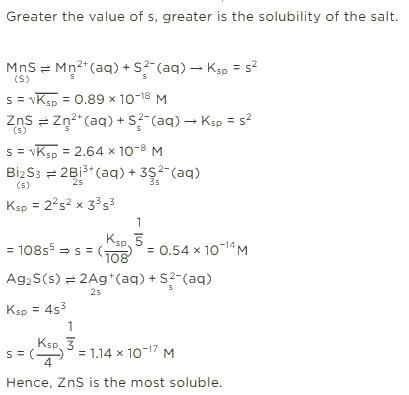All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Ions in Solutions (GC, BC) for MCAT Exam
How many gm of solid NaOH must be added to 100 ml of a buffer solution which is 0.1 M each w.r.t. Acid HA and salt Na+ A- to make the pH of solution 5.5. Given pKa(HA) = 5 (Use antilog (0.5)= 3.16)- a)2.08 × 10-1
- b)3.05 × 10-3
- c)2.01 × 10-2
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many gm of solid NaOH must be added to 100 ml of a buffer solution which is 0.1 M each w.r.t. Acid HA and salt Na+ A- to make the pH of solution 5.5. Given pKa(HA) = 5 (Use antilog (0.5)= 3.16)
a)
2.08 × 10-1
b)
3.05 × 10-3
c)
2.01 × 10-2
d)
None of these

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Suppose x m. mole NaOH was added
Which of the following solution will have pH close to 1.0 ?- a)100 ml of M/100 HCl + 100 ml of M/10 NaOH
- b)55 ml of M/10 HCl + 45 ml of M/10 NaOH
- c)10 ml of M/10 HCl + 90 ml of M/10 NaOH
- d)75 ml of M/5 HCl + 25 ml of M/5 NaOH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solution will have pH close to 1.0 ?
a)
100 ml of M/100 HCl + 100 ml of M/10 NaOH
b)
55 ml of M/10 HCl + 45 ml of M/10 NaOH
c)
10 ml of M/10 HCl + 90 ml of M/10 NaOH
d)
75 ml of M/5 HCl + 25 ml of M/5 NaOH

|
Ashwini Majumdar answered |
Check Every option.
If Ksp for HgSO4 is 6.4 × 10-5, then solubility of this substance in mole per m3 is- a)8 × 10-3
- b)6.4 × 10-5
- c)8 × 10-6
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If Ksp for HgSO4 is 6.4 × 10-5, then solubility of this substance in mole per m3 is
a)
8 × 10-3
b)
6.4 × 10-5
c)
8 × 10-6
d)
None of these
|
|
Ruchi Dasgupta answered |
Ksp = S2
⇒ 6.4 × 10–5 = S2
⇒ S = 8 × 10–3 mole/L
S = 8 × 10–3 × 103 mole/m3
⇒ S = 8 mole/m3
What volume of 0.2 M NH4Cl solution should be added to 100 ml of 0.1 M NH4OH solution to produce a buffer solution of pH = 8.7 ? Given : pKb of NH4OH = 4.7 ; log 2 = 0.3- a)50 ml
- b)100 ml
- c)200 ml
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What volume of 0.2 M NH4Cl solution should be added to 100 ml of 0.1 M NH4OH solution to produce a buffer solution of pH = 8.7 ?
Given : pKb of NH4OH = 4.7 ; log 2 = 0.3
a)
50 ml
b)
100 ml
c)
200 ml
d)
none of these

|
Sparsh Sen answered |
pH = 8.7 ⇒ pOH = 5.3
Basic Buffer
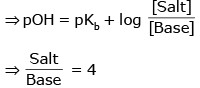
If volume of salt = V ml
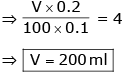
Basic Buffer
If volume of salt = V ml
The ≈ pH of the neutralisation point of 0.1 N ammonium hydroxide with 0.1 N HCl is- a)1
- b)6
- c)7
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ≈ pH of the neutralisation point of 0.1 N ammonium hydroxide with 0.1 N HCl is
a)
1
b)
6
c)
7
d)
9

|
Arnav Chawla answered |
Salt formed : NH4Cl = 0.1 N
Solution will be slightly acidic due to Hydrolysis
Solution will be slightly acidic due to Hydrolysis
Out of the following, amphiprotic species areI : HPO32-II OH-III H2PO4-IV HCO3-- a)I, III, IV
- b)I and III
- c)III and IV
- d)All
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the following, amphiprotic species are
I : HPO32-
II OH-
III H2PO4-
IV HCO3-
a)
I, III, IV
b)
I and III
c)
III and IV
d)
All

|
Maheshwar Chawla answered |
Amphiprotic : can accept and Release H+
Only H2PO–4 & HCO–3
Only H2PO–4 & HCO–3
If 40 ml of 0.2 M KOH is added to 160 ml of 0.1 M HCOOH [Ka = 2 × 10-4]. The pOH of the resulting solution is- a)3.4
- b)3.7
- c)7
- d)10.3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 40 ml of 0.2 M KOH is added to 160 ml of 0.1 M HCOOH [Ka = 2 × 10-4]. The pOH of the resulting solution is
a)
3.4
b)
3.7
c)
7
d)
10.3

|
Kalyan Desai answered |
m. equivalent of KOH = 8
m. equivalent of HCOOH = 16
Remaining m. eq. (HCOOH) = 8
Formed m. eq. (HCOOK) = 8
⇒ Acidic Buffer
pH = pKa = 4 – log2
= 3.7
pOH = 10.3
m. equivalent of HCOOH = 16
Remaining m. eq. (HCOOH) = 8
Formed m. eq. (HCOOK) = 8
⇒ Acidic Buffer
pH = pKa = 4 – log2
= 3.7
pOH = 10.3
The precipitate of CaF2 (Ksp = 1.7 × 10-10) is obtained when equal volumes of the following are mixed- a)10-4 M Ca3+ + 10-4 M F-
- b)10-2 M Ca2+ + 10-3 M F-
- c)10-5 M Ca2+ + 10-3 M F-
- d)10-3 M Ca2+ + 10-5 M F-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The precipitate of CaF2 (Ksp = 1.7 × 10-10) is obtained when equal volumes of the following are mixed
a)
10-4 M Ca3+ + 10-4 M F-
b)
10-2 M Ca2+ + 10-3 M F-
c)
10-5 M Ca2+ + 10-3 M F-
d)
10-3 M Ca2+ + 10-5 M F-

|
Pranav Saha answered |
For ppt Qsp > Ksp
CaF2→ Ca2++2F–
Qsp = (Ca2+) (F–)2
(A) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–14
(B) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–10
(C) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–13
(D) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–15
Only (B) option will get precipitate.
CaF2→ Ca2++2F–
Qsp = (Ca2+) (F–)2
(A) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–14
(B) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–10
(C) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–13
(D) Qsp = 12.5 × 10–15
Only (B) option will get precipitate.
pH of saturated solution of silver salt of monobasic acid HA is found to be 9.Find the Ksp of sparingly soluble salt Ag A(s).Given : Ka(HA) = 10-10- a)1.1 × 10-11
- b) 1.1 × 10-10
- c)10-12
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
pH of saturated solution of silver salt of monobasic acid HA is found to be 9.
Find the Ksp of sparingly soluble salt Ag A(s).
Given : Ka(HA) = 10-10
a)
1.1 × 10-11
b)
1.1 × 10-10
c)
10-12
d)
None of these

|
Pranavi Das answered |
Ksp = S (S–X) = 11 × 10–6 × 10–6
= 1.1 × 10–11
The range of most suitable indicator which should be used for titration of X - Na+ (0.1 M, 10 ml) with 0.1 M HCl should be ( Given : kb(X-) = 10-6 )- a)2-3
- b)3-5
- c)6-8
- d)8-10
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The range of most suitable indicator which should be used for titration of X - Na+ (0.1 M, 10 ml) with 0.1 M HCl should be ( Given : kb(X-) = 10-6 )
a)
2-3
b)
3-5
c)
6-8
d)
8-10

|
Subham Roy answered |
NaX + HCl → NaCl + HX
[HX] at equivalent point = 0.05
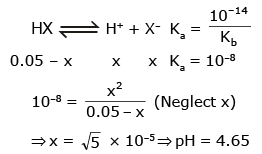
Range of Indicator = 3 to 5
[HX] at equivalent point = 0.05
Range of Indicator = 3 to 5
1 c.c. of 0.1N HCl is added to 99 CC solution of NaCl. The pH of the resulting solution will be- a)7
- b)3
- c)4
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
1 c.c. of 0.1N HCl is added to 99 CC solution of NaCl. The pH of the resulting solution will be
a)
7
b)
3
c)
4
d)
1
|
|
Rishika Deshpande answered |
Given:
- Volume of 0.1N HCl = 1 cc
- Volume of NaCl solution = 99 cc
To find:
The pH of the resulting solution
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the moles of HCl
- Concentration of HCl = 0.1 N
- Volume of HCl = 1 cc
Moles of HCl = Concentration × Volume
= 0.1 N × 1 cc
= 0.1 moles
Step 2: Calculate the moles of NaCl
- Concentration of NaCl = 0.1 N
- Volume of NaCl = 99 cc
Moles of NaCl = Concentration × Volume
= 0.1 N × 99 cc
= 9.9 moles
Step 3: Calculate the moles of H+ ions
- HCl dissociates in water to give H+ and Cl- ions
- The moles of H+ ions will be equal to the moles of HCl added
Moles of H+ ions = Moles of HCl
= 0.1 moles
Step 4: Calculate the total volume of the resulting solution
- The total volume of the resulting solution will be the sum of the volumes of HCl and NaCl solution
Total volume = Volume of HCl + Volume of NaCl solution
= 1 cc + 99 cc
= 100 cc
Step 5: Calculate the concentration of H+ ions
- Concentration is defined as moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution
Concentration of H+ ions = Moles of H+ ions / Total volume
= 0.1 moles / 100 cc
= 0.001 moles/cc
Step 6: Calculate the pH of the resulting solution
- pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the concentration of H+ ions
pH = -log10(Concentration of H+ ions)
= -log10(0.001 moles/cc)
= -(-3)
= 3
Answer:
The pH of the resulting solution will be 3.
- Volume of 0.1N HCl = 1 cc
- Volume of NaCl solution = 99 cc
To find:
The pH of the resulting solution
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the moles of HCl
- Concentration of HCl = 0.1 N
- Volume of HCl = 1 cc
Moles of HCl = Concentration × Volume
= 0.1 N × 1 cc
= 0.1 moles
Step 2: Calculate the moles of NaCl
- Concentration of NaCl = 0.1 N
- Volume of NaCl = 99 cc
Moles of NaCl = Concentration × Volume
= 0.1 N × 99 cc
= 9.9 moles
Step 3: Calculate the moles of H+ ions
- HCl dissociates in water to give H+ and Cl- ions
- The moles of H+ ions will be equal to the moles of HCl added
Moles of H+ ions = Moles of HCl
= 0.1 moles
Step 4: Calculate the total volume of the resulting solution
- The total volume of the resulting solution will be the sum of the volumes of HCl and NaCl solution
Total volume = Volume of HCl + Volume of NaCl solution
= 1 cc + 99 cc
= 100 cc
Step 5: Calculate the concentration of H+ ions
- Concentration is defined as moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution
Concentration of H+ ions = Moles of H+ ions / Total volume
= 0.1 moles / 100 cc
= 0.001 moles/cc
Step 6: Calculate the pH of the resulting solution
- pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the concentration of H+ ions
pH = -log10(Concentration of H+ ions)
= -log10(0.001 moles/cc)
= -(-3)
= 3
Answer:
The pH of the resulting solution will be 3.
The compound whose 0.1 M solution is basic is?- a)Ammonium acetate
- b)Ammonium chloride
- c)Ammonium sulphate
- d)Sodium acetate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound whose 0.1 M solution is basic is?
a)
Ammonium acetate
b)
Ammonium chloride
c)
Ammonium sulphate
d)
Sodium acetate

|
Sahil Saha answered |
Salt of weak acid & strong Base
CH3COONa → CH3COO– + Na+ CH3COO– + H2O CH3COOH + OH–
CH3COOH + OH–
Basic Solution
CH3COONa → CH3COO– + Na+ CH3COO– + H2O
Basic Solution
The pKa of a weak acid (HA) is 4.5. The pOH of an aqueous buffered solution of HA in which 50% of the acid is ionized is:- a)4.5
- b)2.5
- c)9.5
- d)7.0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The pKa of a weak acid (HA) is 4.5. The pOH of an aqueous buffered solution of HA in which 50% of the acid is ionized is:
a)
4.5
b)
2.5
c)
9.5
d)
7.0

|
Saikat Sharma answered |
50% ionised ⇒ [Salt] = [Acid]
⇒ pH = pKa = 4.5
⇒ pOH = 9.5
An aqueous solution contains 0.01 M RNH2 (Kb= 2 × 10-6) & 10-4 M NaOH.The concentration of OH- is nearly:- a)2.414 ×10-4 M
- b)10-4 M
- c)1.414×10-4 M
- d)2×10-4 M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An aqueous solution contains 0.01 M RNH2 (Kb= 2 × 10-6) & 10-4 M NaOH.
The concentration of OH- is nearly:
a)
2.414 ×10-4 M
b)
10-4 M
c)
1.414×10-4 M
d)
2×10-4 M

|
Tejas Joshi answered |
x2 + 10–4 x – 2 × 10–8 = 0
x = 10–4
[OH–] = x + 10–4
= 2 × 10–4
If K1 & K2 be first and second ionisation constant of H3PO4 and K1 >> K2 which is incorrect.- a)
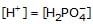
- b)
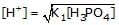
- c)
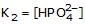
- d)
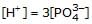
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If K1 & K2 be first and second ionisation constant of H3PO4 and K1 >> K2 which is incorrect.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Rhea Choudhary answered |
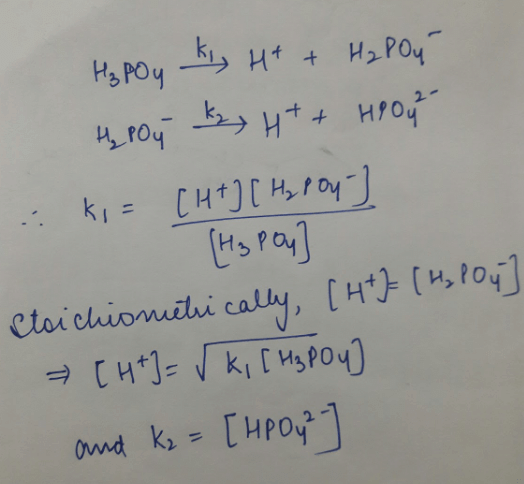
Hence we can see that the only incorrect option is 'd'.
If pKb for fluoride ion at 25°C is 10.83, the ionisation constant of hydrofluoric acid in water at this temperature is :- a)1.74 × 10-5
- b)3.52 × 10-3
- c)6.75 × 10-4
- d)5.38 × 10-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If pKb for fluoride ion at 25°C is 10.83, the ionisation constant of hydrofluoric acid in water at this temperature is :
a)
1.74 × 10-5
b)
3.52 × 10-3
c)
6.75 × 10-4
d)
5.38 × 10-2

|
Saptarshi Menon answered |
H+  H+ + F–
H+ + F–
pKw = pKa + pKb
[For conjugate Acid-Base]
⇒ pKa = 14 – 10.87 = 3.17
Ka = 6.76 × 10–4
pKw = pKa + pKb
[For conjugate Acid-Base]
⇒ pKa = 14 – 10.87 = 3.17
Ka = 6.76 × 10–4
pH of an aqueous solution of NaCl at 85°C should be- a)7
- b)> 7
- c)< 7
- d)0
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
pH of an aqueous solution of NaCl at 85°C should be
a)
7
b)
> 7
c)
< 7
d)
0

|
Arnav Kulkarni answered |
NaCl Solution : pH is the, pH of water.
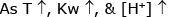
pH at 25°C <7
pH at 25°C <7
The degree of hydrolysis of a salt of weak acid and weak base in it's 0.1 M solution is found to be 50%. If the molarity of the solution is 0.2 M, the percentage hydrolysis of the salt should be- a)100%
- b)50%
- c)25%
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The degree of hydrolysis of a salt of weak acid and weak base in it's 0.1 M solution is found to be 50%. If the molarity of the solution is 0.2 M, the percentage hydrolysis of the salt should be
a)
100%
b)
50%
c)
25%
d)
none of these

|
Rishabh Das answered |
% Hydrolysis does notdepend on the conc. in case of “Weak acid + weak base : Salt”
If equilibrium constant ofCH3COOH + H2O  CH3COO- + H3O+Is 1.8 × 10-5, equilibrium constant forCH3COOH + OH-
CH3COO- + H3O+Is 1.8 × 10-5, equilibrium constant forCH3COOH + OH-  CH3COO- + H2O is
CH3COO- + H2O is- a)1.8 × 10-9
- b)1.8 × 109
- c)5.55 × 10-9
- d)5.55 × 1010
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If equilibrium constant of
CH3COOH + H2O  CH3COO- + H3O+
CH3COO- + H3O+
Is 1.8 × 10-5, equilibrium constant for
CH3COOH + OH-  CH3COO- + H2O is
CH3COO- + H2O is
a)
1.8 × 10-9
b)
1.8 × 109
c)
5.55 × 10-9
d)
5.55 × 1010

|
Sounak Chaudhary answered |
Ka = 1.8 × 10–5
CH3COO– + H2O CH3COOH + OH-
CH3COOH + OH-
Given reaction is reverse of above

CH3COO– + H2O
Given reaction is reverse of above
1 M NaCl and 1 M HCl are present in an aqueous solution. The solution is- a)Not a buffer solution and with pH < 7
- b)Not a buffer solution with pH > 7
- c)A buffer solution with pH < 7
- d)A buffer solution with pH > 7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 M NaCl and 1 M HCl are present in an aqueous solution. The solution is
a)
Not a buffer solution and with pH < 7
b)
Not a buffer solution with pH > 7
c)
A buffer solution with pH < 7
d)
A buffer solution with pH > 7

|
Sravya Banerjee answered |
NaCl + HCl : Not the Buffer and Solution is acidic due to HCl.
⇒ pH < 7.
⇒ pH < 7.
When equal volumes of the following solutions are mixed, precipitation of AgCl (Ksp = 1.8 × 10-10) will occur only with:- a)10-4 M (Ag+) and 10-4 M (Cl-)
- b)10-5 M (Ag+) and 10-5 M (Cl-)
- c)10-6 M (Ag+) and 10-6 M (Cl-)
- d)10-10 M (Ag+) and 10-10 M (Cl-)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When equal volumes of the following solutions are mixed, precipitation of AgCl (Ksp = 1.8 × 10-10) will occur only with:
a)
10-4 M (Ag+) and 10-4 M (Cl-)
b)
10-5 M (Ag+) and 10-5 M (Cl-)
c)
10-6 M (Ag+) and 10-6 M (Cl-)
d)
10-10 M (Ag+) and 10-10 M (Cl-)

|
Puja Nambiar answered |
Same as problem Number = 28
Chapter doubts & questions for Ions in Solutions (GC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Ions in Solutions (GC, BC) - MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Chemical and Physical Foundations
336 videos|223 docs|109 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily