All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Industrial Engineering for Mechanical Engineering Exam
{(x,y)|x+y = 5} is a- a)not a function
- b)a composite function
- c)one-one mapping
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
{(x,y)|x+y = 5} is a
a)
not a function
b)
a composite function
c)
one-one mapping
d)
none of these

|
Freedom Institute answered |
To determine the nature of the set (x, y)| xy = 5, consider the following:
- The set represents a hyperbola, where any x has a unique corresponding y = {5/x}.
- Each pair (x, y) satisfies the relation xy = 5, implying a one-to-one correspondence between x and y.
- This mapping is both injective and bijective, as each x maps to exactly one y and vice versa
Thus, the correct answer is Option C: one-one mapping.
Which of the following is not a advantage of cellular manufacturing system?- a)Short throughput
- b)Better customer service
- c)High degree of material handling
- d)Better quality
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a advantage of cellular manufacturing system?
a)
Short throughput
b)
Better customer service
c)
High degree of material handling
d)
Better quality

|
Madhurima Banerjee answered |
Advantage of Cellular Manufacturing System:
Better customer service
- Cellular manufacturing systems allow for a more efficient and streamlined production process, resulting in shorter lead times and faster response to customer demands. This leads to improved customer service and satisfaction.
Short throughput
- With the implementation of cellular manufacturing systems, the production throughput time is significantly reduced. This is due to the elimination of time-consuming activities such as material transportation and waiting times. The shorter throughput allows for faster production and delivery of products.
Better quality
- Cellular manufacturing systems promote a higher level of quality control. By grouping similar processes together, it becomes easier to identify and address any issues or defects that may arise during production. The close proximity of workers also facilitates quick communication and immediate problem-solving, leading to better quality products.
Not an advantage: High degree of material handling
- The option 'C' states that a high degree of material handling is not an advantage of cellular manufacturing systems. However, this is incorrect. Cellular manufacturing systems actually aim to minimize material handling as much as possible. The layout of the cells is designed to reduce the distance and time required for material transportation, which reduces the chances of errors, damages, and delays.
In a cellular manufacturing system, workers within a cell are responsible for handling the materials required for their specific processes. This eliminates the need for excessive movement of materials between different departments or workstations, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall efficiency. By minimizing material handling, cellular manufacturing systems can achieve cost savings and improved productivity.
Overall, cellular manufacturing systems offer several advantages, including better customer service, shorter throughput, and better quality control. The incorrect option 'C' suggests a high degree of material handling, which is not an advantage of cellular manufacturing systems.
Better customer service
- Cellular manufacturing systems allow for a more efficient and streamlined production process, resulting in shorter lead times and faster response to customer demands. This leads to improved customer service and satisfaction.
Short throughput
- With the implementation of cellular manufacturing systems, the production throughput time is significantly reduced. This is due to the elimination of time-consuming activities such as material transportation and waiting times. The shorter throughput allows for faster production and delivery of products.
Better quality
- Cellular manufacturing systems promote a higher level of quality control. By grouping similar processes together, it becomes easier to identify and address any issues or defects that may arise during production. The close proximity of workers also facilitates quick communication and immediate problem-solving, leading to better quality products.
Not an advantage: High degree of material handling
- The option 'C' states that a high degree of material handling is not an advantage of cellular manufacturing systems. However, this is incorrect. Cellular manufacturing systems actually aim to minimize material handling as much as possible. The layout of the cells is designed to reduce the distance and time required for material transportation, which reduces the chances of errors, damages, and delays.
In a cellular manufacturing system, workers within a cell are responsible for handling the materials required for their specific processes. This eliminates the need for excessive movement of materials between different departments or workstations, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall efficiency. By minimizing material handling, cellular manufacturing systems can achieve cost savings and improved productivity.
Overall, cellular manufacturing systems offer several advantages, including better customer service, shorter throughput, and better quality control. The incorrect option 'C' suggests a high degree of material handling, which is not an advantage of cellular manufacturing systems.
Refer to the network shown in the figure given below
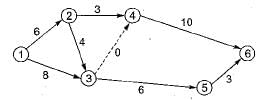
The probability of completion of the project in 24 days is- a)68.2%
- b)84.1%
- c)95.4%
- d)97.7%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer to the network shown in the figure given below

The probability of completion of the project in 24 days is

The probability of completion of the project in 24 days is
a)
68.2%
b)
84.1%
c)
95.4%
d)
97.7%

|
Sravya Tiwari answered |
The critical path is 1-2-3-4-6.
Ts - Scheduled time
= 24 days
Te - Expected time = 20 days
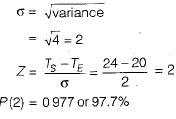
Ts - Scheduled time
= 24 days
Te - Expected time = 20 days
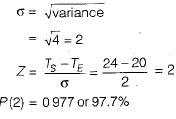
The set {2x|x is any positive rational number } is- a)an infinite set,
- b)a null set,
- c)a finite set,
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The set {2x|x is any positive rational number } is
a)
an infinite set,
b)
a null set,
c)
a finite set,
d)
none of these

|
Deepika Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
To understand the given set, we need to know the meaning of positive rational numbers. Rational numbers are the numbers which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not equal to 0.
Positive rational numbers are the numbers which are greater than 0 and can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are positive integers.
Now, the given set is {2x|x is any positive rational number}. This means that we need to take any positive rational number and multiply it by 2 to get an element of the set.
Let's take some examples to understand this set:
- If we take x = 1/2, then 2x = 1 and 1 is a positive rational number. So, 1 is an element of the set.
- If we take x = 3/4, then 2x = 3/2 and 3/2 is a positive rational number. So, 3/2 is an element of the set.
- If we take x = 2, then 2x = 4 and 4 is not a positive rational number. So, 4 is not an element of the set.
From the above examples, we can see that for any positive rational number x, 2x is also a positive rational number. This means that we can keep multiplying any positive rational number by 2 and we will get infinite positive rational numbers.
Hence, the given set {2x|x is any positive rational number} is an infinite set.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) an infinite set.
To understand the given set, we need to know the meaning of positive rational numbers. Rational numbers are the numbers which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not equal to 0.
Positive rational numbers are the numbers which are greater than 0 and can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are positive integers.
Now, the given set is {2x|x is any positive rational number}. This means that we need to take any positive rational number and multiply it by 2 to get an element of the set.
Let's take some examples to understand this set:
- If we take x = 1/2, then 2x = 1 and 1 is a positive rational number. So, 1 is an element of the set.
- If we take x = 3/4, then 2x = 3/2 and 3/2 is a positive rational number. So, 3/2 is an element of the set.
- If we take x = 2, then 2x = 4 and 4 is not a positive rational number. So, 4 is not an element of the set.
From the above examples, we can see that for any positive rational number x, 2x is also a positive rational number. This means that we can keep multiplying any positive rational number by 2 and we will get infinite positive rational numbers.
Hence, the given set {2x|x is any positive rational number} is an infinite set.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) an infinite set.
The routing function in a production system design is concerned with
- a)man power utilization
- b)optimizing material flow through the plan
- c)quality assurance of the product
- d)machine utilization
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The routing function in a production system design is concerned with
a)
man power utilization
b)
optimizing material flow through the plan
c)
quality assurance of the product
d)
machine utilization
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Routing: It is the path followed by products for being processed at various machine tools and departments. The sequence of operations required for least back-tracking is maintained. So, routing is determination of most economical path to be followed by raw-materials.
In the network diagram shown below:
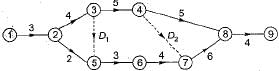
The critical path is along- a)1-2-3-4-8-9
- b)1-2-3-5-6-7-8-9
- c)1-2-3-4-7-8-9
- d)1-2-5-6-7-8-9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the network diagram shown below:

The critical path is along

The critical path is along
a)
1-2-3-4-8-9
b)
1-2-3-5-6-7-8-9
c)
1-2-3-4-7-8-9
d)
1-2-5-6-7-8-9

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
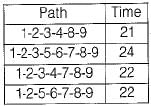
The critical path is along 1 -2-3-5-6-7-8-9 as it has maximum duration.
If E = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, the subset of E satisfying 5 + x > 10 is- a){5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
- b){6, 7, 8, 9},
- c){7, 8, 9},
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If E = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, the subset of E satisfying 5 + x > 10 is
a)
{5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
b)
{6, 7, 8, 9},
c)
{7, 8, 9},
d)
none of these

|
Moumita Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
To satisfy the condition 5 x 10, we need to find the subset of E such that at least one element in the subset is a multiple of 5 and at least one element in the subset is a multiple of 10.
Method:
We can break down the problem into two parts:
1. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 5.
2. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 10.
Solution:
1. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 5:
- The multiples of 5 in E are 5 and 10.
- Therefore, any subset of E that contains 5 or 10 satisfies the condition.
- The subsets of E that contain 5 or 10 are {5}, {10}, {5, 10}, {1, 5, 7}, {2, 5, 8}, {3, 5, 6, 9}, {4, 5, 6, 8, 9} and {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}.
2. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 10:
- The only multiple of 10 in E is 10.
- Therefore, any subset of E that contains 10 satisfies the condition.
- The subsets of E that contain 10 are {10}, {1, 10}, {2, 10}, {3, 10}, {4, 10}, {5, 10}, {6, 10}, {7, 10}, {8, 10}, {9, 10}, {1, 2, 10}, {1, 3, 10}, {1, 4, 10}, {1, 5, 10}, {1, 6, 10}, {1, 7, 10}, {1, 8, 10}, {1, 9, 10}, {2, 3, 10}, {2, 4, 10}, {2, 5, 10}, {2, 6, 10}, {2, 7, 10}, {2, 8, 10}, {2, 9, 10}, {3, 4, 10}, {3, 5, 10}, {3, 6, 10}, {3, 7, 10}, {3, 8, 10}, {3, 9, 10}, {4, 5, 10}, {4, 6, 10}, {4, 7, 10}, {4, 8, 10}, {4, 9, 10}, {5, 6, 10}, {5, 7, 10}, {5, 8, 10}, {5, 9, 10}, {6, 7, 10}, {6, 8, 10}, {6, 9, 10}, {7, 8, 10}, {7, 9, 10} and {8, 9, 10}.
Final Subset:
To satisfy the condition 5 x 10, we need to find the subset of E such that at least one element in the subset is a multiple of 5 and at least one element in the subset is a multiple of 10.
Method:
We can break down the problem into two parts:
1. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 5.
2. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 10.
Solution:
1. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 5:
- The multiples of 5 in E are 5 and 10.
- Therefore, any subset of E that contains 5 or 10 satisfies the condition.
- The subsets of E that contain 5 or 10 are {5}, {10}, {5, 10}, {1, 5, 7}, {2, 5, 8}, {3, 5, 6, 9}, {4, 5, 6, 8, 9} and {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}.
2. Find the subset of E that contains a multiple of 10:
- The only multiple of 10 in E is 10.
- Therefore, any subset of E that contains 10 satisfies the condition.
- The subsets of E that contain 10 are {10}, {1, 10}, {2, 10}, {3, 10}, {4, 10}, {5, 10}, {6, 10}, {7, 10}, {8, 10}, {9, 10}, {1, 2, 10}, {1, 3, 10}, {1, 4, 10}, {1, 5, 10}, {1, 6, 10}, {1, 7, 10}, {1, 8, 10}, {1, 9, 10}, {2, 3, 10}, {2, 4, 10}, {2, 5, 10}, {2, 6, 10}, {2, 7, 10}, {2, 8, 10}, {2, 9, 10}, {3, 4, 10}, {3, 5, 10}, {3, 6, 10}, {3, 7, 10}, {3, 8, 10}, {3, 9, 10}, {4, 5, 10}, {4, 6, 10}, {4, 7, 10}, {4, 8, 10}, {4, 9, 10}, {5, 6, 10}, {5, 7, 10}, {5, 8, 10}, {5, 9, 10}, {6, 7, 10}, {6, 8, 10}, {6, 9, 10}, {7, 8, 10}, {7, 9, 10} and {8, 9, 10}.
Final Subset:
The domain of {(1,7), (2,6)} is
- a)(1, 6)
- b)(7, 6)
- c)(1, 2)
- d){6, 7}
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The domain of {(1,7), (2,6)} is
a)
(1, 6)
b)
(7, 6)
c)
(1, 2)
d)
{6, 7}

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Explanation:
Domain of a Relation:
- The domain of a relation is the set of all possible input values (first elements in the ordered pairs) in the relation.
- In this case, the ordered pairs are (1,7) and (2,6).
- The possible input values are 1 and 2.
Determining the Domain:
- The domain of the relation {(1,7), (2,6)} is the set of all possible input values, which are 1 and 2.
- Therefore, the domain of the relation is {1, 2}.
Conclusion:
- The correct answer is option C: (1, 2), as it represents the set of possible input values for the given relation.
Domain of a Relation:
- The domain of a relation is the set of all possible input values (first elements in the ordered pairs) in the relation.
- In this case, the ordered pairs are (1,7) and (2,6).
- The possible input values are 1 and 2.
Determining the Domain:
- The domain of the relation {(1,7), (2,6)} is the set of all possible input values, which are 1 and 2.
- Therefore, the domain of the relation is {1, 2}.
Conclusion:
- The correct answer is option C: (1, 2), as it represents the set of possible input values for the given relation.
Consider the following functions of inventory:
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.Which of the above functions are valid?- a)1,2 and 3
- b)1,3 and 4
- c)2, 3 and 4
- d)1,2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following functions of inventory:
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.
1. to decouple or separate parts of the production process.
2. to provide a stock of goods that will provide a selection for customers.
3. to take advantage of quantity discounts.
4. to hedge against inflation.
Which of the above functions are valid?
a)
1,2 and 3
b)
1,3 and 4
c)
2, 3 and 4
d)
1,2, 3 and 4

|
Kstxbrvr 100 answered |
Inventory is stored because to fulfill customers demand on time not decouple production system
In PERT, the distribution of activity times is assumed to be- a)normal
- b)gamma
- c)beta
- d)exponential
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In PERT, the distribution of activity times is assumed to be
a)
normal
b)
gamma
c)
beta
d)
exponential
|
|
Sparsh Chakraborty answered |
Pertaining to the Distribution of Activity Times in PERT Analysis
Introduction:
In Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), the distribution of activity times plays a crucial role in estimating the project duration, identifying critical activities, and managing project risks. PERT is a probabilistic technique used in project management to analyze and represent the uncertainty associated with project schedules.
Understanding the Distribution of Activity Times:
The distribution of activity times represents the probability of completion time for each activity in a project. It helps in determining the project's overall duration and the likelihood of meeting deadlines. Different probability distributions can be used to model activity times in PERT, but the most commonly assumed distribution is the Beta distribution.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Beta distribution. The Beta distribution is used in PERT because it allows for modeling activity times that are bounded by best-case and worst-case estimates, as well as incorporating uncertainties associated with each estimate.
Reasons for Choosing the Beta Distribution:
The Beta distribution is preferred in PERT for the following reasons:
1. Bounded Estimates: The Beta distribution can handle activity time estimates that have known minimum and maximum values. This is important in project management as activities have upper and lower limits.
2. Flexibility: The Beta distribution offers flexibility in representing various shapes of probability distributions. It allows for skewed or symmetrical distributions, depending on the project's nature.
3. Combining Multiple Estimates: PERT often involves combining multiple estimates from different experts or sources. The Beta distribution allows for combining these estimates using weighted averages, which helps in incorporating different perspectives and reducing biases.
4. Easy Interpretation: The Beta distribution's parameters (alpha and beta) have intuitive interpretations. The alpha parameter represents the optimistic estimate, while the beta parameter represents the pessimistic estimate. The mean and standard deviation of the Beta distribution can be easily calculated and used for project planning and risk analysis.
5. Empirical Evidence: The Beta distribution has been found to be a good approximation for many real-world project activities. It has been widely used in practice and has shown satisfactory results in estimating project durations.
Conclusion:
In PERT analysis, the distribution of activity times is assumed to follow a Beta distribution. This distribution allows for modeling bounded estimates, combining multiple estimates, and providing flexibility in representing different shapes of probability distributions. It is an essential component in estimating project durations, identifying critical activities, and managing project risks.
Introduction:
In Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), the distribution of activity times plays a crucial role in estimating the project duration, identifying critical activities, and managing project risks. PERT is a probabilistic technique used in project management to analyze and represent the uncertainty associated with project schedules.
Understanding the Distribution of Activity Times:
The distribution of activity times represents the probability of completion time for each activity in a project. It helps in determining the project's overall duration and the likelihood of meeting deadlines. Different probability distributions can be used to model activity times in PERT, but the most commonly assumed distribution is the Beta distribution.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
The correct answer is option 'C' - Beta distribution. The Beta distribution is used in PERT because it allows for modeling activity times that are bounded by best-case and worst-case estimates, as well as incorporating uncertainties associated with each estimate.
Reasons for Choosing the Beta Distribution:
The Beta distribution is preferred in PERT for the following reasons:
1. Bounded Estimates: The Beta distribution can handle activity time estimates that have known minimum and maximum values. This is important in project management as activities have upper and lower limits.
2. Flexibility: The Beta distribution offers flexibility in representing various shapes of probability distributions. It allows for skewed or symmetrical distributions, depending on the project's nature.
3. Combining Multiple Estimates: PERT often involves combining multiple estimates from different experts or sources. The Beta distribution allows for combining these estimates using weighted averages, which helps in incorporating different perspectives and reducing biases.
4. Easy Interpretation: The Beta distribution's parameters (alpha and beta) have intuitive interpretations. The alpha parameter represents the optimistic estimate, while the beta parameter represents the pessimistic estimate. The mean and standard deviation of the Beta distribution can be easily calculated and used for project planning and risk analysis.
5. Empirical Evidence: The Beta distribution has been found to be a good approximation for many real-world project activities. It has been widely used in practice and has shown satisfactory results in estimating project durations.
Conclusion:
In PERT analysis, the distribution of activity times is assumed to follow a Beta distribution. This distribution allows for modeling bounded estimates, combining multiple estimates, and providing flexibility in representing different shapes of probability distributions. It is an essential component in estimating project durations, identifying critical activities, and managing project risks.
Select the odd one:- a)Concurrent engineering
- b)Simultaneous engineering
- c)Integrated product development
- d)Reliability
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the odd one:
a)
Concurrent engineering
b)
Simultaneous engineering
c)
Integrated product development
d)
Reliability
|
|
Akshara Rane answered |
Options (b) and (c) are different names of concurrent engineering.
Which of the following aspects are true pretaining to product layout?
1. efficient flow of materials
2. most suited for mass production
3. requirement for greater space ara
4. high set up cost for the special purpose machines- a)1 and 2
- b)2 and 3
- c)3 and 4
- d)1,2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following aspects are true pretaining to product layout?
1. efficient flow of materials
2. most suited for mass production
3. requirement for greater space ara
4. high set up cost for the special purpose machines
1. efficient flow of materials
2. most suited for mass production
3. requirement for greater space ara
4. high set up cost for the special purpose machines
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 and 3
c)
3 and 4
d)
1,2 and 4
|
|
Sanskriti Chakraborty answered |
The salient features of product layout are:
(i) requires less, floor area for placing the machines.
(ii) less overall manufacturing time for the product.
(iii) there is better utilization of machines and labour.
(iv) requires specilized and strict supervision.
(v) automation in material, handling is cost effective.
(vi) flow of material is smooth and continuous.
(vii) less through put time.
(i) requires less, floor area for placing the machines.
(ii) less overall manufacturing time for the product.
(iii) there is better utilization of machines and labour.
(iv) requires specilized and strict supervision.
(v) automation in material, handling is cost effective.
(vi) flow of material is smooth and continuous.
(vii) less through put time.
In applying Vogel’s approximation method to a profit maximation problem, row and column penalties are determined by- a)finding the largest unit cost in each row or column.
- b)finding the sum of the unit costs in each row or column.
- c)finding the difference between the two lowest unit costs in each row and column.
- d)finding the difference between the two highest unit costs in each row and column.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In applying Vogel’s approximation method to a profit maximation problem, row and column penalties are determined by
a)
finding the largest unit cost in each row or column.
b)
finding the sum of the unit costs in each row or column.
c)
finding the difference between the two lowest unit costs in each row and column.
d)
finding the difference between the two highest unit costs in each row and column.
|
|
Devansh Nambiar answered |
The concept of Vogel’s Approximation Method can be well understood through an illustration given below :
The difference between two least cost cells are calculated for each row and column, which can be seen in the iteration given for each row and column.
The area under β-distribution curve is divided into two equal halves by a vertical oridnate through
- a)optimistic time
- b)pessimistic time
- c)expected time
- d)most likely time
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The area under β-distribution curve is divided into two equal halves by a vertical oridnate through
a)
optimistic time
b)
pessimistic time
c)
expected time
d)
most likely time
|
|
Arshiya Dey answered |
The curve of a function represents the total amount of space between the curve and the x-axis in a given interval. It can be thought of as the accumulation of all the "slices" of space under the curve within that interval.
The area under the curve can be calculated using various methods such as integration or numerical approximation techniques like the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule. Integration is the most common method used to find the exact value of the area under a curve.
The area under the curve can have different interpretations depending on the context. For example, in a graph representing a velocity-time relationship, the area under the curve would represent the displacement or distance traveled.
The area under the curve can also have significance in probability and statistics. For a probability density function, the area under the curve represents the probability of an event occurring within a certain range.
In summary, the area under the curve is a fundamental concept in calculus that represents the accumulation of space between a curve and the x-axis in a given interval. It can be calculated using integration or numerical approximation methods and can have different interpretations depending on the context.
The area under the curve can be calculated using various methods such as integration or numerical approximation techniques like the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule. Integration is the most common method used to find the exact value of the area under a curve.
The area under the curve can have different interpretations depending on the context. For example, in a graph representing a velocity-time relationship, the area under the curve would represent the displacement or distance traveled.
The area under the curve can also have significance in probability and statistics. For a probability density function, the area under the curve represents the probability of an event occurring within a certain range.
In summary, the area under the curve is a fundamental concept in calculus that represents the accumulation of space between a curve and the x-axis in a given interval. It can be calculated using integration or numerical approximation methods and can have different interpretations depending on the context.
In a M/M/1 queue, the service rate is- a)Poisson
- b)Exponential
- c)Linear
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a M/M/1 queue, the service rate is
a)
Poisson
b)
Exponential
c)
Linear
d)
None of the above

|
Mehul Choudhury answered |
Explanation:
In a M/M/1 queue, the service rate is Poisson. Let's understand this in detail.
M/M/1 Queue:
The notation M/M/1 represents a queueing system with exponential interarrival times, exponential service times, and a single server. This type of queueing system is commonly used to model situations where customers arrive randomly and are served one at a time in a first-come, first-served manner.
Interarrival Times:
In an M/M/1 queue, the interarrival times between customer arrivals are assumed to follow an exponential distribution. This means that the time between successive customer arrivals is random and has a memoryless property. The exponential distribution is often used to model arrival processes because it has this memoryless property and is mathematically tractable.
Service Times:
Similarly, in an M/M/1 queue, the service times for each customer are assumed to follow an exponential distribution. This means that the time taken to serve a customer is random and has a memoryless property. The exponential distribution is often used to model service times because it has this memoryless property and is mathematically tractable.
Memoryless Property:
The memoryless property of the exponential distribution means that the future behavior of the system does not depend on its past behavior. In the context of a queueing system, this means that the time until the next customer arrival or the time until the current customer completes service does not depend on how long the system has been idle or how long the current customer has been in service.
Poisson Process:
The assumption of exponential interarrival times and exponential service times leads to the arrival process and service process being modeled as Poisson processes. A Poisson process is a stochastic process that counts the number of events (in this case, customer arrivals and service completions) that occur within a given time interval. The arrival rate of the Poisson process is equal to the average number of customer arrivals per unit time, and the service rate is equal to the average number of service completions per unit time.
Conclusion:
Since the service rate in an M/M/1 queue is modeled as a Poisson process, the correct answer is option 'A' - Poisson.
In a M/M/1 queue, the service rate is Poisson. Let's understand this in detail.
M/M/1 Queue:
The notation M/M/1 represents a queueing system with exponential interarrival times, exponential service times, and a single server. This type of queueing system is commonly used to model situations where customers arrive randomly and are served one at a time in a first-come, first-served manner.
Interarrival Times:
In an M/M/1 queue, the interarrival times between customer arrivals are assumed to follow an exponential distribution. This means that the time between successive customer arrivals is random and has a memoryless property. The exponential distribution is often used to model arrival processes because it has this memoryless property and is mathematically tractable.
Service Times:
Similarly, in an M/M/1 queue, the service times for each customer are assumed to follow an exponential distribution. This means that the time taken to serve a customer is random and has a memoryless property. The exponential distribution is often used to model service times because it has this memoryless property and is mathematically tractable.
Memoryless Property:
The memoryless property of the exponential distribution means that the future behavior of the system does not depend on its past behavior. In the context of a queueing system, this means that the time until the next customer arrival or the time until the current customer completes service does not depend on how long the system has been idle or how long the current customer has been in service.
Poisson Process:
The assumption of exponential interarrival times and exponential service times leads to the arrival process and service process being modeled as Poisson processes. A Poisson process is a stochastic process that counts the number of events (in this case, customer arrivals and service completions) that occur within a given time interval. The arrival rate of the Poisson process is equal to the average number of customer arrivals per unit time, and the service rate is equal to the average number of service completions per unit time.
Conclusion:
Since the service rate in an M/M/1 queue is modeled as a Poisson process, the correct answer is option 'A' - Poisson.
Hybrid layout is a combination of- a)process and fixed-position layout
- b)process and product layout
- c)product and fixed-position layout
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hybrid layout is a combination of
a)
process and fixed-position layout
b)
process and product layout
c)
product and fixed-position layout
d)
none of the above
|
|
Nandita Chakraborty answered |
Hybrid Layout in Manufacturing
Hybrid layout in manufacturing refers to a combination of two or more types of layouts to maximize efficiency and productivity. The different types of layouts include process layout, product layout, and fixed-position layout.
The Correct Answer
The correct answer to the given question is option B, which is process and product layout. This type of hybrid layout is commonly used in manufacturing facilities where the production process involves a variety of products that require different processes to manufacture.
Explanation
The process layout arranges similar equipment and functions together in one department, while the product layout organizes the production line based on the sequence of tasks required for a specific product. A hybrid layout that combines these two layouts allows manufacturers to produce different products while maintaining an efficient and optimized production flow.
Advantages of Hybrid Layout
- Flexibility: Hybrid layout provides flexibility in production as it can accommodate different product designs and production processes.
- Efficiency: Hybrid layout is more efficient than a single layout as it maximizes the use of equipment and resources, reduces material handling, and minimizes the production time.
- Better quality: Hybrid layout ensures better quality as it allows manufacturers to specialize in specific processes, resulting in higher quality products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hybrid layout in manufacturing refers to a combination of different types of layouts to maximize efficiency and productivity. The process and product layout hybrid is commonly used in facilities that produce different products that require different processes. This type of hybrid layout provides flexibility, efficiency, and better quality in production.
Hybrid layout in manufacturing refers to a combination of two or more types of layouts to maximize efficiency and productivity. The different types of layouts include process layout, product layout, and fixed-position layout.
The Correct Answer
The correct answer to the given question is option B, which is process and product layout. This type of hybrid layout is commonly used in manufacturing facilities where the production process involves a variety of products that require different processes to manufacture.
Explanation
The process layout arranges similar equipment and functions together in one department, while the product layout organizes the production line based on the sequence of tasks required for a specific product. A hybrid layout that combines these two layouts allows manufacturers to produce different products while maintaining an efficient and optimized production flow.
Advantages of Hybrid Layout
- Flexibility: Hybrid layout provides flexibility in production as it can accommodate different product designs and production processes.
- Efficiency: Hybrid layout is more efficient than a single layout as it maximizes the use of equipment and resources, reduces material handling, and minimizes the production time.
- Better quality: Hybrid layout ensures better quality as it allows manufacturers to specialize in specific processes, resulting in higher quality products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hybrid layout in manufacturing refers to a combination of different types of layouts to maximize efficiency and productivity. The process and product layout hybrid is commonly used in facilities that produce different products that require different processes. This type of hybrid layout provides flexibility, efficiency, and better quality in production.
Which one of the following methods can be used for forecasting the sales potential of a new product?- a)Time series analysis
- b)Jury of Executive Opinion method
- c)Sales Force Composite method
- d)Direct Survey method
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following methods can be used for forecasting the sales potential of a new product?
a)
Time series analysis
b)
Jury of Executive Opinion method
c)
Sales Force Composite method
d)
Direct Survey method

|
Divya Kulkarni answered |
Introduction:
Forecasting the sales potential of a new product is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions regarding production, marketing, and profitability. Various methods can be used for this purpose, but one of the most effective methods is the Direct Survey method.
Explanation:
The Direct Survey method involves directly surveying potential customers or target market to gather data and insights about their preferences, buying behavior, and willingness to purchase the new product. This method can be carried out through different approaches, such as online surveys, face-to-face interviews, or telephone surveys.
Advantages of the Direct Survey method:
1. Accuracy: Directly surveying potential customers allows for more accurate data collection as it captures their opinions and preferences directly.
2. Real-time information: Since surveys are conducted in real-time, businesses can obtain up-to-date information on market trends and customer preferences.
3. Customization: Surveys can be tailored to specific target markets, enabling businesses to gather insights relevant to their product and target audience.
4. Quantitative and qualitative data: Direct surveys can provide both quantitative data (e.g., number of potential customers, buying intent) and qualitative data (e.g., feedback, suggestions), giving businesses a comprehensive understanding of the market.
5. Flexibility: The Direct Survey method can be adapted and modified based on the specific needs and requirements of the business, making it a versatile forecasting tool.
Comparison with other methods:
While other methods such as Time Series Analysis, Jury of Executive Opinion method, and Sales Force Composite method can also be useful in forecasting sales potential, the Direct Survey method offers distinct advantages.
- Time Series Analysis relies on historical data, which might not accurately reflect the preferences and behaviors of potential customers for a new product.
- The Jury of Executive Opinion method relies on the subjective opinions and judgments of a group of executives, which may not always be accurate or representative of the market.
- The Sales Force Composite method relies on the sales team's estimates, which may be biased or influenced by internal factors.
Conclusion:
In summary, the Direct Survey method is an effective and reliable approach for forecasting the sales potential of a new product. By directly surveying potential customers, businesses can gather accurate and real-time data, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and overall business profitability.
Forecasting the sales potential of a new product is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions regarding production, marketing, and profitability. Various methods can be used for this purpose, but one of the most effective methods is the Direct Survey method.
Explanation:
The Direct Survey method involves directly surveying potential customers or target market to gather data and insights about their preferences, buying behavior, and willingness to purchase the new product. This method can be carried out through different approaches, such as online surveys, face-to-face interviews, or telephone surveys.
Advantages of the Direct Survey method:
1. Accuracy: Directly surveying potential customers allows for more accurate data collection as it captures their opinions and preferences directly.
2. Real-time information: Since surveys are conducted in real-time, businesses can obtain up-to-date information on market trends and customer preferences.
3. Customization: Surveys can be tailored to specific target markets, enabling businesses to gather insights relevant to their product and target audience.
4. Quantitative and qualitative data: Direct surveys can provide both quantitative data (e.g., number of potential customers, buying intent) and qualitative data (e.g., feedback, suggestions), giving businesses a comprehensive understanding of the market.
5. Flexibility: The Direct Survey method can be adapted and modified based on the specific needs and requirements of the business, making it a versatile forecasting tool.
Comparison with other methods:
While other methods such as Time Series Analysis, Jury of Executive Opinion method, and Sales Force Composite method can also be useful in forecasting sales potential, the Direct Survey method offers distinct advantages.
- Time Series Analysis relies on historical data, which might not accurately reflect the preferences and behaviors of potential customers for a new product.
- The Jury of Executive Opinion method relies on the subjective opinions and judgments of a group of executives, which may not always be accurate or representative of the market.
- The Sales Force Composite method relies on the sales team's estimates, which may be biased or influenced by internal factors.
Conclusion:
In summary, the Direct Survey method is an effective and reliable approach for forecasting the sales potential of a new product. By directly surveying potential customers, businesses can gather accurate and real-time data, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and overall business profitability.
Process Xhas a fixed cost of Rs. 50,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs. 10 per unit. Process Y has a fixed cost of Rs. 20,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs. 25 unit. At which value, total costs of processes X and Y will be equal- a)1200
- b)1400
- c)1800
- d)2000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Process Xhas a fixed cost of Rs. 50,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs. 10 per unit. Process Y has a fixed cost of Rs. 20,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs. 25 unit. At which value, total costs of processes X and Y will be equal
a)
1200
b)
1400
c)
1800
d)
2000
|
|
Mehul Yadav answered |
TCX ⇒ TCY
⇒ 50,000 + 10 N = 20,000 + 25 N
∴ 15 N = 30,000
∴ N = 2,000 unit
⇒ 50,000 + 10 N = 20,000 + 25 N
∴ 15 N = 30,000
∴ N = 2,000 unit
Which of the following is needed to use the transportation model?- a)Capacity of the sources
- b)Demand of the destinations
- c)Unit shipping cost
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is needed to use the transportation model?
a)
Capacity of the sources
b)
Demand of the destinations
c)
Unit shipping cost
d)
All of these

|
Samridhi Choudhary answered |
Capacity of the sources
- The capacity of the sources refers to the maximum amount of goods or products that can be produced or supplied from each source. This is an essential factor in the transportation model as it determines the limit on how much can be transported from each source to the destinations.
Demand of the destinations
- The demand of the destinations is the amount of goods or products that need to be delivered to each destination. This information is crucial in the transportation model as it helps in determining the total demand that needs to be met and how to allocate the transportation resources efficiently.
Unit shipping cost
- The unit shipping cost is the cost associated with transporting one unit of goods or products from a source to a destination. This cost factor is important in the transportation model as it helps in calculating the total transportation cost and optimizing the transportation routes to minimize costs.
All of these
- All of the above factors are needed to use the transportation model effectively. The capacity of the sources, demand of the destinations, and unit shipping cost are all critical inputs that are required to formulate and solve the transportation problem. By considering all these factors, the transportation model can help in determining the most cost-effective and efficient way to transport goods from sources to destinations.
In ABC analysis of inventory control ‘A’ items have- a)very high cost
- b)intermediate cost
- c)low cost
- d)very low cost
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In ABC analysis of inventory control ‘A’ items have
a)
very high cost
b)
intermediate cost
c)
low cost
d)
very low cost

|
Anmol Choudhary answered |
In ABC analyses, item ‘A’ are high usage, valued item and extra care is required for these items.
Suitability of process layout not applied for- a)job-shop manufacturing
- b)frequent changes in product design
- c)low-volume, high variety manufacturing environment
- d)low variety, high-volume production system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Suitability of process layout not applied for
a)
job-shop manufacturing
b)
frequent changes in product design
c)
low-volume, high variety manufacturing environment
d)
low variety, high-volume production system

|
Anshul Chakraborty answered |
Suitability of product layout:
1. Assembly line such as automobile factory.
2. Low variety, high-volume production system
3. For standardised products, which have quite stable demand in near future.
1. Assembly line such as automobile factory.
2. Low variety, high-volume production system
3. For standardised products, which have quite stable demand in near future.
Suitability of process layout:
1. For non-standardised product.
2. For low-volume, high variety manufacturing environment.
3. For frequent changes in product design.
4. For job-shop manufacturing.
5. For very expensive machines like CNC milling, CMM etc
1. For non-standardised product.
2. For low-volume, high variety manufacturing environment.
3. For frequent changes in product design.
4. For job-shop manufacturing.
5. For very expensive machines like CNC milling, CMM etc
A constraint in equation 5x1 - 3x2 ≤ -5 is converted as, (3x2 + α1) - (5x1 + -s1) = 5
Then 's1' is called as- a)basic variable
- b)artificial variable
- c)surplus variable
- d)non-basic variable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A constraint in equation 5x1 - 3x2 ≤ -5 is converted as, (3x2 + α1) - (5x1 + -s1) = 5
Then 's1' is called as
Then 's1' is called as
a)
basic variable
b)
artificial variable
c)
surplus variable
d)
non-basic variable

|
Ashwin Kulkarni answered |
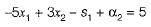
This is used to convert constraint in equation.
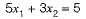
Thus s1 is the surplus variable.
In value engineering important consideration is given to- a)cost reduction
- b)profit maximization
- c)function concept
- d)customer satisfaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In value engineering important consideration is given to
a)
cost reduction
b)
profit maximization
c)
function concept
d)
customer satisfaction

|
Subhankar Khanna answered |
Value engineering is the application of the concept of value analysis at the design or premanufacturing stage of the component part with a view to cut down the unnecessary cost, without impairing the function or utility of the product.
In order for a transportation matrix which has six rows and four columns not to degenerate, what is the number of occupied cells, in the matrix?- a)6
- b)9
- c)14
- d)23
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In order for a transportation matrix which has six rows and four columns not to degenerate, what is the number of occupied cells, in the matrix?
a)
6
b)
9
c)
14
d)
23
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Number of cells for non-degenerate solution
= 6 + 4 - 1 = 9
= 6 + 4 - 1 = 9
In a queuing problem, if the arrivals are completely random, then the probability distribution of number of arrivals in a given time follows - a)Poisson distribution
- b)Normal distribution
- c)Binomial distribution
- d)Exponential distribution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a queuing problem, if the arrivals are completely random, then the probability distribution of number of arrivals in a given time follows
a)
Poisson distribution
b)
Normal distribution
c)
Binomial distribution
d)
Exponential distribution

|
Gauri Roy answered |
Correct Answer :- C
Explanation : Number of arrivals per unit time is estimated by the Poisson's distribution.
Most of the large scale modern industry using automation adopt- a)process layout
- b)product layout
- c)group layout
- d)fixed position layout
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the large scale modern industry using automation adopt
a)
process layout
b)
product layout
c)
group layout
d)
fixed position layout
|
|
Sai Reddy answered |
Process Layout in Large Scale Modern Industry Using Automation
Process layout is a type of plant layout in which similar operations are grouped together. In large scale modern industry using automation, process layout is the most commonly adopted layout. Let's discuss the reasons behind it.
1. Flexibility:
Process layout provides maximum flexibility as it is not limited to a specific product. The machines and equipment are arranged in such a way that they can be used for different types of products. This means that the production process can be easily changed or modified as per the requirement.
2. Automation:
Automation is a key factor in modern industry. With the help of automation, the production process can be automated to a great extent. In a process layout, machines and equipment are arranged in a way that they can be easily automated. This leads to higher productivity, better quality, and reduced costs.
3. Reduced Material Handling:
In a process layout, similar operations are grouped together. This means that the material movement is minimized as the raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods are all handled in the same area. This reduces the material handling cost and time.
4. Better Utilization of Equipment:
In a process layout, machines and equipment are arranged in such a way that they can be used for different types of products. This means that the equipment can be utilized to its maximum capacity. This leads to better utilization of equipment and reduces the idle time.
5. Reduced Cost:
Process layout helps to reduce the cost of production. The reduced material handling cost, better utilization of equipment, and increased productivity due to automation all contribute to reducing the overall cost of production.
Conclusion:
Thus, process layout is the most commonly adopted layout in large scale modern industry using automation. It provides maximum flexibility, automation, reduced material handling, better utilization of equipment, and reduced cost of production.
Process layout is a type of plant layout in which similar operations are grouped together. In large scale modern industry using automation, process layout is the most commonly adopted layout. Let's discuss the reasons behind it.
1. Flexibility:
Process layout provides maximum flexibility as it is not limited to a specific product. The machines and equipment are arranged in such a way that they can be used for different types of products. This means that the production process can be easily changed or modified as per the requirement.
2. Automation:
Automation is a key factor in modern industry. With the help of automation, the production process can be automated to a great extent. In a process layout, machines and equipment are arranged in a way that they can be easily automated. This leads to higher productivity, better quality, and reduced costs.
3. Reduced Material Handling:
In a process layout, similar operations are grouped together. This means that the material movement is minimized as the raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods are all handled in the same area. This reduces the material handling cost and time.
4. Better Utilization of Equipment:
In a process layout, machines and equipment are arranged in such a way that they can be used for different types of products. This means that the equipment can be utilized to its maximum capacity. This leads to better utilization of equipment and reduces the idle time.
5. Reduced Cost:
Process layout helps to reduce the cost of production. The reduced material handling cost, better utilization of equipment, and increased productivity due to automation all contribute to reducing the overall cost of production.
Conclusion:
Thus, process layout is the most commonly adopted layout in large scale modern industry using automation. It provides maximum flexibility, automation, reduced material handling, better utilization of equipment, and reduced cost of production.
Which one of the following is not a function of production control?- a)Forecasting
- b)Routing
- c)Scheduling
- d)Dispatching
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a function of production control?
a)
Forecasting
b)
Routing
c)
Scheduling
d)
Dispatching

|
Athira Pillai answered |
Introduction:
Production control is an essential function in manufacturing operations that involves planning, coordinating, and controlling various activities to ensure efficient and effective production. It encompasses several key activities such as forecasting, routing, scheduling, and dispatching. However, forecasting is not considered a direct function of production control.
Explanation:
1. Forecasting:
Forecasting is the process of estimating future demand for a product or service based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps organizations in determining the production levels, resource requirements, and inventory management. While forecasting plays a crucial role in production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Instead, it is typically performed by specialized forecasting teams or departments within an organization.
2. Routing:
Routing involves determining the most appropriate sequence of operations and the path that a product or service should follow during the production process. It includes identifying the specific machines, workstations, or departments that will be involved in each operation. Routing helps in optimizing the flow of materials, minimizing transportation costs, and ensuring smooth production operations.
3. Scheduling:
Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times for each operation in the production process. It involves allocating resources such as machines, equipment, and labor to specific tasks and activities. Scheduling helps in balancing workloads, meeting delivery deadlines, and maximizing production efficiency.
4. Dispatching:
Dispatching involves releasing work orders to the shop floor or specific workstations, assigning tasks to workers, and providing necessary instructions for carrying out the operations. It ensures that the production activities are executed as per the planned schedule and that the required resources are available.
Conclusion:
While forecasting is a crucial aspect of production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Production control primarily focuses on activities such as routing, scheduling, and dispatching, which involve the coordination and control of production operations to ensure efficient and effective production.
Production control is an essential function in manufacturing operations that involves planning, coordinating, and controlling various activities to ensure efficient and effective production. It encompasses several key activities such as forecasting, routing, scheduling, and dispatching. However, forecasting is not considered a direct function of production control.
Explanation:
1. Forecasting:
Forecasting is the process of estimating future demand for a product or service based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps organizations in determining the production levels, resource requirements, and inventory management. While forecasting plays a crucial role in production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Instead, it is typically performed by specialized forecasting teams or departments within an organization.
2. Routing:
Routing involves determining the most appropriate sequence of operations and the path that a product or service should follow during the production process. It includes identifying the specific machines, workstations, or departments that will be involved in each operation. Routing helps in optimizing the flow of materials, minimizing transportation costs, and ensuring smooth production operations.
3. Scheduling:
Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times for each operation in the production process. It involves allocating resources such as machines, equipment, and labor to specific tasks and activities. Scheduling helps in balancing workloads, meeting delivery deadlines, and maximizing production efficiency.
4. Dispatching:
Dispatching involves releasing work orders to the shop floor or specific workstations, assigning tasks to workers, and providing necessary instructions for carrying out the operations. It ensures that the production activities are executed as per the planned schedule and that the required resources are available.
Conclusion:
While forecasting is a crucial aspect of production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Production control primarily focuses on activities such as routing, scheduling, and dispatching, which involve the coordination and control of production operations to ensure efficient and effective production.
The standard time for an operation has been calculated as 20 min. The worker was rated at 80%. If the relaxation and other allowances were 25%, then the observed time would be- a)25 min
- b)20 min
- c)15.5 min
- d)16 min
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard time for an operation has been calculated as 20 min. The worker was rated at 80%. If the relaxation and other allowances were 25%, then the observed time would be
a)
25 min
b)
20 min
c)
15.5 min
d)
16 min

|
Puja Sharma answered |
Standard time = Normal time + Allowances
= (observed time x rating factor) + allowances
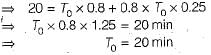
= (observed time x rating factor) + allowances
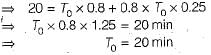
Consider a single server queuing model with Poisson arrivals (λ = 4/hour) and exponential service (μ = 4/hour). The number in the system is restricted to a maximum of 10. The probability that a person who comes in leaves without joining the queue is- a)1/11
- b)1/10
- c)1/9
- d)1/2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a single server queuing model with Poisson arrivals (λ = 4/hour) and exponential service (μ = 4/hour). The number in the system is restricted to a maximum of 10. The probability that a person who comes in leaves without joining the queue is
a)
1/11
b)
1/10
c)
1/9
d)
1/2

|
Poulomi Patel answered |

Probability that a person who comes in leaves without joining the queue i.e.
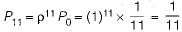
Routing in production planning and controls refers to the
- a)balancing of load on machines
- b)authorization of work to be performed
- c)progress of operations to be performed
- d)sequence of operations to be performed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Routing in production planning and controls refers to the
a)
balancing of load on machines
b)
authorization of work to be performed
c)
progress of operations to be performed
d)
sequence of operations to be performed

|
Machine Experts answered |
Routing determines what work is to be done and where and how it will be done. Taking from raw material to the finished product, routing decides the path and sequence of operations to be performed on the job from one machine to another.
There are four steps in the process of production planning and control:
There are four steps in the process of production planning and control:
- Routing: Routing can be defined as the process of deciding the path (route) of work and the sequence of operations.
- Scheduling: Scheduling function determines when an operation is to be performed, or when work is to be completed.
- Dispatching: It is the action, doing or implementation stage. It comes after routing and scheduling. Dispatching means starting the process of production. It provides the necessary authority to start the work.
- Expedition or follow-up: It is designed to keep track of the work effort. The aim is to ensure that what is intended and planned is being implemented. It maintains proper records of work, delays, and bottleneck. Such records can be used in the future to control production.
Aluminium tie pin and gold tie pin, both serve the purpose of keeping the tie in position, but the gold pin has significance due to:- a)exchange value
- b)use value
- c)esteem value
- d)cost value
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium tie pin and gold tie pin, both serve the purpose of keeping the tie in position, but the gold pin has significance due to:
a)
exchange value
b)
use value
c)
esteem value
d)
cost value
|
|
Pritam Jain answered |
Esteem Value: The properties, features or attractiveness of an object makes its ownership desirable.
Use Value: The properties or qualities which accomplish a use, work or service.
Cost Value: The sum of labour, material and other cost required to produce the object (also called as Economic value).
Exchange Value: The properties or qualities of, an object that make it possible to exchange it for something else that one wants.
Use Value: The properties or qualities which accomplish a use, work or service.
Cost Value: The sum of labour, material and other cost required to produce the object (also called as Economic value).
Exchange Value: The properties or qualities of, an object that make it possible to exchange it for something else that one wants.
Consider the following work sampling data: Working time = 60%, average rating = 90%, relaxation allowance = 12.5% actual output during the study = 1000 units and study duration = 480 minutes. The standard time per unit (in minutes) will be- a)0.2592
- b)0.2916
- c)0.3240
- d)0.4860
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following work sampling data: Working time = 60%, average rating = 90%, relaxation allowance = 12.5% actual output during the study = 1000 units and study duration = 480 minutes. The standard time per unit (in minutes) will be
a)
0.2592
b)
0.2916
c)
0.3240
d)
0.4860
|
|
Tarun Chatterjee answered |
Calculation of Standard Time per Unit
1. Working time: Working time = 60%
2. Rating factor: Average rating = 90%
3. Relaxation allowance: Relaxation allowance = 12.5%
4. Actual output: Actual output during the study = 1000 units
5. Study duration: Study duration = 480 minutes
Calculating the Standard Time per Unit:
- Standard time per unit = (Study duration * Working time * Rating factor) / (Actual output * (1 - Relaxation allowance))
- Standard time per unit = (480 * 0.60 * 0.90) / (1000 * (1 - 0.125))
- Standard time per unit = (259.2) / (1000 * 0.875)
- Standard time per unit = 259.2 / 875
- Standard time per unit = 0.2916 minutes
Therefore, the standard time per unit is 0.2916 minutes. Hence, option b) 0.2916 is the correct answer.
1. Working time: Working time = 60%
2. Rating factor: Average rating = 90%
3. Relaxation allowance: Relaxation allowance = 12.5%
4. Actual output: Actual output during the study = 1000 units
5. Study duration: Study duration = 480 minutes
Calculating the Standard Time per Unit:
- Standard time per unit = (Study duration * Working time * Rating factor) / (Actual output * (1 - Relaxation allowance))
- Standard time per unit = (480 * 0.60 * 0.90) / (1000 * (1 - 0.125))
- Standard time per unit = (259.2) / (1000 * 0.875)
- Standard time per unit = 259.2 / 875
- Standard time per unit = 0.2916 minutes
Therefore, the standard time per unit is 0.2916 minutes. Hence, option b) 0.2916 is the correct answer.
The number of customers arriving at a railway reservation counter is Poisson distributed with an arrival rate of eight customers per hour. The reservation clerk at this counter at this counter takes six minutes per customer on an average with an exponentially distributed service time. The average number of the customers in the queue will be- a)3
- b)3.2
- c)4
- d)4.2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of customers arriving at a railway reservation counter is Poisson distributed with an arrival rate of eight customers per hour. The reservation clerk at this counter at this counter takes six minutes per customer on an average with an exponentially distributed service time. The average number of the customers in the queue will be
a)
3
b)
3.2
c)
4
d)
4.2

|
Varun Mukherjee answered |
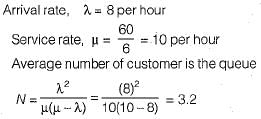
Group technology is connected with- a)process layout
- b)product layout
- c)hybrid layout
- d)fixed-position layout
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Group technology is connected with
a)
process layout
b)
product layout
c)
hybrid layout
d)
fixed-position layout
|
|
Amrita Chauhan answered |
Cellular or Group layout: Cellular layout is based on the group technology in which large variety of products are needed in small volumes (or batches). The cellular layout or GT is thus a combination of process and product layout. Therefore, it possesses the features of both
The layout of ship-building industry should be- a)process layout
- b)group layout
- c)fixed location layout
- d)product layout
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The layout of ship-building industry should be
a)
process layout
b)
group layout
c)
fixed location layout
d)
product layout

|
Ranjeet Kumar answered |
A big ship/ aircraft cannot be moved. Hence machines and worker required to move for doing their job. Hence fixed position layout.
In manufacturing management, the term dispatching is used to describe- a)dispatch of sales order
- b)dispatch of faculty mail
- c)dispatch of finished product to the user
- d)dispatch of work orders through shop floor
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In manufacturing management, the term dispatching is used to describe
a)
dispatch of sales order
b)
dispatch of faculty mail
c)
dispatch of finished product to the user
d)
dispatch of work orders through shop floor

|
Samarth Ghoshal answered |
Dispatching: It is execution of planning. It is concerned with starting the work (or process), it therefore ensure that the plans are properly implemented. It is the physical handling over of a manufacturing order to the operating faciiity. it can be defined as release of orders and instructions for the starting of production for any item in accordance with the route sheet and schedule charts.
Shadow price in linear programming refers to the- a)lowest sales price
- b)maximum cost per item
- c)value assigned to one unit
- d)cost of bought-out items
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Shadow price in linear programming refers to the
a)
lowest sales price
b)
maximum cost per item
c)
value assigned to one unit
d)
cost of bought-out items
|
|
Niharika Iyer answered |
Shadow price in Linear Programming
Shadow price in linear programming refers to the value assigned to one unit of a particular resource or constraint. It is the change in the objective function value per unit increase in the availability of a resource or constraint.
Significance of Shadow Price
The shadow price provides valuable information about the problem and helps in decision-making. It indicates the opportunity cost of using a resource or constraint. It helps in determining the economic feasibility of the problem and identifying the critical resources.
Calculation of Shadow Price
The shadow price can be calculated using the dual simplex method or sensitivity analysis. In the dual simplex method, the shadow price is the negative of the reduced cost of the corresponding dual variable. In sensitivity analysis, the shadow price is the change in the objective function value due to a unit increase in the availability of a resource or constraint.
Interpretation of Shadow Price
A positive shadow price indicates that an increase in the availability of a resource or constraint will increase the objective function value. A negative shadow price indicates that a decrease in the availability of a resource or constraint will increase the objective function value. A zero shadow price indicates that the resource or constraint is not binding.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the shadow price in linear programming refers to the value assigned to one unit of a particular resource or constraint. It provides valuable information about the problem and helps in decision-making. The shadow price can be calculated using the dual simplex method or sensitivity analysis.
Shadow price in linear programming refers to the value assigned to one unit of a particular resource or constraint. It is the change in the objective function value per unit increase in the availability of a resource or constraint.
Significance of Shadow Price
The shadow price provides valuable information about the problem and helps in decision-making. It indicates the opportunity cost of using a resource or constraint. It helps in determining the economic feasibility of the problem and identifying the critical resources.
Calculation of Shadow Price
The shadow price can be calculated using the dual simplex method or sensitivity analysis. In the dual simplex method, the shadow price is the negative of the reduced cost of the corresponding dual variable. In sensitivity analysis, the shadow price is the change in the objective function value due to a unit increase in the availability of a resource or constraint.
Interpretation of Shadow Price
A positive shadow price indicates that an increase in the availability of a resource or constraint will increase the objective function value. A negative shadow price indicates that a decrease in the availability of a resource or constraint will increase the objective function value. A zero shadow price indicates that the resource or constraint is not binding.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the shadow price in linear programming refers to the value assigned to one unit of a particular resource or constraint. It provides valuable information about the problem and helps in decision-making. The shadow price can be calculated using the dual simplex method or sensitivity analysis.
The arrival rate and the service time are usually assumed to respectively follow the- a)normal distribution and exponential law
- b)poisson’s distribution and exponential law
- c)exponential law and Erlang distribution law
- d)binomial distribution and normal distribution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The arrival rate and the service time are usually assumed to respectively follow the
a)
normal distribution and exponential law
b)
poisson’s distribution and exponential law
c)
exponential law and Erlang distribution law
d)
binomial distribution and normal distribution
|
|
Suyash Patel answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : The arrival rate and the service time are usually assumed to respectively follow the binomial distribution and normal distribution.
Which of the following is not a performance related objective for a good facility plant layout?- a)Better product quality
- b)Easy plant maintenance
- c)Minimum worker movement
- d)Minimum setup cost
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a performance related objective for a good facility plant layout?
a)
Better product quality
b)
Easy plant maintenance
c)
Minimum worker movement
d)
Minimum setup cost

|
Megha Choudhury answered |
Minimum worker movement is the objective related to material movement.
Which of the following is last step of product development process?- a)Generation of ideas
- b)Product testing
- c)Product support
- d)Advanced design
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is last step of product development process?
a)
Generation of ideas
b)
Product testing
c)
Product support
d)
Advanced design

|
Rithika Reddy answered |
The process of product development involves few systematic steps. These are as follows:
1. Identification of the needs of customers
2. Generation of ideas to fulfill needs
3. Evaluation for fitness of ideas
4. Selection of feasible idea
5. Advanced product planning
6. Advanced design
7: Prototype
8. Product evaluation and improvement
9. Product support
1. Identification of the needs of customers
2. Generation of ideas to fulfill needs
3. Evaluation for fitness of ideas
4. Selection of feasible idea
5. Advanced product planning
6. Advanced design
7: Prototype
8. Product evaluation and improvement
9. Product support
The matrix in assignment model is- a)square maxtrix
- b)rectangular matrix
- c)diagonal matrix
- d)unit matrix
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The matrix in assignment model is
a)
square maxtrix
b)
rectangular matrix
c)
diagonal matrix
d)
unit matrix

|
Athira Pillai answered |
Assignment model can be solved by conventional linear programming approach or transportation model approach, it is square matrix, having equal number of rows and columns. The objective is to assign one item from row to one item from column so that total cost of assignement is minimum.
Consider the following statements:
1. - TMU stands for time movement unit.
2. 1 TMU = 0.001 minute.
3. The times for basic motions in Basic motion time study are given in one thousand of minute.Which of these statements are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)1 and 3
- c)1,2 and 3
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. - TMU stands for time movement unit.
2. 1 TMU = 0.001 minute.
3. The times for basic motions in Basic motion time study are given in one thousand of minute.
1. - TMU stands for time movement unit.
2. 1 TMU = 0.001 minute.
3. The times for basic motions in Basic motion time study are given in one thousand of minute.
Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 3
c)
1,2 and 3
d)
none of these
|
|
Avantika Sen answered |
(i) TMU stands for time measurement unit.
(ii) 1 TMU = 0.00001 hour or 0.0006 minute.
(iii) The times for basic motions in Basic motion study are given in the thousands of minute.
(ii) 1 TMU = 0.00001 hour or 0.0006 minute.
(iii) The times for basic motions in Basic motion study are given in the thousands of minute.
Which of the following layout technique not uses any standard symbols for specifying the activities?- a)Operation process layout
- b)String diagram
- c)Flow process chart
- d)Flow diagram
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following layout technique not uses any standard symbols for specifying the activities?
a)
Operation process layout
b)
String diagram
c)
Flow process chart
d)
Flow diagram
|
|
Vaibhav Khanna answered |
Operation process layout - uses operation and inspection symbol
Flow process layout - Uses all symbols
Flow diagram - Uses all symbols
String diagram - No symbols are used. It uses a drawing board to represent machines or work station. Strings are used in place of lines. For multiple products, strings of different colours are used.
Flow process layout - Uses all symbols
Flow diagram - Uses all symbols
String diagram - No symbols are used. It uses a drawing board to represent machines or work station. Strings are used in place of lines. For multiple products, strings of different colours are used.
The steps followed for the development of linear programming model are
1. state of problem in the form of a linear programming model
2. determine the decision variables
3. write the objective function
4. develop inequations (or equations) for the constraints.
The correct order is- a)1, 2, 3, 4
- b)2, 1,3, 4
- c)4, 1 2, 3
- d)4, 3 ,2 , 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The steps followed for the development of linear programming model are
1. state of problem in the form of a linear programming model
2. determine the decision variables
3. write the objective function
4. develop inequations (or equations) for the constraints.
The correct order is
1. state of problem in the form of a linear programming model
2. determine the decision variables
3. write the objective function
4. develop inequations (or equations) for the constraints.
The correct order is
a)
1, 2, 3, 4
b)
2, 1,3, 4
c)
4, 1 2, 3
d)
4, 3 ,2 , 1
|
|
Aniket Saini answered |
Linear Programming Model Development Process
The correct order of steps followed for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3. Let's discuss each step in detail:
Step 4: Develop Inequations (or Equations) for the Constraints
- This step involves formulating the constraints that restrict the feasible region of the problem.
- Constraints are the limitations or restrictions that must be adhered to in order to find the optimal solution.
- Constraints can be represented as inequalities (inequations) or equalities (equations).
- These constraints can include limitations on resources, capacity, demand, time, etc.
Step 1: State the Problem in the Form of a Linear Programming Model
- In this step, the problem is transformed into a mathematical model based on linear relationships.
- The decision variables, objective function, and constraints are defined.
- The problem is analyzed to identify the goal or objective that needs to be maximized or minimized.
Step 2: Determine the Decision Variables
- Decision variables are the unknown quantities that need to be optimized in the problem.
- They represent the choices or decisions that the decision-maker can make.
- Decision variables are usually denoted by symbols and can be continuous or discrete.
Step 3: Write the Objective Function
- The objective function represents the goal or objective that needs to be optimized.
- It is a mathematical representation of the quantity that needs to be maximized or minimized.
- The objective function is typically a linear equation, although it can also be nonlinear in some cases.
Correct Order: 4, 1, 2, 3
- The correct order of steps for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3.
- First, we need to formulate the constraints (inequations or equations) that define the limitations of the problem.
- Then, we state the problem in the form of a linear programming model by defining the objective function and decision variables.
- Finally, we determine the decision variables and write the objective function based on the problem requirements.
Summary:
The correct order for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3. Constraints are formulated first, followed by stating the problem in the form of a linear programming model, determining the decision variables, and writing the objective function. This sequential process allows for the systematic formulation and optimization of the problem.
The correct order of steps followed for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3. Let's discuss each step in detail:
Step 4: Develop Inequations (or Equations) for the Constraints
- This step involves formulating the constraints that restrict the feasible region of the problem.
- Constraints are the limitations or restrictions that must be adhered to in order to find the optimal solution.
- Constraints can be represented as inequalities (inequations) or equalities (equations).
- These constraints can include limitations on resources, capacity, demand, time, etc.
Step 1: State the Problem in the Form of a Linear Programming Model
- In this step, the problem is transformed into a mathematical model based on linear relationships.
- The decision variables, objective function, and constraints are defined.
- The problem is analyzed to identify the goal or objective that needs to be maximized or minimized.
Step 2: Determine the Decision Variables
- Decision variables are the unknown quantities that need to be optimized in the problem.
- They represent the choices or decisions that the decision-maker can make.
- Decision variables are usually denoted by symbols and can be continuous or discrete.
Step 3: Write the Objective Function
- The objective function represents the goal or objective that needs to be optimized.
- It is a mathematical representation of the quantity that needs to be maximized or minimized.
- The objective function is typically a linear equation, although it can also be nonlinear in some cases.
Correct Order: 4, 1, 2, 3
- The correct order of steps for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3.
- First, we need to formulate the constraints (inequations or equations) that define the limitations of the problem.
- Then, we state the problem in the form of a linear programming model by defining the objective function and decision variables.
- Finally, we determine the decision variables and write the objective function based on the problem requirements.
Summary:
The correct order for the development of a linear programming model is 4, 1, 2, 3. Constraints are formulated first, followed by stating the problem in the form of a linear programming model, determining the decision variables, and writing the objective function. This sequential process allows for the systematic formulation and optimization of the problem.
ABC analysis divides on-hand inventory into three classes, generally based on- a)item quality
- b)unit price
- c)annual rupee volume
- d)the number of units on hand
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ABC analysis divides on-hand inventory into three classes, generally based on
a)
item quality
b)
unit price
c)
annual rupee volume
d)
the number of units on hand

|
Sravya Tiwari answered |
ABC analysis is a technique used in inventory management to categorize items based on their annual rupee volume. The three classes are:
1. Class A: These are high-value items that account for a significant portion of the annual rupee volume, typically around 80%. These items are critical to the business and require careful management to ensure that they are always available.
2. Class B: These are medium-value items that account for around 15% of the annual rupee volume. They are important but not critical to the business, and require less management than Class A items.
3. Class C: These are low-value items that account for the remaining 5% of the annual rupee volume. They are typically low-cost items that are readily available and require minimal management.
The purpose of ABC analysis is to help businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts. By focusing on the most important items, businesses can ensure that they always have the inventory they need to meet customer demand, while minimizing the cost of carrying excess inventory.
In practice, ABC analysis involves calculating the annual rupee volume for each item in inventory and then ranking them from highest to lowest. The items are then divided into the three classes based on their cumulative percentage of the annual rupee volume.
Overall, ABC analysis is a valuable tool for inventory management that can help businesses optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs.
1. Class A: These are high-value items that account for a significant portion of the annual rupee volume, typically around 80%. These items are critical to the business and require careful management to ensure that they are always available.
2. Class B: These are medium-value items that account for around 15% of the annual rupee volume. They are important but not critical to the business, and require less management than Class A items.
3. Class C: These are low-value items that account for the remaining 5% of the annual rupee volume. They are typically low-cost items that are readily available and require minimal management.
The purpose of ABC analysis is to help businesses prioritize their inventory management efforts. By focusing on the most important items, businesses can ensure that they always have the inventory they need to meet customer demand, while minimizing the cost of carrying excess inventory.
In practice, ABC analysis involves calculating the annual rupee volume for each item in inventory and then ranking them from highest to lowest. The items are then divided into the three classes based on their cumulative percentage of the annual rupee volume.
Overall, ABC analysis is a valuable tool for inventory management that can help businesses optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs.
Cellular manufacturing is suitable for- a)a single product in large volumes
- b)one-off production of several varieties
- c)products with similar features made in batches
- d)large variety of products in large volumes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellular manufacturing is suitable for
a)
a single product in large volumes
b)
one-off production of several varieties
c)
products with similar features made in batches
d)
large variety of products in large volumes
|
|
Sahil Majumdar answered |
In cellular manufacturing, the product are divided into the group based on their production similarity, design similarity etc. and according machines are arrange in the form of cell.
ln a queuing problem, if the arrivals are completely random, then the probability distribution, of number of arrivals in a given time follows:- a)Poisson distribution
- b)Normal distribution
- c)Binomial distribution
- d)Exponential distribution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ln a queuing problem, if the arrivals are completely random, then the probability distribution, of number of arrivals in a given time follows:
a)
Poisson distribution
b)
Normal distribution
c)
Binomial distribution
d)
Exponential distribution
|
|
Rashi Chauhan answered |
Number of arrival in queuing problem follow poisson distribution.
Chapter doubts & questions for Industrial Engineering - Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Industrial Engineering - Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering
45 videos|314 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup