GATE Exam > GATE Questions > The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic ...
Start Learning for Free
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)
- a)T2
- b)T
- c)T3/2
- d)T5/2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are describ...
The average energy is given by
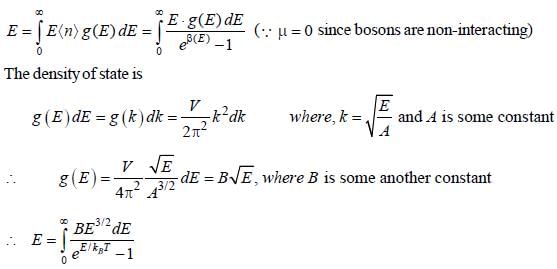
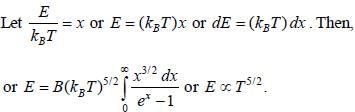
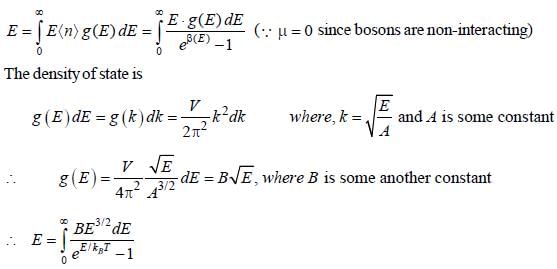
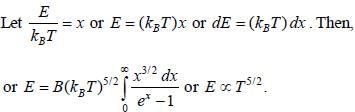
Most Upvoted Answer
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are describ...
= ħω(k), where E is the energy of the excitation, ħ is the reduced Planck's constant, ω is the angular frequency, and k is the wave vector. These excitations are known as magnons or spin waves.
Magnons are collective excitations of the spins of the electrons in a ferromagnetic material. They can be thought of as quanta of spin waves, similar to how photons are quanta of electromagnetic waves.
The dispersion relation E = ħω(k) describes the relationship between the energy and wave vector of the magnons. It tells us how the energy of the magnons depends on their momentum. In a ferromagnetic material, the dispersion relation is usually quadratic, meaning that the energy of the magnons increases with the square of their momentum.
The fact that magnons are bosonic in nature means that they obey Bose-Einstein statistics. This means that multiple magnons can occupy the same quantum state, leading to phenomena such as Bose-Einstein condensation, where a large number of magnons can occupy the lowest energy state.
The study of magnons and their properties is important in understanding the behavior of ferromagnetic materials and developing technologies such as spintronics, which utilize the spin of electrons for information processing and storage.
Magnons are collective excitations of the spins of the electrons in a ferromagnetic material. They can be thought of as quanta of spin waves, similar to how photons are quanta of electromagnetic waves.
The dispersion relation E = ħω(k) describes the relationship between the energy and wave vector of the magnons. It tells us how the energy of the magnons depends on their momentum. In a ferromagnetic material, the dispersion relation is usually quadratic, meaning that the energy of the magnons increases with the square of their momentum.
The fact that magnons are bosonic in nature means that they obey Bose-Einstein statistics. This means that multiple magnons can occupy the same quantum state, leading to phenomena such as Bose-Einstein condensation, where a large number of magnons can occupy the lowest energy state.
The study of magnons and their properties is important in understanding the behavior of ferromagnetic materials and developing technologies such as spintronics, which utilize the spin of electrons for information processing and storage.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The excitations of ferromagnetic are bosonic in nature and are described by a dispersion relation E ∝ k2, where 'E' is the energy and 'k' is the wavevector of die excitation. The average energy of the 3 -dimensional ferromagnet vanes with temperature as (assuming die bosonic excitations to be non-interacting)a)T2b)Tc)T3/2d)T5/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















