:
k1 = A e^(-Ea/RT1)
k2 = A e^(-Ea/RT2)
Dividing k2 by k1, we get:
k2/k1 = e^(Ea/R * (1/T1 - 1/T2))
Substituting the given values, we get:
2 = e^(Ea/8.314 * (1/298 - 1/318))
Taking natural logarithm on both sides, we get:
ln2 = Ea/8.314 * (1/298 - 1/318)
Solving for Ea, we get:
Ea = ln2 * 8.314 / (1/298 - 1/318)
Ea = 27.09 kJ mol^-1 (approx.)
Therefore, the activation energy of the reaction is 27 kJ mol^-1.
Indicator used in redox titration is- a)Eriochrome black T
- b)Methyl orange
- c)Phenolphthalein
- d)Methylene blue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Indicator used in redox titration is
a)
Eriochrome black T
b)
Methyl orange
c)
Phenolphthalein
d)
Methylene blue

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
A common example of a redox titration is treating a solution of iodine with a reducing agent to produce iodide using a starch indicator to help detect the endpoint. Iodine (I2) can be reduced to iodide (I−) by e.g. thiosulfate (S2O32−), and when all iodine is spent the blue colour disappears.
The complementary strand for the following single strand of DNA is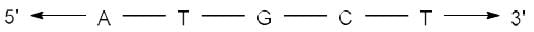
- a)

- b)
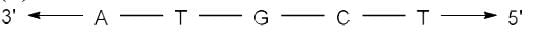
- c)
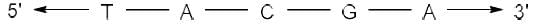
- d)
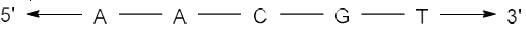
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The complementary strand for the following single strand of DNA is
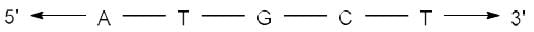
a)

b)
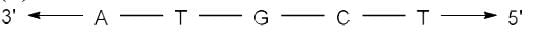
c)
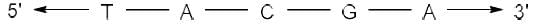
d)
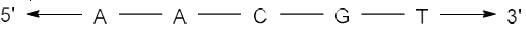

|
Asf Institute answered |
- In DNA, Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C).
- Hence, on replication of DNA in M phase, complementary nucleotides for each base pair will be added as follows:
(i) A - T
(ii) T - A
(iii) G - C
(iv) C - G - Since replication occurs in 5'-3' direction, so the complementary strand will be formed in 3'-5' direction.
- Hence the sequence of complementary strand formed upon replication will be:

Assume that the reaction of MeMgBr with ethylacetate proceeds with 100% conversion to give tert-butanol. The volume of 0.2 M solution of MeMgBr required to convert 10 mL of a 0.025 M solution of ethylacetate to tert-butanol is __________ mL. (Round off to one decimal place)
Correct answer is between '2.5,2.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that the reaction of MeMgBr with ethylacetate proceeds with 100% conversion to give tert-butanol. The volume of 0.2 M solution of MeMgBr required to convert 10 mL of a 0.025 M solution of ethylacetate to tert-butanol is __________ mL. (Round off to one decimal place)

|
Tabasum S answered |
1.25 i think
The average speed of H2, N2 and O2 gas molecules is in the order- a)H2 > N2 > O2
- b)O2 > N2 > H2
- c)H2O2 > N2
- d)N2 > O2 > H2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The average speed of H2, N2 and O2 gas molecules is in the order
a)
H2 > N2 > O2
b)
O2 > N2 > H2
c)
H2O2 > N2
d)
N2 > O2 > H2

|
Tarun Singh answered |
The average speed,
H2 = M = 2; O2 = M = 16; N2 = 14 = M
Correct option is (a)
Based on the information given below, the isoelectric point (pI) of lysine is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)
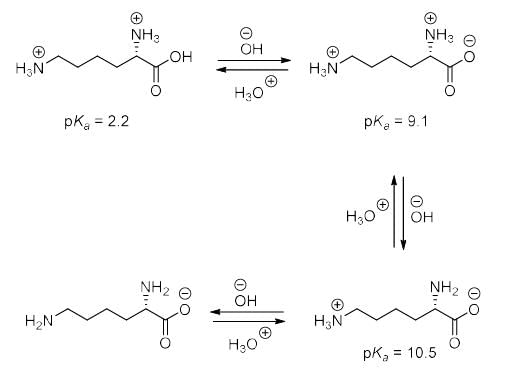
Correct answer is between '9.8,9.8'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the information given below, the isoelectric point (pI) of lysine is __________. (Round off to one decimal place)



|
Veda Institute answered |
Here pka1 is 9.1
pka2 is 10.5
so the isoelectronic point of lysine is (9.1+10.5)/2=9.8
pka2 is 10.5
so the isoelectronic point of lysine is (9.1+10.5)/2=9.8
The correct order of wavelength (λmax) of the halide to metal charge-transfer band of [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ (I), [Co(NH3)5Br]2+ (II) and [Co(NH3)5I]2+ (III), is- a)III < II < I
- b)I < II < III
- c)II < III < I
- d)I < III < II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of wavelength (λmax) of the halide to metal charge-transfer band of [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ (I), [Co(NH3)5Br]2+ (II) and [Co(NH3)5I]2+ (III), is
a)
III < II < I
b)
I < II < III
c)
II < III < I
d)
I < III < II

|
Varun Yadav answered |
Down the group, Electronegativity decreases from Cl to I . So, in III less energy is required for the electron in Iodine to transfer, than that of Chlorine. As energy decreases wavelength(λmax) increases from Cl to I.
The number of unpaired electron(s) is K2NiF6 is _________ .
Correct answer is '0'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of unpaired electron(s) is K2NiF6 is _________ .

|
Mrinalini Sen answered |
This means there are 2 unpaired electrons left in 3d orbital. Hence, K 2 N i F 6 has 2 unpaired electrons.
The amount (in grams) of NaOH (MW = 40) required for complete neutralization of one mole of the following compound is _______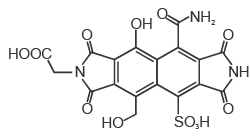
Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount (in grams) of NaOH (MW = 40) required for complete neutralization of one mole of the following compound is _______

|
Priya Kaushik answered |
For neutrilastion one oh is required for one acidic h...in the given que 4 acidic h r there so ans will be 160
The number of normal modes of vibration in naphthalene is :- a)55
- b)54
- c)48
- d)49
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of normal modes of vibration in naphthalene is :
a)
55
b)
54
c)
48
d)
49

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Naphthalene is made from crude oil or coal tar. It is also produced when things burn, so naphthalene is found in cigarette smoke, car exhaust, and smoke from forest fires. It is used as an insecticide and pest repellent. Naphthalene was first registered as a pesticide in the United States in 1948. It have 48 no of vibration modes.
Among the following compounds, the one having the lowest boiling point is- a)SnCl4
- b)GeCl4
- c)SiCl4
- d)CCl4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following compounds, the one having the lowest boiling point is
a)
SnCl4
b)
GeCl4
c)
SiCl4
d)
CCl4

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
Ans.
c-cl bond in ccl4 is more polar than sicl4.so that in ccl4 high intermolecular attractions is there and that result in high boiling point.
So, Option (c) is answer
Among the following, the number of aromatic compound(s) is ___________.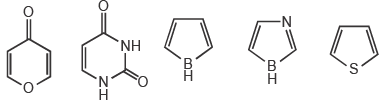
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the number of aromatic compound(s) is ___________.

|
Vipin Singh answered |
Only 1 2 5 are aromatic in nature so correct ans will 3.
in 3 &4 only 4 pi electrons so not aromatic.
in 3 &4 only 4 pi electrons so not aromatic.
The total number of degrees of freedom of an HBr molecule that is constrained to translate along a straight line but does not have any constraints for its rotation and vibration is- a)6
- b)5
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of degrees of freedom of an HBr molecule that is constrained to translate along a straight line but does not have any constraints for its rotation and vibration is
a)
6
b)
5
c)
4
d)
3
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
- The total degree of freedom of a molecule is 3N where N refers to its atomicity.
- Ideally, it should be 6 (∵ HBr is a diatomic linear molecule).
- But it is constrained to move along a straight line (i.e. assuming that it can move only along one axis).
- Therefore, the total translational degree of freedom would be 1.
- Hence, overall it would be 4.
The effective nuclear charge of helium atom is 1.7. The first ionization energy of helium atom in eV is- a)13.6
- b)23.1
- c) 39.3
- d) 27.2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The effective nuclear charge of helium atom is 1.7. The first ionization energy of helium atom in eV is
a)
13.6
b)
23.1
c)
39.3
d)
27.2

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
Helium has a structure 1s2. The electron is being removed from the same orbital as in hydrogen's case. It is close to the nucleus and unscreened. The value of the first ionization energy (24.6 eV) of helium is much higher than hydrogen (13.6 eV). It is well known that the energy of 13.6 eV is given by applying the Bohr formula, while for the first ionization energy of 24.6 eV of helium so far no one was able to formulate any successful formula.
The correct option for the major products of the following reaction is
- a)
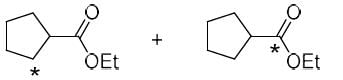
- b)
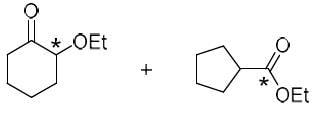
- c)
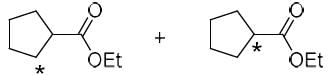
- d)
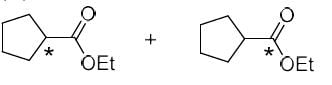
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct option for the major products of the following reaction is

a)

b)

c)
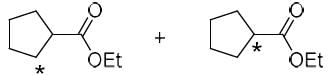
d)


|
Ameya Rane answered |
This is the reaction named by favorskii rearrangement in which base abstracts the proton from left carbon of carbonyl group and withdraws the leaving group Cl by rearrangement and makes ester.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemistry - CY - IIT JAM Past Year Papers and Model Test Paper (All Branches) 2025 is part of IIT JAM exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for IIT JAM 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemistry - CY - IIT JAM Past Year Papers and Model Test Paper (All Branches) in English & Hindi are available as part of IIT JAM exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup