All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) >
All Questions
All questions of Organizations Facilitating Business for CA Foundation Exam
Maslow suggests that human needs are arranged in a series of levels, a hierarchy of importance. Which of the following statements are relevant to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory?- a)The hierarchy is not necessarily in a fixed order
- b)A satisfied need is no longer a motivator
- c)A need is not necessarily fully satisfied before a subsequent need arises
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maslow suggests that human needs are arranged in a series of levels, a hierarchy of importance. Which of the following statements are relevant to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory?
a)
The hierarchy is not necessarily in a fixed order
b)
A satisfied need is no longer a motivator
c)
A need is not necessarily fully satisfied before a subsequent need arises
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory suggests that human needs are organized in a hierarchical order of importance. The theory proposes that individuals have five levels of needs, and these needs must be fulfilled in a specific order.
Relevant Statements:
A: The hierarchy is not necessarily in a fixed order
- According to Maslow, the hierarchy of needs is not rigidly fixed. While there is a general progression from lower to higher level needs, individual circumstances and personal differences can lead to variations in the order of importance.
B: A satisfied need is no longer a motivator
- Maslow's theory states that once a need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a motivator. For example, once an individual's physiological needs for food, water, and shelter are met, they are no longer motivated by these needs and can move on to the next level.
C: A need is not necessarily fully satisfied before a subsequent need arises
- Maslow's theory acknowledges that a need does not have to be fully satisfied before the next need in the hierarchy emerges. For example, an individual may still have some social needs while they are working towards fulfilling their esteem needs.
Conclusion:
All of the above statements (A, B, and C) are relevant to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory. The theory recognizes that the hierarchy is not fixed, a satisfied need is no longer a motivator, and needs can coexist and emerge at different stages of fulfillment.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory suggests that human needs are organized in a hierarchical order of importance. The theory proposes that individuals have five levels of needs, and these needs must be fulfilled in a specific order.
Relevant Statements:
A: The hierarchy is not necessarily in a fixed order
- According to Maslow, the hierarchy of needs is not rigidly fixed. While there is a general progression from lower to higher level needs, individual circumstances and personal differences can lead to variations in the order of importance.
B: A satisfied need is no longer a motivator
- Maslow's theory states that once a need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a motivator. For example, once an individual's physiological needs for food, water, and shelter are met, they are no longer motivated by these needs and can move on to the next level.
C: A need is not necessarily fully satisfied before a subsequent need arises
- Maslow's theory acknowledges that a need does not have to be fully satisfied before the next need in the hierarchy emerges. For example, an individual may still have some social needs while they are working towards fulfilling their esteem needs.
Conclusion:
All of the above statements (A, B, and C) are relevant to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory. The theory recognizes that the hierarchy is not fixed, a satisfied need is no longer a motivator, and needs can coexist and emerge at different stages of fulfillment.
As a manager moves to higher positions in an organisation the ability to make ______ becomes ______ important.- a)Programmed; less
- b)Non-programmed; more
- c)Non-programmed; less
- d)Programmed; much more
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As a manager moves to higher positions in an organisation the ability to make ______ becomes ______ important.
a)
Programmed; less
b)
Non-programmed; more
c)
Non-programmed; less
d)
Programmed; much more
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Answer
- b)Non-programmed; more
The amount of quality output for amount of input means- a)Productivity
- b)Production
- c)Sales increase
- d)Increase in profits
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of quality output for amount of input means
a)
Productivity
b)
Production
c)
Sales increase
d)
Increase in profits
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
-
Productivity is commonly defined as a ratio between the output volume and the volume of inputs. In other words, it measures how efficiently production inputs, such as labour and capital, are being used in an economy to produce a given level of output.
A trapezium based prism with two parallel sides 8 cm and 14 cm respectively and distance between two parallel sides is 8 cm. Find the height of the prism if the volume of the prism is 1056 ?
- a) 11 cm
- b) 10 cm
- c) 9 cm
- d) 12 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A trapezium based prism with two parallel sides 8 cm and 14 cm respectively and distance between two parallel sides is 8 cm. Find the height of the prism if the volume of the prism is 1056 ?
a)
11 cmb)
10 cmc)
9 cmd)
12 cm|
|
Nilesh Desai answered |
Volume of prism = (Base area) × height.
Base Area = Area of trapezium
= 1/2(8 + 14) × 8 = 88
∴ 1056 = 88 × height
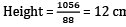
Base Area = Area of trapezium
= 1/2(8 + 14) × 8 = 88
∴ 1056 = 88 × height
Contingency theories of leadership are based on the belief that:- a)there is no single style of leadership appropriate to all situations
- b)there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all managers
- c)there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all situations
- d)none of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Contingency theories of leadership are based on the belief that:
a)
there is no single style of leadership appropriate to all situations
b)
there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all managers
c)
there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all situations
d)
none of the above.

|
Ipsita Rane answered |
Contingency theories of leadership believe that there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all situations. Let's explore this further:
What are Contingency Theories of Leadership?
Contingency theories of leadership propose that the effectiveness of a leader depends on the situation at hand. Different situations call for different leadership styles. The theory suggests that there is no one-size-fits-all leadership style that can be applied to all situations.
What is the single style of leadership appropriate to all situations?
Contingency theories propose that the most effective leadership style depends on the situation. Therefore, there is no single style of leadership that can be applied to all situations. Instead, leaders must adapt their style to fit the situation at hand.
Why is this important?
Understanding contingency theories of leadership is important because it helps leaders to develop a more nuanced approach to leadership. Rather than relying on a single leadership style, leaders can learn to adapt their style to fit the situation. This can lead to more effective leadership and better outcomes for the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, contingency theories of leadership propose that there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all situations. Leaders must be able to adapt their style to fit the situation at hand in order to be effective. Understanding this concept is important for developing a more nuanced approach to leadership.
What are Contingency Theories of Leadership?
Contingency theories of leadership propose that the effectiveness of a leader depends on the situation at hand. Different situations call for different leadership styles. The theory suggests that there is no one-size-fits-all leadership style that can be applied to all situations.
What is the single style of leadership appropriate to all situations?
Contingency theories propose that the most effective leadership style depends on the situation. Therefore, there is no single style of leadership that can be applied to all situations. Instead, leaders must adapt their style to fit the situation at hand.
Why is this important?
Understanding contingency theories of leadership is important because it helps leaders to develop a more nuanced approach to leadership. Rather than relying on a single leadership style, leaders can learn to adapt their style to fit the situation. This can lead to more effective leadership and better outcomes for the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, contingency theories of leadership propose that there is a single style of leadership appropriate to all situations. Leaders must be able to adapt their style to fit the situation at hand in order to be effective. Understanding this concept is important for developing a more nuanced approach to leadership.
Which of the following would be classified by Herzberg as a hygiene factor?- a)Achievement
- b)Promotion
- c)Responsibility
- d)Company policy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following would be classified by Herzberg as a hygiene factor?
a)
Achievement
b)
Promotion
c)
Responsibility
d)
Company policy

|
Freedom Institute answered |
-According to Herzberg, hygiene factors are what causes dissatisfaction among employees in the workplace.
- Herzberg considered the following hygiene factors from highest to lowest importance: company policy, supervision, employee's relationship with their boss, work conditions, salary, and relationships with peers.
-Company policy ould be classified by Herzberg as a hygiene factor
Who proposed that achievement, affiliation and power are three important needs that help explain motivation in workplace situations?- a)McClelland
- b)Herzberg
- c)Alderfer
- d)Maslow
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who proposed that achievement, affiliation and power are three important needs that help explain motivation in workplace situations?
a)
McClelland
b)
Herzberg
c)
Alderfer
d)
Maslow

|
Nitin Kumar answered |
Need theory, also known as Three Needs Theory, proposed by psychologist David McClelland, is a motivational model that attempts to explain how the needs for achievement, power, and affiliation affect the actions of people from a managerial context.
Controlling plays an important role in helping:- a)increase the costs
- b)fixing standards
- c)identify opportunities
- d)time management
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Controlling plays an important role in helping:
a)
increase the costs
b)
fixing standards
c)
identify opportunities
d)
time management

|
Lakshmi Kumar answered |
Controlling plays an important role in helping identify opportunities. This is because controlling involves monitoring and evaluating the performance of various activities within an organization to ensure that they are aligned with the overall goals and objectives. By doing so, controlling allows the management to identify any deviations or gaps between the actual performance and the desired performance.
**Importance of Controlling:**
Controlling is crucial for the success of any organization as it helps in achieving the desired outcomes and maintaining efficiency. It involves setting standards, measuring performance, comparing it with the standards, and taking corrective actions if necessary. By exercising control over various processes, functions, and activities, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement and capitalize on them.
**Identifying Opportunities through Controlling:**
1. **Performance Evaluation:** Controlling involves evaluating the performance of different business functions and processes. This evaluation helps to identify areas where performance is below expectations or potential opportunities for improvement.
2. **Deviation Analysis:** By comparing actual performance with the set standards, controlling enables the identification of any deviations. These deviations can highlight areas where there may be opportunities for improvement or innovation.
3. **Feedback Mechanism:** Controlling provides a feedback mechanism that allows management to gather information about the effectiveness of current strategies, processes, and activities. This feedback can help identify areas where improvements can be made or new opportunities can be explored.
4. **Benchmarking:** Controlling also involves benchmarking, which is the process of comparing an organization's performance with that of its competitors or industry standards. This comparison can help identify areas where the organization is lagging behind or where it has a competitive advantage, thereby highlighting potential opportunities for growth or improvement.
5. **Continuous Improvement:** Controlling promotes a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. By regularly monitoring performance and taking corrective actions, organizations can identify opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
In conclusion, controlling plays a vital role in helping identify opportunities by evaluating performance, analyzing deviations, providing feedback, benchmarking, and promoting continuous improvement. By leveraging these aspects of controlling, organizations can identify potential areas for growth, innovation, and improvement, ultimately leading to their success and sustainability.
**Importance of Controlling:**
Controlling is crucial for the success of any organization as it helps in achieving the desired outcomes and maintaining efficiency. It involves setting standards, measuring performance, comparing it with the standards, and taking corrective actions if necessary. By exercising control over various processes, functions, and activities, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement and capitalize on them.
**Identifying Opportunities through Controlling:**
1. **Performance Evaluation:** Controlling involves evaluating the performance of different business functions and processes. This evaluation helps to identify areas where performance is below expectations or potential opportunities for improvement.
2. **Deviation Analysis:** By comparing actual performance with the set standards, controlling enables the identification of any deviations. These deviations can highlight areas where there may be opportunities for improvement or innovation.
3. **Feedback Mechanism:** Controlling provides a feedback mechanism that allows management to gather information about the effectiveness of current strategies, processes, and activities. This feedback can help identify areas where improvements can be made or new opportunities can be explored.
4. **Benchmarking:** Controlling also involves benchmarking, which is the process of comparing an organization's performance with that of its competitors or industry standards. This comparison can help identify areas where the organization is lagging behind or where it has a competitive advantage, thereby highlighting potential opportunities for growth or improvement.
5. **Continuous Improvement:** Controlling promotes a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. By regularly monitoring performance and taking corrective actions, organizations can identify opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
In conclusion, controlling plays a vital role in helping identify opportunities by evaluating performance, analyzing deviations, providing feedback, benchmarking, and promoting continuous improvement. By leveraging these aspects of controlling, organizations can identify potential areas for growth, innovation, and improvement, ultimately leading to their success and sustainability.
According to Herzberg, which of the following may be regarded as hygiene/maintenance factors?- a)Sense of achievement
- b)Recognition
- c)Personal growth and advancement
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Herzberg, which of the following may be regarded as hygiene/maintenance factors?
a)
Sense of achievement
b)
Recognition
c)
Personal growth and advancement
d)
None of the above

|
Meera Joshi answered |
Hygiene/Maintenance factors according to Herzberg
Hygiene/Maintenance factors are the factors that do not motivate employees, but their absence can lead to dissatisfaction and demotivation. These factors are essential to maintain a baseline level of employee satisfaction and should be met to avoid dissatisfaction.
Examples of hygiene/maintenance factors are:
- Salary and benefits
- Job security
- Working conditions
- Company policies and procedures
- Relationships with co-workers and supervisors
- Status and job title
Explanation of Options
a) Sense of achievement - Sense of achievement is considered a motivator factor according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. It is related to the work itself and the feeling of accomplishment and growth that comes from completing tasks successfully.
b) Recognition - Recognition is also a motivator factor according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. It refers to the acknowledgment and appreciation employees receive for their work, which can boost their morale and motivation.
c) Personal growth and advancement - Personal growth and advancement are also motivator factors according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. They relate to opportunities for learning, development, and career advancement, which can enhance employees' sense of achievement and satisfaction.
d) None of the above - The correct answer is option 'D' because all the options listed are motivator factors, and Herzberg's two-factor theory considers hygiene/maintenance factors as separate from motivator factors.
Conclusion
Herzberg's two-factor theory suggests that hygiene/maintenance factors are essential to maintain a baseline level of employee satisfaction, but they do not motivate employees. On the other hand, motivator factors, such as sense of achievement, recognition, and personal growth and advancement, are essential to enhance employee motivation and job satisfaction.
Hygiene/Maintenance factors are the factors that do not motivate employees, but their absence can lead to dissatisfaction and demotivation. These factors are essential to maintain a baseline level of employee satisfaction and should be met to avoid dissatisfaction.
Examples of hygiene/maintenance factors are:
- Salary and benefits
- Job security
- Working conditions
- Company policies and procedures
- Relationships with co-workers and supervisors
- Status and job title
Explanation of Options
a) Sense of achievement - Sense of achievement is considered a motivator factor according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. It is related to the work itself and the feeling of accomplishment and growth that comes from completing tasks successfully.
b) Recognition - Recognition is also a motivator factor according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. It refers to the acknowledgment and appreciation employees receive for their work, which can boost their morale and motivation.
c) Personal growth and advancement - Personal growth and advancement are also motivator factors according to Herzberg's two-factor theory. They relate to opportunities for learning, development, and career advancement, which can enhance employees' sense of achievement and satisfaction.
d) None of the above - The correct answer is option 'D' because all the options listed are motivator factors, and Herzberg's two-factor theory considers hygiene/maintenance factors as separate from motivator factors.
Conclusion
Herzberg's two-factor theory suggests that hygiene/maintenance factors are essential to maintain a baseline level of employee satisfaction, but they do not motivate employees. On the other hand, motivator factors, such as sense of achievement, recognition, and personal growth and advancement, are essential to enhance employee motivation and job satisfaction.
The first stage of conflict resolution is to - a)Chose a solution
- b)Define the problem
- c)Think through possible solutions
- d)Analyse the problem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The first stage of conflict resolution is to
a)
Chose a solution
b)
Define the problem
c)
Think through possible solutions
d)
Analyse the problem

|
Sai Joshi answered |
**Explanation:**
The first stage of conflict resolution is to define the problem. This is because before any steps can be taken to resolve a conflict, it is important to have a clear understanding of what the problem actually is. Without a clear definition of the problem, it is difficult to identify the underlying issues and find appropriate solutions.
**Importance of Defining the Problem:**
Defining the problem is important for several reasons:
1. **Clarity:** Defining the problem helps to bring clarity to the situation. It allows all parties involved to have a shared understanding of what the conflict is about. This clarity is essential for effective communication and problem-solving.
2. **Focus:** Defining the problem helps to narrow down the focus and identify the key issues that need to be addressed. It prevents unnecessary distractions and ensures that efforts are directed towards resolving the core problem.
3. **Identification of Root Causes:** By defining the problem, it becomes easier to identify the underlying root causes of the conflict. This helps to avoid addressing only the symptoms and instead tackle the real issues, leading to a more effective resolution.
4. **Objective Analysis:** Defining the problem provides a basis for objective analysis. It allows for a systematic evaluation of the situation, considering different perspectives and gathering relevant information. This analysis is crucial for developing appropriate solutions.
**Steps in Defining the Problem:**
To define the problem effectively, it is important to follow a systematic approach. The following steps can be taken:
1. **Identify the Symptoms:** Start by identifying the observable signs or symptoms of the conflict. These can include disagreements, tension, or breakdowns in communication.
2. **Gather Information:** Gather relevant information about the conflict. This can involve talking to the parties involved, reviewing documentation, or conducting interviews.
3. **Analyze the Information:** Analyze the information gathered to identify the underlying issues and causes of the conflict. Look for patterns, common themes, and areas of disagreement.
4. **Refine the Problem Statement:** Based on the analysis, refine the problem statement to clearly articulate the core problem. Use clear and concise language to describe the issue at hand.
By following these steps, the first stage of conflict resolution – defining the problem – can be effectively completed. This sets the foundation for the subsequent stages of conflict resolution, which involve generating possible solutions, analyzing those solutions, and ultimately choosing the best course of action.
The first stage of conflict resolution is to define the problem. This is because before any steps can be taken to resolve a conflict, it is important to have a clear understanding of what the problem actually is. Without a clear definition of the problem, it is difficult to identify the underlying issues and find appropriate solutions.
**Importance of Defining the Problem:**
Defining the problem is important for several reasons:
1. **Clarity:** Defining the problem helps to bring clarity to the situation. It allows all parties involved to have a shared understanding of what the conflict is about. This clarity is essential for effective communication and problem-solving.
2. **Focus:** Defining the problem helps to narrow down the focus and identify the key issues that need to be addressed. It prevents unnecessary distractions and ensures that efforts are directed towards resolving the core problem.
3. **Identification of Root Causes:** By defining the problem, it becomes easier to identify the underlying root causes of the conflict. This helps to avoid addressing only the symptoms and instead tackle the real issues, leading to a more effective resolution.
4. **Objective Analysis:** Defining the problem provides a basis for objective analysis. It allows for a systematic evaluation of the situation, considering different perspectives and gathering relevant information. This analysis is crucial for developing appropriate solutions.
**Steps in Defining the Problem:**
To define the problem effectively, it is important to follow a systematic approach. The following steps can be taken:
1. **Identify the Symptoms:** Start by identifying the observable signs or symptoms of the conflict. These can include disagreements, tension, or breakdowns in communication.
2. **Gather Information:** Gather relevant information about the conflict. This can involve talking to the parties involved, reviewing documentation, or conducting interviews.
3. **Analyze the Information:** Analyze the information gathered to identify the underlying issues and causes of the conflict. Look for patterns, common themes, and areas of disagreement.
4. **Refine the Problem Statement:** Based on the analysis, refine the problem statement to clearly articulate the core problem. Use clear and concise language to describe the issue at hand.
By following these steps, the first stage of conflict resolution – defining the problem – can be effectively completed. This sets the foundation for the subsequent stages of conflict resolution, which involve generating possible solutions, analyzing those solutions, and ultimately choosing the best course of action.
Which management principle does matrix organization violate?- a)Unity of command
- b)Unity of Direction
- c)Espirit de corps
- d)Centralization
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which management principle does matrix organization violate?
a)
Unity of command
b)
Unity of Direction
c)
Espirit de corps
d)
Centralization

|
Niharika Datta answered |
Correct Answer :- a
Explanation : An important feature of matrix organization is that it violates the classical principle of unity of command. The employees in this organization have two bosses-their functional departmental managers and their product managers. So this design has a dual chain of command.
_______ applies to the systematic delegation of authority in an organization-wide context- a)Delegation
- b)Decentralization
- c)Centralization
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_______ applies to the systematic delegation of authority in an organization-wide context
a)
Delegation
b)
Decentralization
c)
Centralization
d)
None of the above

|
Mehul Ghoshal answered |
**Decentralization**
Decentralization refers to the systematic delegation of authority in an organization-wide context. It involves distributing decision-making authority and responsibility to lower levels of an organization rather than concentrating it at the top. This allows for a more flexible and efficient organization structure, as well as increased employee empowerment and motivation.
**Advantages of Decentralization:**
1. **Improved Decision Making:** Decentralization allows decisions to be made by those who are closest to the information and have the necessary expertise. This leads to faster and more accurate decision-making, as well as better problem-solving.
2. **Increased Efficiency:** By delegating authority and responsibility to lower levels, decentralized organizations can respond quickly to changes and adapt to the needs of the market. This flexibility enables them to seize opportunities and make timely adjustments to their strategies.
3. **Employee Empowerment:** Decentralization gives employees more autonomy and control over their work. They are empowered to make decisions and take ownership of their tasks, which leads to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and productivity.
4. **Better Communication and Coordination:** Decentralization encourages better communication and coordination within the organization. With decision-making authority distributed across different levels, there is a greater flow of information, ideas, and feedback.
5. **Development of Management Skills:** Decentralization provides opportunities for employees to develop their management skills. By taking on more responsibility and making decisions, they gain valuable experience and enhance their leadership capabilities.
6. **Reduced Burden on Top Management:** Centralized decision-making can overload top management with numerous decisions, leading to delays and inefficiencies. Decentralization allows top management to focus on strategic issues while empowering lower-level managers to handle operational decisions.
**Conclusion:**
Decentralization is a key concept in organizational management that involves the systematic delegation of authority throughout an organization. It offers numerous advantages, including improved decision-making, increased efficiency, employee empowerment, better communication and coordination, development of management skills, and reduced burden on top management. By implementing decentralization, organizations can create a more effective and agile structure that promotes growth and success.
Decentralization refers to the systematic delegation of authority in an organization-wide context. It involves distributing decision-making authority and responsibility to lower levels of an organization rather than concentrating it at the top. This allows for a more flexible and efficient organization structure, as well as increased employee empowerment and motivation.
**Advantages of Decentralization:**
1. **Improved Decision Making:** Decentralization allows decisions to be made by those who are closest to the information and have the necessary expertise. This leads to faster and more accurate decision-making, as well as better problem-solving.
2. **Increased Efficiency:** By delegating authority and responsibility to lower levels, decentralized organizations can respond quickly to changes and adapt to the needs of the market. This flexibility enables them to seize opportunities and make timely adjustments to their strategies.
3. **Employee Empowerment:** Decentralization gives employees more autonomy and control over their work. They are empowered to make decisions and take ownership of their tasks, which leads to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and productivity.
4. **Better Communication and Coordination:** Decentralization encourages better communication and coordination within the organization. With decision-making authority distributed across different levels, there is a greater flow of information, ideas, and feedback.
5. **Development of Management Skills:** Decentralization provides opportunities for employees to develop their management skills. By taking on more responsibility and making decisions, they gain valuable experience and enhance their leadership capabilities.
6. **Reduced Burden on Top Management:** Centralized decision-making can overload top management with numerous decisions, leading to delays and inefficiencies. Decentralization allows top management to focus on strategic issues while empowering lower-level managers to handle operational decisions.
**Conclusion:**
Decentralization is a key concept in organizational management that involves the systematic delegation of authority throughout an organization. It offers numerous advantages, including improved decision-making, increased efficiency, employee empowerment, better communication and coordination, development of management skills, and reduced burden on top management. By implementing decentralization, organizations can create a more effective and agile structure that promotes growth and success.
Which of the following statements about leadership is false?- a)Leadership does not necessarily take place within a hierarchical structure of an organisation
- b)Not every leader is a manager
- c)When people operate as leaders their role is always clearly established and defined
- d)All the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about leadership is false?
a)
Leadership does not necessarily take place within a hierarchical structure of an organisation
b)
Not every leader is a manager
c)
When people operate as leaders their role is always clearly established and defined
d)
All the above.

|
Srsps answered |
The correct answer is option C.
- It is true to say that not every leader is a manager, nor does leadership necessarily take place within a hierarchical structure of an organization.
- but it is not true to say that when people operate as leaders their role is always clearly established and defined.
- Many people operate as leaders without their roles ever being clearly established. They are leaders because they lead and take decisions themselves.
You can learn more about leadership, power-sharing, federalism, and more topics of Class 10 SST by going through the link:
- but it is not true to say that when people operate as leaders their role is always clearly established and defined.
- Many people operate as leaders without their roles ever being clearly established. They are leaders because they lead and take decisions themselves.
You can learn more about leadership, power-sharing, federalism, and more topics of Class 10 SST by going through the link:
The standard performances need to be adjusted after measuring with:- a)actual performances
- b)costs
- c)time involved
- d)external factors
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard performances need to be adjusted after measuring with:
a)
actual performances
b)
costs
c)
time involved
d)
external factors

|
Sagarika Pillai answered |
The actual performances should be measured with standards and the standard performances need to be adjusted through controlling techniques and review procedures.
Which of the following is a leadership trait?- a)Dominance
- b)Energy
- c)Cognitive ability
- d)All responses are leadership traits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a leadership trait?
a)
Dominance
b)
Energy
c)
Cognitive ability
d)
All responses are leadership traits

|
Muskaan Tiwari answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation : One of the Leadership traits is High Energy which has been reported in various researches. High Energy helps to have more endurance, play a longer game than others, no give up attitude, not frightened from the failure and maintain a balanced equation with others.
Maslow in his hierarchy has not considered:- a)psychological needs
- b)security needs
- c)wealthy needs
- d)existence needs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Maslow in his hierarchy has not considered:
a)
psychological needs
b)
security needs
c)
wealthy needs
d)
existence needs

|
Anuj Roy answered |
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory in psychology that suggests that human needs can be arranged in a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom and higher needs such as self-actualization at the top. However, Maslow's hierarchy does not include wealthy needs.
Explanation:
Psychological Needs: These are basic needs that are necessary for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and warmth. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the most fundamental needs that must be met before other needs can be satisfied.
Security Needs: Once physiological needs are met, individuals require security and safety. This includes physical safety, emotional security, and financial stability. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the second level of needs.
Social Needs: Once the first two levels of needs are met, individuals require social interaction and a sense of belonging. This includes the need for love, friendship, and intimacy. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the third level of needs.
Esteem Needs: Once the first three levels of needs are met, individuals require a sense of accomplishment, recognition, and respect. This includes the need for status, achievement, and self-esteem. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the fourth level of needs.
Self-Actualization Needs: Once the first four levels of needs are met, individuals require self-fulfillment, creativity, and personal growth. This includes the need for self-actualization and the realization of one's full potential. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the highest level of needs.
Wealthy Needs: While financial stability is included in the security needs category, wealthy needs are not explicitly recognized in Maslow's hierarchy. Wealthy needs refer to the desire for material possessions, luxury goods, and financial success beyond what is necessary for basic survival.
In conclusion, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a comprehensive theory that outlines the different levels of human needs. While it does not specifically include wealthy needs, this is because financial stability and security needs are already covered in the hierarchy.
Explanation:
Psychological Needs: These are basic needs that are necessary for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and warmth. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the most fundamental needs that must be met before other needs can be satisfied.
Security Needs: Once physiological needs are met, individuals require security and safety. This includes physical safety, emotional security, and financial stability. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the second level of needs.
Social Needs: Once the first two levels of needs are met, individuals require social interaction and a sense of belonging. This includes the need for love, friendship, and intimacy. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the third level of needs.
Esteem Needs: Once the first three levels of needs are met, individuals require a sense of accomplishment, recognition, and respect. This includes the need for status, achievement, and self-esteem. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the fourth level of needs.
Self-Actualization Needs: Once the first four levels of needs are met, individuals require self-fulfillment, creativity, and personal growth. This includes the need for self-actualization and the realization of one's full potential. Maslow included these needs in his hierarchy as the highest level of needs.
Wealthy Needs: While financial stability is included in the security needs category, wealthy needs are not explicitly recognized in Maslow's hierarchy. Wealthy needs refer to the desire for material possessions, luxury goods, and financial success beyond what is necessary for basic survival.
In conclusion, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a comprehensive theory that outlines the different levels of human needs. While it does not specifically include wealthy needs, this is because financial stability and security needs are already covered in the hierarchy.
Which step in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory deals with achieving one's potential?- a)Esteem
- b)Physiological
- c)Self-actualization
- d)Social
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which step in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory deals with achieving one's potential?
a)
Esteem
b)
Physiological
c)
Self-actualization
d)
Social

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory:
- Physiological: This step deals with the basic needs required for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and sleep.
- Safety: This step refers to the need for security, stability, and protection from physical and emotional harm.
- Social: This step focuses on the need for social interaction, belongingness, and acceptance from others.
- Esteem: This step revolves around the need for self-esteem, recognition, respect, and achievement.
- Self-actualization: This step is the highest level of the hierarchy and pertains to achieving one's full potential, personal growth, and self-fulfillment.
Explanation:
The step in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory that deals with achieving one's potential is self-actualization. This level of the hierarchy involves reaching one's highest level of personal growth and self-fulfillment. It is the stage where individuals strive to become everything they are capable of being and achieve their full potential.
Self-actualization includes various aspects such as pursuing personal interests, engaging in creative activities, seeking personal growth and development, and having a sense of purpose and meaning in life. It is the realization of one's unique abilities and talents, and the ability to express oneself authentically.
Individuals who reach the level of self-actualization are often self-aware, autonomous, and have a strong sense of morality. They are driven by intrinsic motivation and are focused on personal growth rather than external rewards or validation.
In conclusion, self-actualization is the step in Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory that deals with achieving one's potential and experiencing personal fulfillment and growth.
Deviation is a term used in:- a)controlling
- b)motivation
- c)directing
- d)staffing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Deviation is a term used in:
a)
controlling
b)
motivation
c)
directing
d)
staffing

|
Arka Kaur answered |
Deviations in Controlling:
Controlling is a management function that involves monitoring and evaluating the performance of individuals, departments, and the organization as a whole to ensure that goals are being achieved. It involves comparing actual performance with planned performance and taking corrective actions if necessary. Deviation is a term used in the context of controlling and refers to the difference between planned and actual performance.
Identifying Deviations:
- One of the primary purposes of controlling is to identify deviations or variations from the planned performance. These deviations can be positive or negative and can occur at various levels, such as individual tasks, departmental activities, or overall organizational objectives.
- By comparing actual performance with the predetermined standards, managers can determine whether the goals are being met or if there are any significant deviations that need to be addressed.
Analyzing Deviations:
- Once deviations are identified, managers need to analyze the reasons behind them. This analysis helps in understanding the factors that contribute to the deviation and guides decision-making regarding corrective actions.
- For example, if a sales department fails to achieve its target, the manager needs to analyze the reasons for the deviation. It could be due to ineffective sales strategies, lack of motivation among the sales team, or changes in market conditions. Understanding the root cause of the deviation helps in formulating appropriate corrective measures.
Taking Corrective Actions:
- Deviations in performance indicate that something is not going according to plan. Controlling involves taking corrective actions to bring the actual performance back on track and align it with the planned performance.
- Corrective actions can include revising the goals and targets, modifying the strategies and plans, providing additional training and resources, or making changes to the organizational structure or processes.
- The aim of taking corrective actions is to minimize the impact of deviations and ensure that the organization continues to progress towards its objectives effectively.
Conclusion:
- Deviation is a term used in the context of controlling, which is one of the management functions.
- It refers to the difference between planned and actual performance.
- Identifying and analyzing deviations help managers understand the reasons behind them and take appropriate corrective actions.
- Controlling is essential for ensuring that the organization achieves its goals and objectives efficiently.
Controlling is a management function that involves monitoring and evaluating the performance of individuals, departments, and the organization as a whole to ensure that goals are being achieved. It involves comparing actual performance with planned performance and taking corrective actions if necessary. Deviation is a term used in the context of controlling and refers to the difference between planned and actual performance.
Identifying Deviations:
- One of the primary purposes of controlling is to identify deviations or variations from the planned performance. These deviations can be positive or negative and can occur at various levels, such as individual tasks, departmental activities, or overall organizational objectives.
- By comparing actual performance with the predetermined standards, managers can determine whether the goals are being met or if there are any significant deviations that need to be addressed.
Analyzing Deviations:
- Once deviations are identified, managers need to analyze the reasons behind them. This analysis helps in understanding the factors that contribute to the deviation and guides decision-making regarding corrective actions.
- For example, if a sales department fails to achieve its target, the manager needs to analyze the reasons for the deviation. It could be due to ineffective sales strategies, lack of motivation among the sales team, or changes in market conditions. Understanding the root cause of the deviation helps in formulating appropriate corrective measures.
Taking Corrective Actions:
- Deviations in performance indicate that something is not going according to plan. Controlling involves taking corrective actions to bring the actual performance back on track and align it with the planned performance.
- Corrective actions can include revising the goals and targets, modifying the strategies and plans, providing additional training and resources, or making changes to the organizational structure or processes.
- The aim of taking corrective actions is to minimize the impact of deviations and ensure that the organization continues to progress towards its objectives effectively.
Conclusion:
- Deviation is a term used in the context of controlling, which is one of the management functions.
- It refers to the difference between planned and actual performance.
- Identifying and analyzing deviations help managers understand the reasons behind them and take appropriate corrective actions.
- Controlling is essential for ensuring that the organization achieves its goals and objectives efficiently.
Strategic control is implemented with:- a)micro perspective
- b)department perspective
- c)macro perspective
- d)motivational perspective
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Strategic control is implemented with:
a)
micro perspective
b)
department perspective
c)
macro perspective
d)
motivational perspective

|
Anuj Roy answered |
Strategic control is the process of monitoring and adjusting strategies to ensure that they are effective in achieving the desired goals and objectives of an organization. It is implemented with a macro perspective, which means that it focuses on the overall performance of the organization rather than specific departments or individuals.
The following are the reasons why strategic control is implemented with a macro perspective:
1. Aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization: Strategic control is designed to ensure that the strategies of an organization are aligned with its overall goals and objectives. By taking a macro perspective, organizations can ensure that their strategies are in line with their overall mission and vision.
2. Provides a holistic view of performance: A macro perspective allows organizations to see the big picture of their performance. It provides a holistic view of the organization's performance, including its financial, operational, and strategic performance.
3. Focuses on long-term success: A macro perspective is focused on the long-term success of the organization. By monitoring and adjusting strategies at a high level, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieve their long-term goals.
4. Helps to identify areas for improvement: By taking a macro perspective, organizations can identify areas for improvement at a high level. This can help them to make strategic changes that will improve their overall performance.
In conclusion, strategic control is implemented with a macro perspective because it aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization, provides a holistic view of performance, focuses on long-term success, and helps to identify areas for improvement.
The following are the reasons why strategic control is implemented with a macro perspective:
1. Aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization: Strategic control is designed to ensure that the strategies of an organization are aligned with its overall goals and objectives. By taking a macro perspective, organizations can ensure that their strategies are in line with their overall mission and vision.
2. Provides a holistic view of performance: A macro perspective allows organizations to see the big picture of their performance. It provides a holistic view of the organization's performance, including its financial, operational, and strategic performance.
3. Focuses on long-term success: A macro perspective is focused on the long-term success of the organization. By monitoring and adjusting strategies at a high level, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieve their long-term goals.
4. Helps to identify areas for improvement: By taking a macro perspective, organizations can identify areas for improvement at a high level. This can help them to make strategic changes that will improve their overall performance.
In conclusion, strategic control is implemented with a macro perspective because it aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization, provides a holistic view of performance, focuses on long-term success, and helps to identify areas for improvement.
Difficulty in controlling the external factors is a drawback for:- a)controlling
- b)motivation
- c)staffing
- d)organising
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Difficulty in controlling the external factors is a drawback for:
a)
controlling
b)
motivation
c)
staffing
d)
organising

|
Aneena Telson answered |
It is not possible to control external factors like governmental policies and technological changes. but others are possible
Effective control requires:- a)flexibility
- b)rigidity
- c)high cost
- d)high time
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Effective control requires:
a)
flexibility
b)
rigidity
c)
high cost
d)
high time

|
Geetika Basak answered |
Importance of Flexibility in Control
Effective control in any organization is paramount for achieving strategic goals and ensuring operational efficiency. Flexibility plays a crucial role in this aspect. Here's why:
Adaptability to Change
- Flexibility allows organizations to adapt to changing environments, market conditions, and customer preferences.
- Rapid adjustments can lead to improved performance and competitiveness.
Responsive Decision-Making
- When control mechanisms are flexible, managers can make timely decisions without being hindered by rigid processes.
- This responsiveness can enhance problem-solving and innovation.
Encouragement of Creativity
- A flexible control system encourages employees to think creatively and propose new ideas.
- This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and agility within the organization.
Resource Optimization
- Flexibility helps in the optimal allocation of resources, ensuring they are used where they are most effective.
- It minimizes waste and enhances overall efficiency.
Employee Morale and Engagement
- Flexible control mechanisms often lead to higher employee satisfaction and engagement.
- Employees are likely to feel more valued and empowered when they can contribute to decision-making processes.
Conclusion
In summary, flexibility is essential for effective control because it enables organizations to navigate complexities and uncertainties in the business landscape. By fostering adaptability, responsive decision-making, creativity, resource optimization, and employee engagement, organizations can achieve their goals more efficiently and effectively. Embracing flexibility as a core component of control systems is thus vital for sustained success.
Effective control in any organization is paramount for achieving strategic goals and ensuring operational efficiency. Flexibility plays a crucial role in this aspect. Here's why:
Adaptability to Change
- Flexibility allows organizations to adapt to changing environments, market conditions, and customer preferences.
- Rapid adjustments can lead to improved performance and competitiveness.
Responsive Decision-Making
- When control mechanisms are flexible, managers can make timely decisions without being hindered by rigid processes.
- This responsiveness can enhance problem-solving and innovation.
Encouragement of Creativity
- A flexible control system encourages employees to think creatively and propose new ideas.
- This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and agility within the organization.
Resource Optimization
- Flexibility helps in the optimal allocation of resources, ensuring they are used where they are most effective.
- It minimizes waste and enhances overall efficiency.
Employee Morale and Engagement
- Flexible control mechanisms often lead to higher employee satisfaction and engagement.
- Employees are likely to feel more valued and empowered when they can contribute to decision-making processes.
Conclusion
In summary, flexibility is essential for effective control because it enables organizations to navigate complexities and uncertainties in the business landscape. By fostering adaptability, responsive decision-making, creativity, resource optimization, and employee engagement, organizations can achieve their goals more efficiently and effectively. Embracing flexibility as a core component of control systems is thus vital for sustained success.
Maslow and Herzberg are two examples of ___________ theories of motivation.- a)process
- b)content
- c)expectancy
- d)equity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Maslow and Herzberg are two examples of ___________ theories of motivation.
a)
process
b)
content
c)
expectancy
d)
equity

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Maslow’s theory on the hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory are two examples of content theories of motivation. Content theories attempt to explain what motivates individuals. Process theories of motivation attempt to identify the relationships amongst dynamic variables which make up motivation and the actions required to influence behaviour and actions. Expectancy theories of motivation are based on the principle that people are influenced by the expected results of their actions whilst equity theory focuses on people’s feelings of how fairly they have been treated in comparison to others.
A solution to a problem that is arrived at through an unstructured process of decision making is called a:- a)Bounded rationality
- b)Programmed decision
- c)Non-programmed decision
- d)Uncertainty
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution to a problem that is arrived at through an unstructured process of decision making is called a:
a)
Bounded rationality
b)
Programmed decision
c)
Non-programmed decision
d)
Uncertainty

|
Harshad Kapoor answered |
Non-programmed decisions are solutions to problems that are arrived at through an unstructured process of decision making. They are unique and non-repetitive in nature, and require a high level of judgment and creativity. These decisions are made in response to novel, complex, and uncertain situations where there is no pre-established routine or set of rules to follow.
Non-programmed decisions typically involve strategic or organizational issues that require careful analysis and evaluation of multiple alternatives. They are often made at higher levels of management and have a significant impact on the overall direction and success of an organization.
1. Unstructured process: Non-programmed decisions do not follow a pre-determined set of steps or rules. They require a more flexible and creative approach to problem-solving.
2. Complexity: Non-programmed decisions are usually complex and involve multiple factors and considerations. They require a deep understanding of the situation and the ability to analyze and evaluate various options.
3. Novelty: Non-programmed decisions are unique and non-repetitive. They arise from new and unfamiliar situations that have not been encountered before.
4. Judgment and creativity: Non-programmed decisions require a high level of judgment and creativity. They often involve subjective judgments and the ability to think outside the box.
5. Strategic impact: Non-programmed decisions are typically made at higher levels of management and have a significant impact on the organization's strategic direction and long-term success.
6. Uncertainty: Non-programmed decisions are made in uncertain and ambiguous environments. There is often a lack of complete information and a high degree of risk involved.
- Deciding to enter a new market or launch a new product.
- Choosing a strategic alliance or partnership.
- Selecting a new CEO or top executive.
- Deciding on a major organizational restructure.
- Responding to a crisis or emergency situation.
In conclusion, non-programmed decisions are solutions to problems that are arrived at through an unstructured process of decision making. They require judgment, creativity, and careful evaluation of various alternatives. These decisions are unique, complex, and have a significant impact on the organization's strategic direction.
Which nature of organization structure is suitable for aircraft manufacture, aerospace/ construction, consultancy etc?- a)Project
- b)Matrix
- c)Functional
- d)Line
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which nature of organization structure is suitable for aircraft manufacture, aerospace/ construction, consultancy etc?
a)
Project
b)
Matrix
c)
Functional
d)
Line

|
Srestha Shah answered |
Project Organization Structure
The project organization structure is the most suitable nature of organization structure for industries such as aircraft manufacture, aerospace/construction, and consultancy. This structure is characterized by the formation of temporary teams or project groups that are specifically created to work on a particular project or task.
Key Features of Project Organization Structure:
1. Temporary in Nature: Project organization structures are formed for a specific project or task and are disbanded once the project is completed. This allows for flexibility and adaptability to changing project requirements.
2. Cross-Functional Teams: Project teams consist of members from different departments or functional areas within the organization. This enables the utilization of diverse skills, expertise, and perspectives to achieve project goals.
3. Project Manager: A project manager is appointed to oversee the entire project and ensure its successful completion. The project manager is responsible for coordinating the activities of different team members, managing resources, and making critical decisions.
4. Clear Project Objectives: Project organization structures have well-defined project objectives and deliverables. This helps in setting clear expectations and ensures that all team members are aligned towards achieving the desired outcomes.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability: The project structure allows organizations to quickly respond to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and customer requirements. It facilitates the efficient allocation of resources based on project needs.
6. Effective Communication and Collaboration: Project teams often work closely together, promoting effective communication and collaboration. This enhances knowledge sharing, problem-solving, and decision-making capabilities within the organization.
7. Rapid Decision-Making: Project organization structures empower project managers and team members to make quick decisions as they have the authority and accountability for their respective projects.
Benefits of Project Organization Structure:
- Improved project management and coordination
- Utilization of specialized skills and expertise
- Enhanced innovation and creativity
- Efficient resource allocation
- Faster response to market demands
- Increased employee motivation and engagement
Conclusion:
In industries such as aircraft manufacture, aerospace/construction, and consultancy, where projects are often complex, time-bound, and require interdisciplinary collaboration, the project organization structure is the most suitable. It allows organizations to effectively manage projects, utilize diverse skills, respond to changing requirements, and achieve successful project outcomes.
The project organization structure is the most suitable nature of organization structure for industries such as aircraft manufacture, aerospace/construction, and consultancy. This structure is characterized by the formation of temporary teams or project groups that are specifically created to work on a particular project or task.
Key Features of Project Organization Structure:
1. Temporary in Nature: Project organization structures are formed for a specific project or task and are disbanded once the project is completed. This allows for flexibility and adaptability to changing project requirements.
2. Cross-Functional Teams: Project teams consist of members from different departments or functional areas within the organization. This enables the utilization of diverse skills, expertise, and perspectives to achieve project goals.
3. Project Manager: A project manager is appointed to oversee the entire project and ensure its successful completion. The project manager is responsible for coordinating the activities of different team members, managing resources, and making critical decisions.
4. Clear Project Objectives: Project organization structures have well-defined project objectives and deliverables. This helps in setting clear expectations and ensures that all team members are aligned towards achieving the desired outcomes.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability: The project structure allows organizations to quickly respond to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and customer requirements. It facilitates the efficient allocation of resources based on project needs.
6. Effective Communication and Collaboration: Project teams often work closely together, promoting effective communication and collaboration. This enhances knowledge sharing, problem-solving, and decision-making capabilities within the organization.
7. Rapid Decision-Making: Project organization structures empower project managers and team members to make quick decisions as they have the authority and accountability for their respective projects.
Benefits of Project Organization Structure:
- Improved project management and coordination
- Utilization of specialized skills and expertise
- Enhanced innovation and creativity
- Efficient resource allocation
- Faster response to market demands
- Increased employee motivation and engagement
Conclusion:
In industries such as aircraft manufacture, aerospace/construction, and consultancy, where projects are often complex, time-bound, and require interdisciplinary collaboration, the project organization structure is the most suitable. It allows organizations to effectively manage projects, utilize diverse skills, respond to changing requirements, and achieve successful project outcomes.
Responding to employees and involving them in decision making is referred to as- a)Quality of work life
- b)Autonomy
- c)Empowerment
- d)Preaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Responding to employees and involving them in decision making is referred to as
a)
Quality of work life
b)
Autonomy
c)
Empowerment
d)
Preaction

|
Meera Basak answered |
Quality of Work Life and Employee Involvement
Quality of Work Life
Quality of Work Life (QWL) refers to the overall working conditions, environment, and culture in an organization that impacts the well-being and satisfaction levels of employees. It includes various factors such as work-life balance, job security, compensation, organizational policies, and employee benefits. The goal of QWL is to improve the quality of work and life for employees, leading to increased productivity, job satisfaction, and employee retention.
Employee Involvement
Employee involvement refers to the process of involving employees in decision-making processes that directly impact their work and responsibilities. It includes providing employees with the opportunity to participate in decision-making, problem-solving, and goal-setting activities. Employee involvement is essential for creating a positive work environment, building trust and respect between employees and management, and increasing employee motivation and engagement.
Responding to Employees
Responding to employees refers to the act of engaging with employees and addressing their concerns, feedback, and suggestions. It is important to respond to employees in a timely and professional manner to build trust and respect between employees and management. Responding to employees also includes providing employees with the necessary resources, tools, and support to perform their jobs effectively.
Empowerment
Empowerment refers to the process of giving employees the authority, responsibility, and autonomy to make decisions and take actions related to their work. Empowerment is a key component of employee involvement and can lead to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and productivity. Empowered employees feel valued and trusted by their organization, leading to a positive work environment and increased employee retention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quality of work life and employee involvement are essential components of a positive work environment. Responding to employees and involving them in decision-making processes can lead to increased employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity. Empowerment is also important for creating a culture of trust and respect between employees and management.
Quality of Work Life
Quality of Work Life (QWL) refers to the overall working conditions, environment, and culture in an organization that impacts the well-being and satisfaction levels of employees. It includes various factors such as work-life balance, job security, compensation, organizational policies, and employee benefits. The goal of QWL is to improve the quality of work and life for employees, leading to increased productivity, job satisfaction, and employee retention.
Employee Involvement
Employee involvement refers to the process of involving employees in decision-making processes that directly impact their work and responsibilities. It includes providing employees with the opportunity to participate in decision-making, problem-solving, and goal-setting activities. Employee involvement is essential for creating a positive work environment, building trust and respect between employees and management, and increasing employee motivation and engagement.
Responding to Employees
Responding to employees refers to the act of engaging with employees and addressing their concerns, feedback, and suggestions. It is important to respond to employees in a timely and professional manner to build trust and respect between employees and management. Responding to employees also includes providing employees with the necessary resources, tools, and support to perform their jobs effectively.
Empowerment
Empowerment refers to the process of giving employees the authority, responsibility, and autonomy to make decisions and take actions related to their work. Empowerment is a key component of employee involvement and can lead to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and productivity. Empowered employees feel valued and trusted by their organization, leading to a positive work environment and increased employee retention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quality of work life and employee involvement are essential components of a positive work environment. Responding to employees and involving them in decision-making processes can lead to increased employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity. Empowerment is also important for creating a culture of trust and respect between employees and management.
Human resource management helps improve- a)Production
- b)Productivity
- c)Profits
- d)Power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Human resource management helps improve
a)
Production
b)
Productivity
c)
Profits
d)
Power

|
Maheshwar Datta answered |
Human Resource Management is a vital aspect of any organization, as it helps in managing the workforce effectively. The primary goal of HR management is to ensure that the employees are productive and motivated to perform their duties efficiently. The following points explain how HR management helps improve productivity in an organization:
Training and Development: HR management ensures that employees receive adequate training and development opportunities. This helps them acquire new skills and knowledge, which they can use to perform their duties effectively. This, in turn, improves their productivity and efficiency.
Performance Management: HR management sets performance standards for employees and monitors their performance regularly. It provides feedback and coaching to help employees improve their performance. This helps in identifying the areas where employees need to improve and take corrective actions to enhance their productivity.
Employee Engagement: HR management ensures that employees are engaged and motivated to perform their duties. It provides a conducive work environment and takes measures to address employees' concerns. This helps in reducing absenteeism and turnover rates, which improves productivity.
Effective Communication: HR management facilitates effective communication between employees and management. This helps in clarifying expectations, setting goals, and providing feedback. It also helps in resolving conflicts and improving employee morale, which enhances productivity.
Employee Recognition: HR management recognizes and rewards employees for their good performance. This helps in boosting employee morale and motivation, which leads to improved productivity.
In conclusion, HR management plays a crucial role in improving productivity in an organization. By providing training and development opportunities, setting performance standards, engaging employees, facilitating effective communication, and recognizing employee efforts, HR management helps create a productive work environment.
Training and Development: HR management ensures that employees receive adequate training and development opportunities. This helps them acquire new skills and knowledge, which they can use to perform their duties effectively. This, in turn, improves their productivity and efficiency.
Performance Management: HR management sets performance standards for employees and monitors their performance regularly. It provides feedback and coaching to help employees improve their performance. This helps in identifying the areas where employees need to improve and take corrective actions to enhance their productivity.
Employee Engagement: HR management ensures that employees are engaged and motivated to perform their duties. It provides a conducive work environment and takes measures to address employees' concerns. This helps in reducing absenteeism and turnover rates, which improves productivity.
Effective Communication: HR management facilitates effective communication between employees and management. This helps in clarifying expectations, setting goals, and providing feedback. It also helps in resolving conflicts and improving employee morale, which enhances productivity.
Employee Recognition: HR management recognizes and rewards employees for their good performance. This helps in boosting employee morale and motivation, which leads to improved productivity.
In conclusion, HR management plays a crucial role in improving productivity in an organization. By providing training and development opportunities, setting performance standards, engaging employees, facilitating effective communication, and recognizing employee efforts, HR management helps create a productive work environment.
The features of leadership do not include:- a)representation
- b)initiation
- c)planning
- d)motivation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The features of leadership do not include:
a)
representation
b)
initiation
c)
planning
d)
motivation

|
Aditya Das answered |
Leadership is a process of influencing and motivating people towards a common goal. It involves a set of skills and abilities that enable a person to manage a team or group effectively. The features of leadership include various qualities, skills, and abilities that are required to lead a team or group. In this context, the given question is asking about the features of leadership that do not include planning.
Explanation:
Leadership is a complex process that involves various features or characteristics that are essential for effective leadership. The following are some of the features of leadership:
a) Representation: A leader represents the team or group in various settings, including meetings, negotiations, and interactions with other teams or groups. A leader is the face of the team or group and must communicate effectively to represent their interests.
b) Initiation: A leader initiates the process of goal setting, decision making, and problem-solving. A leader must have the ability to identify the needs and goals of the team or group and initiate actions to achieve them.
c) Planning: Planning is not a feature of leadership. While a leader may be involved in the planning process, it is not a defining characteristic of leadership. Planning involves developing strategies and action plans to achieve a goal, which can be done by anyone, not just a leader.
d) Motivation: A leader motivates and inspires team members to work towards a common goal. A leader must have the ability to understand the needs and aspirations of team members and use various motivational strategies to encourage them to perform their best.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the features of leadership include representation, initiation, and motivation. Planning is not a feature of leadership as it is a process that can be done by anyone, not just a leader. A leader may be involved in the planning process but it is not an essential feature of effective leadership.
Explanation:
Leadership is a complex process that involves various features or characteristics that are essential for effective leadership. The following are some of the features of leadership:
a) Representation: A leader represents the team or group in various settings, including meetings, negotiations, and interactions with other teams or groups. A leader is the face of the team or group and must communicate effectively to represent their interests.
b) Initiation: A leader initiates the process of goal setting, decision making, and problem-solving. A leader must have the ability to identify the needs and goals of the team or group and initiate actions to achieve them.
c) Planning: Planning is not a feature of leadership. While a leader may be involved in the planning process, it is not a defining characteristic of leadership. Planning involves developing strategies and action plans to achieve a goal, which can be done by anyone, not just a leader.
d) Motivation: A leader motivates and inspires team members to work towards a common goal. A leader must have the ability to understand the needs and aspirations of team members and use various motivational strategies to encourage them to perform their best.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the features of leadership include representation, initiation, and motivation. Planning is not a feature of leadership as it is a process that can be done by anyone, not just a leader. A leader may be involved in the planning process but it is not an essential feature of effective leadership.
The following phrase is used to describe a leader:- a)relies on control strategies
- b)challenges status quo
- c)uses traditional influence
- d)acts with established culture
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following phrase is used to describe a leader:
a)
relies on control strategies
b)
challenges status quo
c)
uses traditional influence
d)
acts with established culture
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
To describe a leader, the phrase "challenges status quo" is used. Here is a detailed explanation of this phrase:
Challenges status quo:
- Leaders who challenge the status quo are not satisfied with the current state of affairs and actively seek to improve and innovate.
- They question existing practices and norms, encouraging their team members to think critically and explore new ideas.
- These leaders are not afraid to take risks and are willing to disrupt established processes if they believe it will lead to positive change.
- By challenging the status quo, leaders inspire their team members to think outside the box and pursue innovative solutions.
- They create an environment that fosters creativity, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
- Leaders who challenge the status quo often drive organizational growth and success by pushing boundaries and exploring new possibilities.
In conclusion, a leader who challenges the status quo is someone who constantly seeks improvement, encourages innovation, and is not afraid to disrupt established norms for the betterment of the organization.
Douglas McGregor's view that suggests that employees will exercise self-direction and self-control when they are committed to the objectives of the work is called: - a)Theory B
- b)Theory X
- c)Theory Y
- d)Theory A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Douglas McGregor's view that suggests that employees will exercise self-direction and self-control when they are committed to the objectives of the work is called:
a)
Theory B
b)
Theory X
c)
Theory Y
d)
Theory A

|
Palak Choudhary answered |
Theory Y by Douglas McGregor
Theory Y is a management style and philosophy that suggests that employees will exercise self-direction and self-control when they are committed to the objectives of the work. This theory was proposed by Douglas McGregor, a social psychologist, in his book "The Human Side of Enterprise" in 1960. McGregor suggested that managers who adopt Theory Y are more likely to motivate and inspire their employees, resulting in higher levels of job satisfaction and productivity.
Features of Theory Y
Theory Y is founded on the following features:
- Employees have the potential to enjoy work and to be self-motivated.
- Employees seek responsibility and are capable of making significant contributions to the organization.
- Management should create an environment that allows employees to be creative and innovative.
- Management should involve employees in decision-making processes and encourage them to participate in setting organizational goals.
- Management should provide employees with opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Advantages of Theory Y
The advantages of Theory Y include:
- Higher levels of employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- Increased productivity and efficiency.
- Lower levels of absenteeism and turnover.
- Improved quality of work.
- Greater organizational flexibility and adaptability.
Disadvantages of Theory Y
The disadvantages of Theory Y include:
- It can be difficult to implement in organizations with a rigid and hierarchical structure.
- It assumes that all employees are self-motivated and responsible, which is not always the case.
- Some employees may take advantage of the freedom and autonomy provided by Theory Y management.
- It may not be suitable for organizations that have strict regulations and procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Theory Y suggests that employees are capable of self-direction and self-control when they are motivated and committed to the objectives of the work. Managers who adopt Theory Y are more likely to inspire and motivate their employees, resulting in higher levels of job satisfaction and productivity. However, Theory Y may not be suitable for all organizations and may require a significant shift in management style and philosophy.
Theory Y is a management style and philosophy that suggests that employees will exercise self-direction and self-control when they are committed to the objectives of the work. This theory was proposed by Douglas McGregor, a social psychologist, in his book "The Human Side of Enterprise" in 1960. McGregor suggested that managers who adopt Theory Y are more likely to motivate and inspire their employees, resulting in higher levels of job satisfaction and productivity.
Features of Theory Y
Theory Y is founded on the following features:
- Employees have the potential to enjoy work and to be self-motivated.
- Employees seek responsibility and are capable of making significant contributions to the organization.
- Management should create an environment that allows employees to be creative and innovative.
- Management should involve employees in decision-making processes and encourage them to participate in setting organizational goals.
- Management should provide employees with opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Advantages of Theory Y
The advantages of Theory Y include:
- Higher levels of employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- Increased productivity and efficiency.
- Lower levels of absenteeism and turnover.
- Improved quality of work.
- Greater organizational flexibility and adaptability.
Disadvantages of Theory Y
The disadvantages of Theory Y include:
- It can be difficult to implement in organizations with a rigid and hierarchical structure.
- It assumes that all employees are self-motivated and responsible, which is not always the case.
- Some employees may take advantage of the freedom and autonomy provided by Theory Y management.
- It may not be suitable for organizations that have strict regulations and procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Theory Y suggests that employees are capable of self-direction and self-control when they are motivated and committed to the objectives of the work. Managers who adopt Theory Y are more likely to inspire and motivate their employees, resulting in higher levels of job satisfaction and productivity. However, Theory Y may not be suitable for all organizations and may require a significant shift in management style and philosophy.
To achieve goals organizations require employees- a)Control
- b)Direction
- c)Commitment
- d)Cooperation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To achieve goals organizations require employees
a)
Control
b)
Direction
c)
Commitment
d)
Cooperation

|
Tanvi Pillai answered |
Commitment is the key to achieving organizational goals
Organizations require employees who are committed to achieving the goals of the organization. Commitment is essential as it drives employees to work towards the organization's objectives and ensures that they stay focused and motivated.
Importance of commitment in achieving goals
Commitment plays a crucial role in the success of an organization. Here are some reasons why commitment is important:
- Increased productivity: Committed employees are more likely to be productive and efficient in their work. They are dedicated to their tasks and strive to achieve high-quality results.
- Goal alignment: When employees are committed, they align their individual goals with the goals of the organization. This alignment ensures that everyone is working towards a common purpose, leading to better coordination and synergy.
- Retention of talent: Committed employees are more likely to stay with the organization for a longer duration. They are invested in the organization's success and are less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere.
- Positive work environment: Commitment creates a positive work environment where employees are motivated, engaged, and satisfied. This, in turn, leads to higher morale and better teamwork.
- Adaptability to change: Committed employees are more willing to adapt to changes in the organization. They are open to learning new skills and embracing new strategies, which is essential for the growth and success of the organization.
How organizations can foster commitment
Organizations can take several steps to foster commitment among their employees:
- Clear communication: Organizations should communicate their goals, values, and expectations clearly to employees. This clarity helps employees understand what is expected of them and how their work contributes to the overall success of the organization.
- Reward and recognition: Recognizing and rewarding employees for their commitment and achievements can reinforce their dedication and motivate them to continue working towards organizational goals.
- Employee development: Providing opportunities for growth and development can enhance employee commitment. Organizations can offer training programs, mentorship, and career advancement opportunities to help employees enhance their skills and achieve their professional goals.
- Creating a positive work culture: Organizations should foster a positive work culture that promotes collaboration, trust, and employee well-being. A supportive work environment encourages employees to be committed and engaged.
- Leadership support: Strong leadership plays a crucial role in fostering employee commitment. Leaders should lead by example, provide guidance, and create an environment that encourages commitment and accountability.
In conclusion, commitment is vital for organizations to achieve their goals. Committed employees are more productive, aligned with organizational objectives, and contribute to a positive work environment. Organizations can foster commitment by effective communication, recognition, employee development, creating a positive work culture, and providing leadership support.
The concept of span of control was propounded by- a)Graicunas
- b)Fayol
- c)Taylor
- d)Mc Gregor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of span of control was propounded by
a)
Graicunas
b)
Fayol
c)
Taylor
d)
Mc Gregor

|
Sai Kulkarni answered |
The concept of span of control was propounded by Graicunas.
The concept of span of control refers to the number of subordinates that a manager or supervisor can effectively manage. It determines the hierarchical structure and level of authority within an organization.
1. Definition of span of control:
Span of control can be defined as the number of employees that a manager can effectively supervise or control. It determines the extent to which a manager can directly interact with and manage subordinates.
2. Propounder of the concept:
The concept of span of control was propounded by a management theorist named Graicunas. He was a French engineer and management consultant who conducted extensive research on the relationship between the number of subordinates and the effectiveness of management. His research led him to develop the concept of span of control.
3. Importance of span of control:
The concept of span of control is important in determining the structure and efficiency of an organization. It helps in establishing the optimal number of subordinates that a manager can effectively supervise. A proper span of control ensures that managers have the necessary time, resources, and authority to manage their subordinates.
4. Factors affecting span of control:
Several factors can influence the span of control within an organization. These include:
- Complexity of tasks: If the tasks performed by subordinates are complex and require close supervision, the span of control may be narrow. On the other hand, if the tasks are routine and require less supervision, the span of control may be wider.
- Managerial skills: The skills and abilities of the manager also play a role in determining the span of control. A capable and experienced manager may be able to handle a larger number of subordinates effectively.
- Communication technology: Advances in communication technology, such as email, video conferencing, and project management tools, can increase the span of control by facilitating efficient communication and coordination.
- Organizational structure: The structure of the organization, such as centralized or decentralized, can also impact the span of control. In a centralized structure, where decision-making is concentrated at the top, the span of control may be narrower. In a decentralized structure, where decision-making is delegated, the span of control may be wider.
5. Optimal span of control:
Determining the optimal span of control is crucial for the effective functioning of an organization. A narrow span of control may result in a top-heavy organization with too many layers of management, leading to inefficiency and delay in decision-making. On the other hand, a wide span of control may lead to overwhelmed managers who are unable to provide adequate supervision and support to their subordinates. The optimal span of control varies depending on the specific context, tasks, and resources available.
Conclusion:
The concept of span of control, propounded by Graicunas, is an important aspect of organizational design and management. It helps in determining the number of subordinates that a manager can effectively supervise and influences the hierarchical structure and level of authority within an organization. By considering various factors and optimizing the span of control, organizations can ensure efficient communication, coordination, and decision-making.
The concept of span of control refers to the number of subordinates that a manager or supervisor can effectively manage. It determines the hierarchical structure and level of authority within an organization.
1. Definition of span of control:
Span of control can be defined as the number of employees that a manager can effectively supervise or control. It determines the extent to which a manager can directly interact with and manage subordinates.
2. Propounder of the concept:
The concept of span of control was propounded by a management theorist named Graicunas. He was a French engineer and management consultant who conducted extensive research on the relationship between the number of subordinates and the effectiveness of management. His research led him to develop the concept of span of control.
3. Importance of span of control:
The concept of span of control is important in determining the structure and efficiency of an organization. It helps in establishing the optimal number of subordinates that a manager can effectively supervise. A proper span of control ensures that managers have the necessary time, resources, and authority to manage their subordinates.
4. Factors affecting span of control:
Several factors can influence the span of control within an organization. These include:
- Complexity of tasks: If the tasks performed by subordinates are complex and require close supervision, the span of control may be narrow. On the other hand, if the tasks are routine and require less supervision, the span of control may be wider.
- Managerial skills: The skills and abilities of the manager also play a role in determining the span of control. A capable and experienced manager may be able to handle a larger number of subordinates effectively.
- Communication technology: Advances in communication technology, such as email, video conferencing, and project management tools, can increase the span of control by facilitating efficient communication and coordination.
- Organizational structure: The structure of the organization, such as centralized or decentralized, can also impact the span of control. In a centralized structure, where decision-making is concentrated at the top, the span of control may be narrower. In a decentralized structure, where decision-making is delegated, the span of control may be wider.
5. Optimal span of control:
Determining the optimal span of control is crucial for the effective functioning of an organization. A narrow span of control may result in a top-heavy organization with too many layers of management, leading to inefficiency and delay in decision-making. On the other hand, a wide span of control may lead to overwhelmed managers who are unable to provide adequate supervision and support to their subordinates. The optimal span of control varies depending on the specific context, tasks, and resources available.
Conclusion:
The concept of span of control, propounded by Graicunas, is an important aspect of organizational design and management. It helps in determining the number of subordinates that a manager can effectively supervise and influences the hierarchical structure and level of authority within an organization. By considering various factors and optimizing the span of control, organizations can ensure efficient communication, coordination, and decision-making.
Another contingency model of leadership is the path-goal theory. This suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if:- a)path-goal relationships are clarified
- b)their effective performance will satisfy their needs
- c)the necessary direction, guidance, training and support is provided
- d)all the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Another contingency model of leadership is the path-goal theory. This suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if:
a)
path-goal relationships are clarified
b)
their effective performance will satisfy their needs
c)
the necessary direction, guidance, training and support is provided
d)
all the above

|
Rithika Nair answered |
Path-Goal Theory of Leadership
The path-goal theory of leadership is a contingency model that suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if certain conditions are met. These conditions include clarifying path-goal relationships, providing effective performance that satisfies their needs, and providing necessary direction, guidance, training and support.
Clarifying Path-Goal Relationships
Path-goal relationships refer to the relationship between the leader and the subordinate in terms of the goals that need to be achieved. In order for subordinates to see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence, the leader must clarify these relationships so that subordinates understand what is expected of them and how their work contributes to the overall goals of the organization.
Effective Performance that Satisfies Needs
Subordinates will be motivated if they believe that their effective performance will satisfy their needs. This means that the leader must be able to identify the needs of subordinates and ensure that their work is designed in a way that allows them to meet those needs. For example, if a subordinate values job security, the leader must provide them with job security in order to motivate them.
Direction, Guidance, Training and Support
In order for subordinates to be motivated, the leader must provide them with the necessary direction, guidance, training and support. This means that the leader must be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of subordinates and provide them with the necessary training and support to help them improve their performance. Additionally, the leader must be able to provide direction and guidance to subordinates so that they know what is expected of them.
Conclusion
The path-goal theory of leadership is a contingency model that suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if certain conditions are met. These conditions include clarifying path-goal relationships, providing effective performance that satisfies their needs, and providing necessary direction, guidance, training and support. By meeting these conditions, leaders can motivate their subordinates and help them achieve their goals.
The path-goal theory of leadership is a contingency model that suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if certain conditions are met. These conditions include clarifying path-goal relationships, providing effective performance that satisfies their needs, and providing necessary direction, guidance, training and support.
Clarifying Path-Goal Relationships
Path-goal relationships refer to the relationship between the leader and the subordinate in terms of the goals that need to be achieved. In order for subordinates to see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence, the leader must clarify these relationships so that subordinates understand what is expected of them and how their work contributes to the overall goals of the organization.
Effective Performance that Satisfies Needs
Subordinates will be motivated if they believe that their effective performance will satisfy their needs. This means that the leader must be able to identify the needs of subordinates and ensure that their work is designed in a way that allows them to meet those needs. For example, if a subordinate values job security, the leader must provide them with job security in order to motivate them.
Direction, Guidance, Training and Support
In order for subordinates to be motivated, the leader must provide them with the necessary direction, guidance, training and support. This means that the leader must be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of subordinates and provide them with the necessary training and support to help them improve their performance. Additionally, the leader must be able to provide direction and guidance to subordinates so that they know what is expected of them.
Conclusion
The path-goal theory of leadership is a contingency model that suggests that subordinates will see leadership behaviour as a motivating influence if certain conditions are met. These conditions include clarifying path-goal relationships, providing effective performance that satisfies their needs, and providing necessary direction, guidance, training and support. By meeting these conditions, leaders can motivate their subordinates and help them achieve their goals.
The "means" of leadership involve- a)getting results through others
- b)the ability to build cohesive, goal-oriented teams
- c)the process of influencing an organized group toward accomplishing its goals
- d)an interpersonal relation in which others comply because they want to, not because they have to
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The "means" of leadership involve
a)
getting results through others
b)
the ability to build cohesive, goal-oriented teams
c)
the process of influencing an organized group toward accomplishing its goals
d)
an interpersonal relation in which others comply because they want to, not because they have to

|
Hrishikesh Mukherjee answered |
The what? Could you please provide more context or clarify your question?
A concern having textile, chemicals, plastics fertilizers follow departmentation based on- a)process
- b)product
- c)functions
- d)geographical areas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A concern having textile, chemicals, plastics fertilizers follow departmentation based on
a)
process
b)
product
c)
functions
d)
geographical areas

|
Maheshwar Goyal answered |
Departmentation Based on Product
Departmentation is the process of creating different departments or units in an organization to carry out specific tasks efficiently and effectively. There are various ways of departmentation, such as departmentation based on function, product, process, customer, geography, etc. In the case of textile, chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers industries, departmentation based on product is the most suitable approach.
Advantages of Departmentation Based on Product
1. Specialization: When departments are created based on product, each department specializes in a particular product or group of related products. This specialization helps in achieving a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness in the production and marketing of those products.
2. Coordination: Since each department is responsible for a specific product or group of products, it becomes easier to coordinate and integrate the activities of different departments. This ensures that the products are produced and marketed seamlessly.
3. Flexibility: Departmentation based on product allows the organization to be flexible in responding to changes in the market demand. Each product department can adjust its production and marketing strategies according to the changing needs of the market.
4. Accountability: Product-based departments promote accountability because each department is responsible for the production and marketing of its products. This makes it easier to track the performance of each department and take corrective actions when necessary.
5. Customer focus: When departments are based on product, they become more customer-focused. Each department is responsible for meeting the specific needs of its customers, which enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
In conclusion, departmentation based on product is the most suitable approach for textile, chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers industries. It promotes specialization, coordination, flexibility, accountability, and customer focus, which helps in achieving a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness in the production and marketing of products.
Departmentation is the process of creating different departments or units in an organization to carry out specific tasks efficiently and effectively. There are various ways of departmentation, such as departmentation based on function, product, process, customer, geography, etc. In the case of textile, chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers industries, departmentation based on product is the most suitable approach.
Advantages of Departmentation Based on Product
1. Specialization: When departments are created based on product, each department specializes in a particular product or group of related products. This specialization helps in achieving a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness in the production and marketing of those products.
2. Coordination: Since each department is responsible for a specific product or group of products, it becomes easier to coordinate and integrate the activities of different departments. This ensures that the products are produced and marketed seamlessly.
3. Flexibility: Departmentation based on product allows the organization to be flexible in responding to changes in the market demand. Each product department can adjust its production and marketing strategies according to the changing needs of the market.
4. Accountability: Product-based departments promote accountability because each department is responsible for the production and marketing of its products. This makes it easier to track the performance of each department and take corrective actions when necessary.
5. Customer focus: When departments are based on product, they become more customer-focused. Each department is responsible for meeting the specific needs of its customers, which enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
In conclusion, departmentation based on product is the most suitable approach for textile, chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers industries. It promotes specialization, coordination, flexibility, accountability, and customer focus, which helps in achieving a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness in the production and marketing of products.
Which of the factors listed below is not a reason for decision making in organizations being a complex process?- a)People have to make decisions in a historical context
- b)Several stakeholders will have an interest in the decision
- c)Factors in the current context of the organization affect the decision
- d)Modern information systems enable people to evaluate a range of possible outcomes.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the factors listed below is not a reason for decision making in organizations being a complex process?
a)
People have to make decisions in a historical context
b)
Several stakeholders will have an interest in the decision
c)
Factors in the current context of the organization affect the decision
d)
Modern information systems enable people to evaluate a range of possible outcomes.

|
Raghav Ghoshal answered |
Reasons for Decision Making in Organizations Being a Complex Process
Introduction
Decision making in organizations is a complicated process that involves several factors that affect the outcome. These factors may include social, economic, and environmental factors that influence the decision-making process. This article discusses the reasons for decision making in organizations being a complex process.
Historical Context
The historical context in which decisions are made can have a significant impact on the decision-making process. Past decisions, events, and experiences can shape the way decisions are made and can influence the outcome of the decision-making process. It is, therefore, crucial to consider the historical context when making decisions in organizations.
Several Stakeholders
In organizations, several stakeholders will have an interest in the decision being made. These stakeholders may include employees, customers, shareholders, and suppliers. Each stakeholder will have different interests and priorities, and it is essential to consider these interests when making decisions. Failure to consider stakeholders' interests can result in poor decision-making outcomes.
Current Context of the Organization
Factors in the current context of the organization can also affect the decision-making process. These factors may include economic conditions, competition, and technological advancements. It is crucial to consider these external factors when making decisions to ensure that the decisions made align with the organization's goals and objectives.
Modern Information Systems
Modern information systems enable people to evaluate a range of possible outcomes. However, this does not mean that decision making in organizations is not a complex process. The availability of information can sometimes make the decision-making process even more complicated as stakeholders may have different interpretations of the data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, decision making in organizations is a complex process that involves several factors that affect the outcome. These factors may include the historical context, several stakeholders, the current context of the organization, and modern information systems. It is essential to consider these factors when making decisions to ensure that the decisions made align with the organization's goals and objectives.
Introduction
Decision making in organizations is a complicated process that involves several factors that affect the outcome. These factors may include social, economic, and environmental factors that influence the decision-making process. This article discusses the reasons for decision making in organizations being a complex process.
Historical Context
The historical context in which decisions are made can have a significant impact on the decision-making process. Past decisions, events, and experiences can shape the way decisions are made and can influence the outcome of the decision-making process. It is, therefore, crucial to consider the historical context when making decisions in organizations.
Several Stakeholders
In organizations, several stakeholders will have an interest in the decision being made. These stakeholders may include employees, customers, shareholders, and suppliers. Each stakeholder will have different interests and priorities, and it is essential to consider these interests when making decisions. Failure to consider stakeholders' interests can result in poor decision-making outcomes.
Current Context of the Organization
Factors in the current context of the organization can also affect the decision-making process. These factors may include economic conditions, competition, and technological advancements. It is crucial to consider these external factors when making decisions to ensure that the decisions made align with the organization's goals and objectives.
Modern Information Systems
Modern information systems enable people to evaluate a range of possible outcomes. However, this does not mean that decision making in organizations is not a complex process. The availability of information can sometimes make the decision-making process even more complicated as stakeholders may have different interpretations of the data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, decision making in organizations is a complex process that involves several factors that affect the outcome. These factors may include the historical context, several stakeholders, the current context of the organization, and modern information systems. It is essential to consider these factors when making decisions to ensure that the decisions made align with the organization's goals and objectives.
The overall process of decision making in, for example, staff selection includes which of these stages?- a)Deciding which candidate to appoint
- b)Identifying the need for a new member of staff
- c)Agreeing the job specification
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The overall process of decision making in, for example, staff selection includes which of these stages?
a)
Deciding which candidate to appoint
b)
Identifying the need for a new member of staff
c)
Agreeing the job specification
d)
All of the above

|
Vaishnavi Gupta answered |
The overall process of decision making in staff selection includes the following stages:
1. Identifying the need for a new member of staff:
This stage involves recognizing the requirement for an additional staff member within an organization. It may be due to increased workload, expansion of business operations, or filling a vacant position.
2. Agreeing the job specification:
Once the need for a new staff member is identified, the next step is to define the job specification. This involves determining the specific responsibilities, qualifications, skills, and experience required for the position.
3. Advertising the job:
After agreeing on the job specification, the organization advertises the job opening to attract potential candidates. This can be done through various channels such as online job portals, newspapers, or recruitment agencies.
4. Receiving and reviewing applications:
In this stage, the organization receives applications from interested candidates and reviews them based on the job requirements. The review process involves assessing the qualifications, skills, and experience of each applicant to shortlist potential candidates for further evaluation.
5. Conducting interviews:
The shortlisted candidates are invited for interviews, which can be conducted in various formats such as face-to-face interviews, telephonic interviews, or video interviews. The purpose of the interview is to assess the candidate's suitability for the role, their communication skills, and their ability to handle job-specific tasks.
6. Assessing candidates through tests and assessments:
In addition to interviews, organizations may also use tests and assessments to evaluate the candidates further. These assessments can include aptitude tests, personality assessments, or practical tasks relevant to the job role.
7. Making the final decision:
After completing the interview and assessment process, the organization evaluates all the information gathered on each candidate and makes the final decision. This involves comparing the qualifications, skills, experience, and overall fit of each candidate against the job requirements and organizational culture.
8. Deciding which candidate to appoint:
The last stage of the decision-making process in staff selection is selecting the most suitable candidate for the job. The decision is based on the evaluation of the candidate's performance in the interviews, assessments, and their overall fit with the organization's requirements.
In conclusion, the overall process of decision making in staff selection includes identifying the need for a new staff member, agreeing on the job specification, advertising the job, reviewing applications, conducting interviews, assessing candidates through tests and assessments, making the final decision, and ultimately deciding which candidate to appoint.
1. Identifying the need for a new member of staff:
This stage involves recognizing the requirement for an additional staff member within an organization. It may be due to increased workload, expansion of business operations, or filling a vacant position.
2. Agreeing the job specification:
Once the need for a new staff member is identified, the next step is to define the job specification. This involves determining the specific responsibilities, qualifications, skills, and experience required for the position.
3. Advertising the job:
After agreeing on the job specification, the organization advertises the job opening to attract potential candidates. This can be done through various channels such as online job portals, newspapers, or recruitment agencies.
4. Receiving and reviewing applications:
In this stage, the organization receives applications from interested candidates and reviews them based on the job requirements. The review process involves assessing the qualifications, skills, and experience of each applicant to shortlist potential candidates for further evaluation.
5. Conducting interviews:
The shortlisted candidates are invited for interviews, which can be conducted in various formats such as face-to-face interviews, telephonic interviews, or video interviews. The purpose of the interview is to assess the candidate's suitability for the role, their communication skills, and their ability to handle job-specific tasks.
6. Assessing candidates through tests and assessments:
In addition to interviews, organizations may also use tests and assessments to evaluate the candidates further. These assessments can include aptitude tests, personality assessments, or practical tasks relevant to the job role.
7. Making the final decision:
After completing the interview and assessment process, the organization evaluates all the information gathered on each candidate and makes the final decision. This involves comparing the qualifications, skills, experience, and overall fit of each candidate against the job requirements and organizational culture.
8. Deciding which candidate to appoint:
The last stage of the decision-making process in staff selection is selecting the most suitable candidate for the job. The decision is based on the evaluation of the candidate's performance in the interviews, assessments, and their overall fit with the organization's requirements.
In conclusion, the overall process of decision making in staff selection includes identifying the need for a new staff member, agreeing on the job specification, advertising the job, reviewing applications, conducting interviews, assessing candidates through tests and assessments, making the final decision, and ultimately deciding which candidate to appoint.
Which of the following statements is false about the behavioral theories of leadership?- a)Consideration is a people-oriented dimension of leadership behavior
- b)Production-centered leader behavior focuses on tasks and has little concern for people
- c)Leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments
- d)Employee-centered leader behavior focuses on people and the quality of the social system.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false about the behavioral theories of leadership?
a)
Consideration is a people-oriented dimension of leadership behavior
b)
Production-centered leader behavior focuses on tasks and has little concern for people
c)
Leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments
d)
Employee-centered leader behavior focuses on people and the quality of the social system.

|
Anu Sen answered |
< b="" />Explanation: < />
The false statement about the behavioral theories of leadership is option 'C' which states that leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments.
< b="" />Understanding Behavioral Theories of Leadership: < />
Behavioral theories of leadership focus on the actions and behaviors of leaders rather than their traits or characteristics. These theories suggest that effective leadership can be learned and developed through specific behaviors and actions. Two important dimensions of leadership behavior identified in these theories are consideration and initiating structure.
< b="" />Consideration: < />
Consideration is a people-oriented dimension of leadership behavior. Leaders high in consideration show concern for the needs, feelings, and well-being of their followers. They establish a supportive and positive work environment, build relationships, and show empathy. Consideration is important for promoting job satisfaction, motivation, and creating a positive work culture.
< b="" />Production-Centered Leader Behavior: < />
Production-centered leader behavior focuses on tasks and has little concern for people. Leaders who exhibit this behavior prioritize achieving goals, meeting deadlines, and completing tasks efficiently. They may be task-oriented and focused on the bottom line, but they may not pay much attention to the needs and well-being of their followers. This type of behavior can sometimes lead to a lack of employee satisfaction and motivation.
< b="" />Initiating Structure: < />
Initiating structure refers to the extent to which a leader defines and structures the roles, tasks, and responsibilities of their followers. Leaders high in initiating structure provide clear instructions, set goals, and establish procedures and rules. They ensure that tasks are organized and coordinated effectively. This behavior is important for creating clarity, reducing ambiguity, and facilitating task performance.
< b="" />Explanation of False Statement: < />
The false statement in option 'C' suggests that leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments. However, this statement is incorrect. Leaders high in initiating structure actively set deadlines and make individual task assignments to ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively. By providing clear instructions and establishing timelines, leaders can enhance task performance and productivity.
In conclusion, option 'C' is the false statement about the behavioral theories of leadership because leaders high in initiating structure do set deadlines and make individual task assignments.
The false statement about the behavioral theories of leadership is option 'C' which states that leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments.
< b="" />Understanding Behavioral Theories of Leadership: < />
Behavioral theories of leadership focus on the actions and behaviors of leaders rather than their traits or characteristics. These theories suggest that effective leadership can be learned and developed through specific behaviors and actions. Two important dimensions of leadership behavior identified in these theories are consideration and initiating structure.
< b="" />Consideration: < />
Consideration is a people-oriented dimension of leadership behavior. Leaders high in consideration show concern for the needs, feelings, and well-being of their followers. They establish a supportive and positive work environment, build relationships, and show empathy. Consideration is important for promoting job satisfaction, motivation, and creating a positive work culture.
< b="" />Production-Centered Leader Behavior: < />
Production-centered leader behavior focuses on tasks and has little concern for people. Leaders who exhibit this behavior prioritize achieving goals, meeting deadlines, and completing tasks efficiently. They may be task-oriented and focused on the bottom line, but they may not pay much attention to the needs and well-being of their followers. This type of behavior can sometimes lead to a lack of employee satisfaction and motivation.
< b="" />Initiating Structure: < />
Initiating structure refers to the extent to which a leader defines and structures the roles, tasks, and responsibilities of their followers. Leaders high in initiating structure provide clear instructions, set goals, and establish procedures and rules. They ensure that tasks are organized and coordinated effectively. This behavior is important for creating clarity, reducing ambiguity, and facilitating task performance.
< b="" />Explanation of False Statement: < />
The false statement in option 'C' suggests that leaders high in initiating structure do not set deadlines or make individual task assignments. However, this statement is incorrect. Leaders high in initiating structure actively set deadlines and make individual task assignments to ensure that work is completed efficiently and effectively. By providing clear instructions and establishing timelines, leaders can enhance task performance and productivity.
In conclusion, option 'C' is the false statement about the behavioral theories of leadership because leaders high in initiating structure do set deadlines and make individual task assignments.
Decision making situations can be categorized along a scale which ranges from:- a)Certainty to risk to uncertainty to ambiguity
- b)Certainty to uncertainty to risk
- c)Certainty to risk to uncertainty
- d)Uncertainty to certainty to risk
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Decision making situations can be categorized along a scale which ranges from:
a)
Certainty to risk to uncertainty to ambiguity
b)
Certainty to uncertainty to risk
c)
Certainty to risk to uncertainty
d)
Uncertainty to certainty to risk

|
Akshay Saini answered |
Decision Making Situations
Introduction:
Decision making situations can be categorized along a scale that ranges from certainty to risk to uncertainty to ambiguity. Each category represents a different level of information and understanding available to the decision maker. Understanding these categories can help individuals make more informed and effective decisions.
Categories of Decision Making Situations:
1. Certainty:
In situations of certainty, the decision maker has complete information about the outcome of each possible action. The consequences of each decision are known and can be accurately predicted. In such situations, decision making is relatively straightforward as there is a clear cause and effect relationship between actions and outcomes.
2. Risk:
In situations of risk, the decision maker has some information about the probabilities of different outcomes. Although the exact outcome is not known, the decision maker can make informed decisions by assessing the likelihood of different outcomes and their potential impact. Risk can be managed through various techniques such as probability analysis, risk assessment, and risk mitigation strategies.
3. Uncertainty:
In situations of uncertainty, the decision maker lacks complete information and is unable to accurately estimate probabilities or predict outcomes. The decision maker may have limited data or conflicting information, making it difficult to assess the potential outcomes. In such situations, decision making becomes more challenging and requires judgment, intuition, and experience.
4. Ambiguity:
In situations of ambiguity, the decision maker not only lacks information but also faces an unclear or ill-defined problem. The decision maker may not fully understand the problem or the available options, leading to confusion and complexity. Ambiguous situations often require creative thinking, exploration of multiple perspectives, and the ability to tolerate ambiguity.
Conclusion:
Understanding the different categories of decision making situations can help individuals approach decision making in a more systematic and informed manner. By recognizing the level of certainty, risk, uncertainty, or ambiguity in a particular situation, decision makers can apply appropriate strategies and techniques to make better decisions. It is important to note that decision making is not always black and white, and situations may fall on a spectrum between these categories.
Introduction:
Decision making situations can be categorized along a scale that ranges from certainty to risk to uncertainty to ambiguity. Each category represents a different level of information and understanding available to the decision maker. Understanding these categories can help individuals make more informed and effective decisions.
Categories of Decision Making Situations:
1. Certainty:
In situations of certainty, the decision maker has complete information about the outcome of each possible action. The consequences of each decision are known and can be accurately predicted. In such situations, decision making is relatively straightforward as there is a clear cause and effect relationship between actions and outcomes.
2. Risk:
In situations of risk, the decision maker has some information about the probabilities of different outcomes. Although the exact outcome is not known, the decision maker can make informed decisions by assessing the likelihood of different outcomes and their potential impact. Risk can be managed through various techniques such as probability analysis, risk assessment, and risk mitigation strategies.
3. Uncertainty:
In situations of uncertainty, the decision maker lacks complete information and is unable to accurately estimate probabilities or predict outcomes. The decision maker may have limited data or conflicting information, making it difficult to assess the potential outcomes. In such situations, decision making becomes more challenging and requires judgment, intuition, and experience.
4. Ambiguity:
In situations of ambiguity, the decision maker not only lacks information but also faces an unclear or ill-defined problem. The decision maker may not fully understand the problem or the available options, leading to confusion and complexity. Ambiguous situations often require creative thinking, exploration of multiple perspectives, and the ability to tolerate ambiguity.
Conclusion:
Understanding the different categories of decision making situations can help individuals approach decision making in a more systematic and informed manner. By recognizing the level of certainty, risk, uncertainty, or ambiguity in a particular situation, decision makers can apply appropriate strategies and techniques to make better decisions. It is important to note that decision making is not always black and white, and situations may fall on a spectrum between these categories.
When determining the most appropriate form of leadership, which of the following should be considered?- a)The manager
- b)The work environment
- c)The group
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When determining the most appropriate form of leadership, which of the following should be considered?
a)
The manager
b)
The work environment
c)
The group
d)
All the above

|
Srsps answered |
Factors to Consider When Determining the Most Appropriate Form of Leadership:
1. The Manager:
- The skills, experience, and leadership style of the manager play a crucial role in determining the appropriate form of leadership.
- The manager's ability to communicate, motivate, and guide their team members can influence the leadership approach they adopt.
2. The Work Environment:
- The nature of the work environment, including its culture, structure, and dynamics, can impact the choice of leadership style.
- Factors such as the level of autonomy, teamwork requirements, and the need for innovation can influence the preferred leadership approach.
3. The Group:
- The characteristics and preferences of the group being led are important considerations.
- Factors such as the level of expertise, motivation, and communication styles of the group members can influence the leadership style that is most effective.
4. All of the Above:
- Considering all the factors mentioned above is essential to determine the most appropriate form of leadership.
- Each factor alone may not provide a complete picture, so a holistic approach that takes into account the manager, work environment, and group dynamics is necessary.
Therefore, the most appropriate form of leadership is determined by considering the manager, work environment, and group dynamics. It is crucial to assess these factors collectively to choose a leadership style that aligns with the needs and goals of the organization and its members.
1. The Manager:
- The skills, experience, and leadership style of the manager play a crucial role in determining the appropriate form of leadership.
- The manager's ability to communicate, motivate, and guide their team members can influence the leadership approach they adopt.
2. The Work Environment:
- The nature of the work environment, including its culture, structure, and dynamics, can impact the choice of leadership style.
- Factors such as the level of autonomy, teamwork requirements, and the need for innovation can influence the preferred leadership approach.
3. The Group:
- The characteristics and preferences of the group being led are important considerations.
- Factors such as the level of expertise, motivation, and communication styles of the group members can influence the leadership style that is most effective.
4. All of the Above:
- Considering all the factors mentioned above is essential to determine the most appropriate form of leadership.
- Each factor alone may not provide a complete picture, so a holistic approach that takes into account the manager, work environment, and group dynamics is necessary.
Therefore, the most appropriate form of leadership is determined by considering the manager, work environment, and group dynamics. It is crucial to assess these factors collectively to choose a leadership style that aligns with the needs and goals of the organization and its members.
An employee's experiences in a situation or position outside his or her current organization is a referent comparison called:- a)Self-outside
- b)Other-inside
- c)Other-outside
- d)Self-inside
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An employee's experiences in a situation or position outside his or her current organization is a referent comparison called:
a)
Self-outside
b)
Other-inside
c)
Other-outside
d)
Self-inside

|
Bhaskar Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that an employee's experiences in a situation or position outside his or her current organization is a referent comparison called "Self-outside".
Explanation:
A referent comparison is a cognitive process in which individuals evaluate themselves by comparing their experiences, abilities, and achievements to those of others. It helps individuals to assess their own performance and determine their self-worth.
In the context of the question, the referent comparison is specifically about an employee's experiences in a situation or position outside their current organization. This means that the employee is comparing their own experiences in a different organization or role to their current situation.
When an employee compares their experiences from outside their current organization, it can provide them with valuable insights and perspectives. They can evaluate their own skills, knowledge, and achievements in relation to what they have experienced in the past.
By comparing themselves to their past experiences, employees can identify areas of growth and improvement. They can also gain a better understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, and how they can apply their past experiences to their current role.
This referent comparison, known as "Self-outside", allows employees to gain a broader perspective and learn from their previous experiences. It can also help them set goals and make decisions about their career path.
Overall, referent comparisons are an important cognitive process that individuals use to evaluate themselves and their experiences. In the context of an employee's experiences in a situation or position outside their current organization, the referent comparison is called "Self-outside". This comparison can provide valuable insights and help employees assess their own performance and potential for growth.
Explanation:
A referent comparison is a cognitive process in which individuals evaluate themselves by comparing their experiences, abilities, and achievements to those of others. It helps individuals to assess their own performance and determine their self-worth.
In the context of the question, the referent comparison is specifically about an employee's experiences in a situation or position outside their current organization. This means that the employee is comparing their own experiences in a different organization or role to their current situation.
When an employee compares their experiences from outside their current organization, it can provide them with valuable insights and perspectives. They can evaluate their own skills, knowledge, and achievements in relation to what they have experienced in the past.
By comparing themselves to their past experiences, employees can identify areas of growth and improvement. They can also gain a better understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, and how they can apply their past experiences to their current role.
This referent comparison, known as "Self-outside", allows employees to gain a broader perspective and learn from their previous experiences. It can also help them set goals and make decisions about their career path.
Overall, referent comparisons are an important cognitive process that individuals use to evaluate themselves and their experiences. In the context of an employee's experiences in a situation or position outside their current organization, the referent comparison is called "Self-outside". This comparison can provide valuable insights and help employees assess their own performance and potential for growth.
The difference between human resource management and personnel management is - a)Insignificant
- b)Marginal
- c)Narrow
- d)Wide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between human resource management and personnel management is
a)
Insignificant
b)
Marginal
c)
Narrow
d)
Wide

|
Puja Singh answered |
Human Resource Management and Personnel Management are two different terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences.
1. Definition:
- Personnel Management refers to the traditional approach to managing people in organizations. It is mainly concerned with hiring, training, compensation, and disciplinary actions of employees.
- Human Resource Management, on the other hand, is a modern and strategic approach that focuses on managing people as assets to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It is concerned with the development of employees, creating a positive work environment, and aligning employee goals with organizational goals.
2. Scope:
- Personnel Management has a narrow scope and is limited to managing administrative tasks, such as maintaining employee records, payroll, and benefits.
- Human Resource Management has a wider scope that covers not only administrative tasks but also strategic planning, performance management, talent acquisition, and development of employees.
3. Approach:
- Personnel Management takes a reactive approach to handling employee issues. It waits for a problem to arise before taking action.
- Human Resource Management takes a proactive approach and seeks to prevent problems from occurring by creating a positive work environment, providing training, and development opportunities for employees.
4. Employee relations:
- Personnel Management focuses on maintaining good relations with employees to ensure compliance with rules and regulations.
- Human Resource Management focuses on building relationships with employees to create a positive work environment, increase employee engagement, and improve productivity.
In conclusion, the difference between Personnel Management and Human Resource Management is significant. While Personnel Management is concerned with administrative tasks, Human Resource Management is a strategic approach that focuses on managing people as assets to achieve organizational goals and objectives.
1. Definition:
- Personnel Management refers to the traditional approach to managing people in organizations. It is mainly concerned with hiring, training, compensation, and disciplinary actions of employees.
- Human Resource Management, on the other hand, is a modern and strategic approach that focuses on managing people as assets to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It is concerned with the development of employees, creating a positive work environment, and aligning employee goals with organizational goals.
2. Scope:
- Personnel Management has a narrow scope and is limited to managing administrative tasks, such as maintaining employee records, payroll, and benefits.
- Human Resource Management has a wider scope that covers not only administrative tasks but also strategic planning, performance management, talent acquisition, and development of employees.
3. Approach:
- Personnel Management takes a reactive approach to handling employee issues. It waits for a problem to arise before taking action.
- Human Resource Management takes a proactive approach and seeks to prevent problems from occurring by creating a positive work environment, providing training, and development opportunities for employees.
4. Employee relations:
- Personnel Management focuses on maintaining good relations with employees to ensure compliance with rules and regulations.
- Human Resource Management focuses on building relationships with employees to create a positive work environment, increase employee engagement, and improve productivity.
In conclusion, the difference between Personnel Management and Human Resource Management is significant. While Personnel Management is concerned with administrative tasks, Human Resource Management is a strategic approach that focuses on managing people as assets to achieve organizational goals and objectives.
Leadership has a lot of characteristics and a leader must not maintain this trait in his behaviour: - a)coexistence
- b)taking responsibility
- c)avoiding responsibility
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Leadership has a lot of characteristics and a leader must not maintain this trait in his behaviour:
a)
coexistence
b)
taking responsibility
c)
avoiding responsibility
d)
All of the above.

|
Sahil Malik answered |
Leadership Characteristics
Leadership is a quality that is an essential requirement for any organization, group or team. A leader is someone who is able to inspire, motivate and guide others towards achieving a common goal. There are several characteristics that define a good leader, such as integrity, communication skills, vision, and adaptability. However, there are also certain traits that a leader should not have in his/her behaviour, which are discussed below.
Avoiding Responsibility
One of the traits that a leader must not maintain in his/her behaviour is avoiding responsibility. A good leader takes responsibility for his/her actions, decisions and outcomes. They are willing to be accountable for the success and failure of the team, and they do not shy away from making difficult decisions or taking bold actions when necessary. A leader who avoids responsibility is likely to be seen as weak and indecisive, which can undermine the confidence and trust of the team.
Coexistence
Coexistence is not a trait that a leader should avoid. In fact, it is a characteristic that is highly desirable for a good leader. Coexistence means the ability to work in harmony with others, to be respectful and tolerant of different perspectives and opinions, and to be able to collaborate effectively towards achieving a common goal. A leader who is able to coexist with others is likely to be able to build strong relationships and foster a positive and productive team culture.
Taking Responsibility
Taking responsibility is another trait that is highly desirable for a good leader. A leader who takes responsibility is able to inspire trust and confidence in the team, and is seen as someone who is accountable and reliable. They are willing to take ownership of problems and challenges, and are proactive in finding solutions and implementing actions. A leader who takes responsibility is also more likely to be respected and admired by the team, which can help to build a strong and loyal following.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leadership is a complex and multifaceted quality that requires a combination of positive traits and behaviours. While there are several characteristics that define a good leader, there are also certain traits that a leader should avoid, such as avoiding responsibility. By cultivating positive traits and behaviours, and avoiding negative ones, leaders can inspire, motivate and guide their teams towards achieving success.
Leadership is a quality that is an essential requirement for any organization, group or team. A leader is someone who is able to inspire, motivate and guide others towards achieving a common goal. There are several characteristics that define a good leader, such as integrity, communication skills, vision, and adaptability. However, there are also certain traits that a leader should not have in his/her behaviour, which are discussed below.
Avoiding Responsibility
One of the traits that a leader must not maintain in his/her behaviour is avoiding responsibility. A good leader takes responsibility for his/her actions, decisions and outcomes. They are willing to be accountable for the success and failure of the team, and they do not shy away from making difficult decisions or taking bold actions when necessary. A leader who avoids responsibility is likely to be seen as weak and indecisive, which can undermine the confidence and trust of the team.
Coexistence
Coexistence is not a trait that a leader should avoid. In fact, it is a characteristic that is highly desirable for a good leader. Coexistence means the ability to work in harmony with others, to be respectful and tolerant of different perspectives and opinions, and to be able to collaborate effectively towards achieving a common goal. A leader who is able to coexist with others is likely to be able to build strong relationships and foster a positive and productive team culture.
Taking Responsibility
Taking responsibility is another trait that is highly desirable for a good leader. A leader who takes responsibility is able to inspire trust and confidence in the team, and is seen as someone who is accountable and reliable. They are willing to take ownership of problems and challenges, and are proactive in finding solutions and implementing actions. A leader who takes responsibility is also more likely to be respected and admired by the team, which can help to build a strong and loyal following.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leadership is a complex and multifaceted quality that requires a combination of positive traits and behaviours. While there are several characteristics that define a good leader, there are also certain traits that a leader should avoid, such as avoiding responsibility. By cultivating positive traits and behaviours, and avoiding negative ones, leaders can inspire, motivate and guide their teams towards achieving success.
Which of the following is false about motivator — hygiene theory (Herzberg)?- a)Motivators include achievement and the work itself
- b)Empirical research strongly supports the theory
- c)Dissatisfiers and satisfiers fall on two different continua
- d)Company policies are a hygiene factor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is false about motivator — hygiene theory (Herzberg)?
a)
Motivators include achievement and the work itself
b)
Empirical research strongly supports the theory
c)
Dissatisfiers and satisfiers fall on two different continua
d)
Company policies are a hygiene factor

|
Sparsh Chauhan answered |
Unfortunately, you have not provided the options for us to determine which statement is false about a motivator. Please provide the options so that we can assist you further.
The process of monitoring performance monitoring it with goals and correcting any significant deviations is known as - a)Planning
- b)Organising
- c)Leading
- d)Controlling.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of monitoring performance monitoring it with goals and correcting any significant deviations is known as
a)
Planning
b)
Organising
c)
Leading
d)
Controlling.

|
Devanshi Rane answered |
Explanation:
Performance monitoring is an essential part of managing any organization or project. It involves tracking and evaluating the progress of activities and tasks to ensure that they are being carried out effectively and efficiently. This process helps in identifying any deviations or discrepancies from the desired goals or standards and taking corrective actions to address them.
Monitoring Performance:
Monitoring performance involves regularly assessing and reviewing the activities and tasks being performed. It includes gathering relevant data and information, analyzing it, and comparing it with the predetermined goals or standards. This step helps in identifying any gaps or variations that may exist and require attention.
Setting Goals:
Setting goals is an important step in the performance monitoring process. Goals provide a clear direction and define what needs to be achieved. They act as benchmarks against which actual performance can be measured. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to be effective in monitoring performance.
Correcting Deviations:
When significant deviations from the goals or standards are identified during the monitoring process, corrective actions need to be taken. Correcting deviations involves analyzing the root causes of the deviations and implementing appropriate measures to address them. This may involve making changes to the processes, reallocating resources, providing additional training or support, or modifying the goals or expectations.
Controlling:
The process of monitoring performance, setting goals, and correcting significant deviations is known as controlling. Controlling involves establishing standards or benchmarks, measuring actual performance against these standards, comparing the results, and taking corrective actions as necessary. It ensures that the organization or project stays on track and achieves its objectives.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, monitoring performance, setting goals, and correcting significant deviations are essential components of the controlling process. This process helps in ensuring that activities and tasks are being carried out effectively and efficiently, and any discrepancies are addressed in a timely manner. By regularly monitoring performance and taking corrective actions, organizations can improve their overall performance and achieve their desired outcomes.
Performance monitoring is an essential part of managing any organization or project. It involves tracking and evaluating the progress of activities and tasks to ensure that they are being carried out effectively and efficiently. This process helps in identifying any deviations or discrepancies from the desired goals or standards and taking corrective actions to address them.
Monitoring Performance:
Monitoring performance involves regularly assessing and reviewing the activities and tasks being performed. It includes gathering relevant data and information, analyzing it, and comparing it with the predetermined goals or standards. This step helps in identifying any gaps or variations that may exist and require attention.
Setting Goals:
Setting goals is an important step in the performance monitoring process. Goals provide a clear direction and define what needs to be achieved. They act as benchmarks against which actual performance can be measured. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to be effective in monitoring performance.
Correcting Deviations:
When significant deviations from the goals or standards are identified during the monitoring process, corrective actions need to be taken. Correcting deviations involves analyzing the root causes of the deviations and implementing appropriate measures to address them. This may involve making changes to the processes, reallocating resources, providing additional training or support, or modifying the goals or expectations.
Controlling:
The process of monitoring performance, setting goals, and correcting significant deviations is known as controlling. Controlling involves establishing standards or benchmarks, measuring actual performance against these standards, comparing the results, and taking corrective actions as necessary. It ensures that the organization or project stays on track and achieves its objectives.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, monitoring performance, setting goals, and correcting significant deviations are essential components of the controlling process. This process helps in ensuring that activities and tasks are being carried out effectively and efficiently, and any discrepancies are addressed in a timely manner. By regularly monitoring performance and taking corrective actions, organizations can improve their overall performance and achieve their desired outcomes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Organizations Facilitating Business - Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Organizations Facilitating Business - Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme)
21 videos|91 docs|24 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











