All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
History for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of The Struggle Begins for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
The Ilbert bill is associated with- a) Lord Dufferin
- b) Lord Mayo
- c) Lord Canning
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Ilbert bill is associated with
a)
Lord Dufferin
b)
Lord Mayo
c)
Lord Canning
d)
None of the above
|
|
Maitri Desai answered |
Explanation:
The Ilbert Bill was a legislative initiative introduced in 1883 by a British Indian official, Sir Courtenay Ilbert, who was then the Law Member of the Viceroy's Council.
Background:
During the colonial era, the Indian Civil Service (ICS) was dominated by British officials, who held almost all senior positions in the administration. However, by the late 19th century, a small number of Indians had also started to enter the ICS, and some of them were even appointed as district magistrates or judges.
The Ilbert Bill:
The Ilbert Bill was intended to remove the legal disqualification of Indian judges and magistrates from trying European offenders. It proposed that Indian judges and magistrates would be allowed to try European offenders in criminal cases.
However, the bill faced strong opposition from the British community in India, who feared that it would undermine their social and political dominance. Many British officials also argued that Indian judges and magistrates were not sufficiently trained or experienced to handle cases involving Europeans.
Outcome:
The opposition to the bill was so strong that it was eventually watered down to allow Indian judges and magistrates to try only European offenders who were not of British descent. Even this limited version of the bill was fiercely debated, and it was eventually withdrawn.
In conclusion, the Ilbert Bill was a significant moment in the history of Indian nationalism and anti-colonialism, as it highlighted the discrimination faced by Indians in the colonial legal system.
The Ilbert Bill was a legislative initiative introduced in 1883 by a British Indian official, Sir Courtenay Ilbert, who was then the Law Member of the Viceroy's Council.
Background:
During the colonial era, the Indian Civil Service (ICS) was dominated by British officials, who held almost all senior positions in the administration. However, by the late 19th century, a small number of Indians had also started to enter the ICS, and some of them were even appointed as district magistrates or judges.
The Ilbert Bill:
The Ilbert Bill was intended to remove the legal disqualification of Indian judges and magistrates from trying European offenders. It proposed that Indian judges and magistrates would be allowed to try European offenders in criminal cases.
However, the bill faced strong opposition from the British community in India, who feared that it would undermine their social and political dominance. Many British officials also argued that Indian judges and magistrates were not sufficiently trained or experienced to handle cases involving Europeans.
Outcome:
The opposition to the bill was so strong that it was eventually watered down to allow Indian judges and magistrates to try only European offenders who were not of British descent. Even this limited version of the bill was fiercely debated, and it was eventually withdrawn.
In conclusion, the Ilbert Bill was a significant moment in the history of Indian nationalism and anti-colonialism, as it highlighted the discrimination faced by Indians in the colonial legal system.
Consider the following statements: - The Indian National Congress (INC) was founded with the aim of establishing a democratic and nationalist movement in India.
- A.O. Hume is credited with the foundation of the INC as a measure to prevent any possible uprising against the British rule.
How many of the statements given above are correct?- a)Only 1
- b)Only 2
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
- The Indian National Congress (INC) was founded with the aim of establishing a democratic and nationalist movement in India.
- A.O. Hume is credited with the foundation of the INC as a measure to prevent any possible uprising against the British rule.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only 1
b)
Only 2
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
None

|
Shraddha Mukherjee answered |
Overview of the Indian National Congress (INC)
The Indian National Congress (INC) played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence. The statements provided about the INC are both accurate and illustrate its historical significance.
Statement 1: Democratic and Nationalist Movement
- The INC was indeed founded in 1885 with the intention of creating a platform for the voices of Indians in the political sphere.
- Its primary aim was to establish a democratic framework and foster a sense of nationalism among Indians.
- The INC sought to address the socio-economic issues faced by Indians and aimed for greater representation in governance.
Statement 2: A.O. Hume's Role
- Allan Octavian Hume, a retired British civil servant, is credited with founding the INC.
- He established the party as a response to the growing discontent and to provide a peaceful outlet for political expression.
- Hume's initiative aimed to prevent any violent uprising against British rule by channeling Indian aspirations through constitutional means.
Conclusion: Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements accurately reflect the origins and objectives of the INC.
- The party was indeed formed to nurture a democratic ethos and to prevent unrest, fulfilling a crucial role in India's transition towards independence.
In summary, both statements regarding the INC are correct, making option 'C' the right choice.
The Indian National Congress (INC) played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence. The statements provided about the INC are both accurate and illustrate its historical significance.
Statement 1: Democratic and Nationalist Movement
- The INC was indeed founded in 1885 with the intention of creating a platform for the voices of Indians in the political sphere.
- Its primary aim was to establish a democratic framework and foster a sense of nationalism among Indians.
- The INC sought to address the socio-economic issues faced by Indians and aimed for greater representation in governance.
Statement 2: A.O. Hume's Role
- Allan Octavian Hume, a retired British civil servant, is credited with founding the INC.
- He established the party as a response to the growing discontent and to provide a peaceful outlet for political expression.
- Hume's initiative aimed to prevent any violent uprising against British rule by channeling Indian aspirations through constitutional means.
Conclusion: Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements accurately reflect the origins and objectives of the INC.
- The party was indeed formed to nurture a democratic ethos and to prevent unrest, fulfilling a crucial role in India's transition towards independence.
In summary, both statements regarding the INC are correct, making option 'C' the right choice.
- Statement I: The early nationalists within the Indian National Congress focused on immediate constitutional reforms to bring about self-government.
- Statement II: The demand for self-government was inspired by the models of dominion status granted to colonies like Canada and Australia.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
- Statement I: The early nationalists within the Indian National Congress focused on immediate constitutional reforms to bring about self-government.
- Statement II: The demand for self-government was inspired by the models of dominion status granted to colonies like Canada and Australia.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Chirag Kulkarni answered |
Understanding the Statements
The two statements provided discuss the early nationalists in the Indian National Congress and their demands for self-government.
Statement I: Focus on Constitutional Reforms
- The early nationalists, including leaders like Dadabhai Naoroji and Gopal Krishna Gokhale, primarily sought constitutional reforms.
- Their goal was to achieve self-government through gradual and peaceful means, aiming for an increase in Indian representation within the British colonial administration.
Statement II: Inspiration from Dominion Status
- The demand for self-government among Indian nationalists was indeed inspired by the dominion status models from countries like Canada and Australia.
- These countries had achieved a level of autonomy while still being part of the British Empire, which served as a reference point for Indian leaders advocating for similar reforms.
Assessment of the Correctness
- Both statements are correct. The early nationalists did focus on immediate constitutional reforms to achieve self-government (Statement I).
- Additionally, their aspirations were influenced by the successful models of dominion status in other British colonies (Statement II).
- Statement II provides a solid explanation of the motivations behind the demands articulated in Statement I.
Conclusion
Given that both statements are correct and Statement II explains the rationale behind Statement I, the correct answer is option 'B': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
The two statements provided discuss the early nationalists in the Indian National Congress and their demands for self-government.
Statement I: Focus on Constitutional Reforms
- The early nationalists, including leaders like Dadabhai Naoroji and Gopal Krishna Gokhale, primarily sought constitutional reforms.
- Their goal was to achieve self-government through gradual and peaceful means, aiming for an increase in Indian representation within the British colonial administration.
Statement II: Inspiration from Dominion Status
- The demand for self-government among Indian nationalists was indeed inspired by the dominion status models from countries like Canada and Australia.
- These countries had achieved a level of autonomy while still being part of the British Empire, which served as a reference point for Indian leaders advocating for similar reforms.
Assessment of the Correctness
- Both statements are correct. The early nationalists did focus on immediate constitutional reforms to achieve self-government (Statement I).
- Additionally, their aspirations were influenced by the successful models of dominion status in other British colonies (Statement II).
- Statement II provides a solid explanation of the motivations behind the demands articulated in Statement I.
Conclusion
Given that both statements are correct and Statement II explains the rationale behind Statement I, the correct answer is option 'B': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
Consider the following pairs:
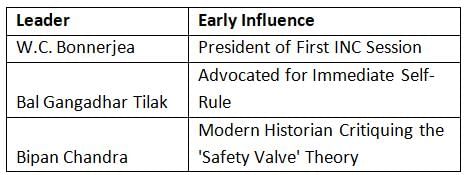
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- a)Only one pair
- b)All three pairs
- c)Only two pairs
- d)None of the pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
All three pairs
c)
Only two pairs
d)
None of the pairs
|
|
Gathe Jayant answered |
Correct answer is perhaps c as all the pairs are correctly match
Which among the following were the factors of Indian nationalism? 1. Worldwide upsurge of the concepts of the nationalism 2. Indian Renaissance 3. Strong reaction to the British imperialistic policies in India 4. Right of self-determination initiated by the French Revolution Choose from the following options:- a) 1 and 2 Only
- b) 2 and 3 Only
- c) 1, 2 and 4 only
- d) All of them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following were the factors of Indian nationalism?
1. Worldwide upsurge of the concepts of the nationalism
2. Indian Renaissance
3. Strong reaction to the British imperialistic policies in India
4. Right of self-determination initiated by the French Revolution
Choose from the following options:
a)
1 and 2 Only
b)
2 and 3 Only
c)
1, 2 and 4 only
d)
All of them
|
|
Snehal Chauhan answered |
Factors of Indian Nationalism:
1. Worldwide upsurge of the concepts of nationalism:
During the 19th century, nationalism was spreading across the world, with countries like Italy and Germany gaining independence and forming their own nation-states. This inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own nation-state.
2. Indian Renaissance:
The Indian Renaissance was a cultural awakening that occurred during the 19th century. It saw a revival of Indian culture, traditions, and values, and it also led to the growth of Indian literature, art, and music. The Indian Renaissance played a crucial role in the growth of Indian nationalism, as it instilled a sense of pride in Indian culture and heritage.
3. Strong reaction to the British imperialistic policies in India:
The British colonized India in the 18th century and ruled over it for almost 200 years. During this time, the British implemented various policies that were detrimental to the Indian people, such as the exploitative land revenue system, the imposition of high tariffs, and the suppression of Indian industries. These policies led to widespread poverty, unemployment, and discontent among Indians, which fueled the growth of Indian nationalism.
4. Right of self-determination initiated by the French Revolution:
The French Revolution of 1789 brought about the concept of the right of self-determination, which means that people have the right to choose their own government and determine their own destiny. This concept inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own government that would work for the betterment of the Indian people.
Conclusion:
All of the above factors played a crucial role in the growth of Indian nationalism. The worldwide upsurge of nationalism and the Indian Renaissance instilled a sense of pride in Indian culture and heritage, while the British imperialistic policies and the concept of the right of self-determination inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own nation-state.
1. Worldwide upsurge of the concepts of nationalism:
During the 19th century, nationalism was spreading across the world, with countries like Italy and Germany gaining independence and forming their own nation-states. This inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own nation-state.
2. Indian Renaissance:
The Indian Renaissance was a cultural awakening that occurred during the 19th century. It saw a revival of Indian culture, traditions, and values, and it also led to the growth of Indian literature, art, and music. The Indian Renaissance played a crucial role in the growth of Indian nationalism, as it instilled a sense of pride in Indian culture and heritage.
3. Strong reaction to the British imperialistic policies in India:
The British colonized India in the 18th century and ruled over it for almost 200 years. During this time, the British implemented various policies that were detrimental to the Indian people, such as the exploitative land revenue system, the imposition of high tariffs, and the suppression of Indian industries. These policies led to widespread poverty, unemployment, and discontent among Indians, which fueled the growth of Indian nationalism.
4. Right of self-determination initiated by the French Revolution:
The French Revolution of 1789 brought about the concept of the right of self-determination, which means that people have the right to choose their own government and determine their own destiny. This concept inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own government that would work for the betterment of the Indian people.
Conclusion:
All of the above factors played a crucial role in the growth of Indian nationalism. The worldwide upsurge of nationalism and the Indian Renaissance instilled a sense of pride in Indian culture and heritage, while the British imperialistic policies and the concept of the right of self-determination inspired Indians to fight for their own independence and form their own nation-state.
What was the result of British rule in India? 1. A professional civil service 2. A unified judiciary 3. Codified Civil and criminal laws 4. English education Choose from the following options.- a) 1 and 2 Only
- b) 2 and 3 Only
- c) 1 and 4 Only
- d) All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the result of British rule in India?
1. A professional civil service
2. A unified judiciary
3. Codified Civil and criminal laws
4. English education
Choose from the following options.
a)
1 and 2 Only
b)
2 and 3 Only
c)
1 and 4 Only
d)
All of the above
|
|
Debanshi Sengupta answered |
The British rule in India lasted for almost two centuries and had a significant impact on the country's social, economic, and political systems. The following are the results of British rule in India:
1. Professional Civil Service: The British introduced a professional civil service in India which was based on merit and impartiality. The Indian Civil Service (ICS) was established in 1858, and it provided a framework for administration that was efficient and fair.
2. Unified Judiciary: The British established a unified judiciary system in India which was based on English common law. The judiciary system was independent of the executive and legislative branches of government, and it provided a forum for resolving disputes and enforcing laws.
3. Codified Civil and Criminal Laws: The British codified civil and criminal laws in India, which replaced the traditional laws that were based on religion and customs. The Indian Penal Code, the Criminal Procedure Code, and the Civil Procedure Code were some of the important legal codes that were introduced by the British.
4. English Education: The British introduced English education in India, which provided Indians with access to modern education and knowledge. The establishment of universities, colleges, and schools helped in the spread of Western education, which had a significant impact on the intellectual and social development of India.
In conclusion, the British rule in India had both positive and negative impacts on the country. While the British introduced modern systems of governance and education, they also exploited India's resources and suppressed its people. The legacy of British rule in India continues to shape the country's social and political systems.
1. Professional Civil Service: The British introduced a professional civil service in India which was based on merit and impartiality. The Indian Civil Service (ICS) was established in 1858, and it provided a framework for administration that was efficient and fair.
2. Unified Judiciary: The British established a unified judiciary system in India which was based on English common law. The judiciary system was independent of the executive and legislative branches of government, and it provided a forum for resolving disputes and enforcing laws.
3. Codified Civil and Criminal Laws: The British codified civil and criminal laws in India, which replaced the traditional laws that were based on religion and customs. The Indian Penal Code, the Criminal Procedure Code, and the Civil Procedure Code were some of the important legal codes that were introduced by the British.
4. English Education: The British introduced English education in India, which provided Indians with access to modern education and knowledge. The establishment of universities, colleges, and schools helped in the spread of Western education, which had a significant impact on the intellectual and social development of India.
In conclusion, the British rule in India had both positive and negative impacts on the country. While the British introduced modern systems of governance and education, they also exploited India's resources and suppressed its people. The legacy of British rule in India continues to shape the country's social and political systems.
Which of the following political associations were formed before the Indian National Congress?1. British Indian Association 2. Indian League 3. Poona Sarvajanik Sabha 4. Madras Mahajan Sabha 5. Bombay Presidency Association Choose from the following options.- a)1, 2 and 3 Only
- b)2, 3 and 4 Only
- c)1, 4 and 5 only
- d)All of them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following political associations were formed before the Indian National Congress?
1. British Indian Association
2. Indian League
3. Poona Sarvajanik Sabha
4. Madras Mahajan Sabha
5. Bombay Presidency Association
Choose from the following options.
a)
1, 2 and 3 Only
b)
2, 3 and 4 Only
c)
1, 4 and 5 only
d)
All of them
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Political Associations Before Indian National Congress:
- 1836-Bangabhasha Prakasika Sabha
- 1843-Bengal British India Society
- 1851--British Indian Association
- 1866-East India Association
- 1875-Indian League
- 1876--Indian Association of Calcutta or Indian National Association
- 1867-Poona Sarvajanik Sabha
- 1885-Bombay Presidency Association
- 1884-Madras Mahajan Sabha
The Indian League was started by- a) Surendra Nath Banerjee
- b) Anand Mohan Bose
- c) Dadabhai Naoroji
- d) Shishir Kumar Ghosh
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Indian League was started by
a)
Surendra Nath Banerjee
b)
Anand Mohan Bose
c)
Dadabhai Naoroji
d)
Shishir Kumar Ghosh
|
|
Rajesh Kulkarni answered |
Indian League was started by Shishir Kumar Ghosh, a prominent lawyer and social activist from Bengal. The Indian League was founded in 1875 under the guidance of Ghosh with the objective of promoting political, social, and economic rights for Indians and to counter the dominance of the British in India.
History of Indian League
The Indian League was established at a time when the Indian National Congress was not yet formed, and political consciousness among Indians was on the rise. The League was established in Calcutta and had its headquarters in the city. Ghosh was its first president, and other prominent members included Anand Mohan Bose and S.N. Banerjee.
Objectives of Indian League
The Indian League had various objectives, including:
1. To fight against the British rule in India and promote self-government.
2. To promote social and economic progress for Indians.
3. To promote unity among Indians and foster a sense of nationalism.
4. To encourage Indians to participate in the political process and fight for their rights.
Achievements of Indian League
The Indian League played a crucial role in promoting political consciousness among Indians and preparing the ground for the Indian National Congress. The League also organized various protests and campaigns against the British rule and played a key role in the Swadeshi Movement.
The League also worked towards promoting social and economic progress for Indians. It established schools, hospitals, and other institutions for the benefit of the Indian community.
Conclusion
The Indian League was a significant organization in the history of India's struggle for independence. It played a crucial role in promoting political, social, and economic rights for Indians and preparing the ground for the Indian National Congress. The League's contributions to India's struggle for independence continue to be remembered and celebrated to this day.
History of Indian League
The Indian League was established at a time when the Indian National Congress was not yet formed, and political consciousness among Indians was on the rise. The League was established in Calcutta and had its headquarters in the city. Ghosh was its first president, and other prominent members included Anand Mohan Bose and S.N. Banerjee.
Objectives of Indian League
The Indian League had various objectives, including:
1. To fight against the British rule in India and promote self-government.
2. To promote social and economic progress for Indians.
3. To promote unity among Indians and foster a sense of nationalism.
4. To encourage Indians to participate in the political process and fight for their rights.
Achievements of Indian League
The Indian League played a crucial role in promoting political consciousness among Indians and preparing the ground for the Indian National Congress. The League also organized various protests and campaigns against the British rule and played a key role in the Swadeshi Movement.
The League also worked towards promoting social and economic progress for Indians. It established schools, hospitals, and other institutions for the benefit of the Indian community.
Conclusion
The Indian League was a significant organization in the history of India's struggle for independence. It played a crucial role in promoting political, social, and economic rights for Indians and preparing the ground for the Indian National Congress. The League's contributions to India's struggle for independence continue to be remembered and celebrated to this day.
Consider the following statements. 1. The English language helped Nationalist leaders from different linguistic regions to communicate with each other 2. The introduction of a modern system of education afforded opportunities for assimilation of modern Western ideas 3. English educated class provided leadership to the Indian political associations Which of these statements is/are correct?- a) 1 Only
- b) 2 and 3 Only
- c) 2 Only
- d) All of them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements.
1. The English language helped Nationalist leaders from different linguistic regions to communicate with each other
2. The introduction of a modern system of education afforded opportunities for assimilation of modern Western ideas
3. English educated class provided leadership to the Indian political associations
Which of these statements is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 and 3 Only
c)
2 Only
d)
All of them
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
- The English system of education had been conceived rulers in the self-interest of efficient administration, liberal and radical thought of European writers like Shelley, John Stuart Mill, Rousseau, Paine, Spencer Voltaire helped many Indians imbibe modern rational, secular, democratic and nationalist ideas.
- The English language helped nationalist leaders from different linguistic regions to communicate with each other. Those among the educated who took up liberal professions (lawyers, doctors, etc.) often visited England for higher education.
- There they saw the working of modern political institutions in a free country and compared that system with the Indian situation where even basic rights were denied to the citizens.
- This ever-expanding English educated class formed the middle-class intelligentsia who constituted the nucleus for the newly arising political unrest. It was this section which provided leadership to the Indian political associations.
Consider the following statements.
1. Indian provinces were under direct British rule, and the princely states were under indirect British rule
2. British impacted political Unity in India
Which of these statements are correct?
- a)1 Only
- b)2 Only
- c)Both of them
- d)Neither of them
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements.
1. Indian provinces were under direct British rule, and the princely states were under indirect British rule
2. British impacted political Unity in India
Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both of them
d)
Neither of them
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
- While Indian provinces were under direct' British rule, the princely states were under 'indirect British rule.
- The British sword imposed political unity in India.
- A professional civil service, a unified judiciary and codified civil and criminal laws throughout the length and breadth of the country imparted a new dimension of political unity to the hitherto cultural unity that had existed in India for centuries.
Madras Mahajan Sabha was founded by- a) Mahadev Govind Ranade
- b) Firoz Shah Mehta
- c) BR Ambedkar
- d) M V Raghavachari
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Madras Mahajan Sabha was founded by
a)
Mahadev Govind Ranade
b)
Firoz Shah Mehta
c)
BR Ambedkar
d)
M V Raghavachari
|
|
Meera Kapoor answered |
You have to remember the political associations and their founders. They are super important.
- Statement I: A.O. Hume played a crucial role in the formation of the Indian National Congress to serve as a safety valve for the discontent among Indians.
- Statement II: The Safety Valve Theory suggests that the Indian National Congress (INC) was created to offer a peaceful means for Indians to express their rising discontent and to avert a potential violent revolution.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
- Statement I: A.O. Hume played a crucial role in the formation of the Indian National Congress to serve as a safety valve for the discontent among Indians.
- Statement II: The Safety Valve Theory suggests that the Indian National Congress (INC) was created to offer a peaceful means for Indians to express their rising discontent and to avert a potential violent revolution.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct

|
Garima Choudhary answered |
Understanding the Statements
The two statements relate to the formation of the Indian National Congress (INC) and the context surrounding its establishment.
Statement I: A.O. Hume's Role
- A.O. Hume, a retired British civil servant, indeed played a vital role in founding the INC in 1885.
- His intention was to create a platform for the expression of Indian political aspirations, allowing educated Indians to voice their concerns.
- Hume's involvement can be viewed as an attempt to channel rising discontent among Indians in a non-revolutionary manner.
Statement II: Safety Valve Theory
- The safety valve theory posits that the British government encouraged the formation of the INC to mitigate potential unrest and rebellion.
- By providing a legitimate political forum, the British aimed to absorb and placate the growing frustration and demands of Indian nationalists.
- This theory suggests a strategic move by colonial authorities to maintain control by offering a controlled outlet for political expression.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate in their assertions regarding Hume's involvement and the British intention behind the INC's formation.
- Statement II serves as a correct explanation for Statement I, highlighting the colonial strategy to prevent unrest.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- This reflects the nuanced understanding of colonial strategies and the emergence of nationalist movements in India.
The two statements relate to the formation of the Indian National Congress (INC) and the context surrounding its establishment.
Statement I: A.O. Hume's Role
- A.O. Hume, a retired British civil servant, indeed played a vital role in founding the INC in 1885.
- His intention was to create a platform for the expression of Indian political aspirations, allowing educated Indians to voice their concerns.
- Hume's involvement can be viewed as an attempt to channel rising discontent among Indians in a non-revolutionary manner.
Statement II: Safety Valve Theory
- The safety valve theory posits that the British government encouraged the formation of the INC to mitigate potential unrest and rebellion.
- By providing a legitimate political forum, the British aimed to absorb and placate the growing frustration and demands of Indian nationalists.
- This theory suggests a strategic move by colonial authorities to maintain control by offering a controlled outlet for political expression.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate in their assertions regarding Hume's involvement and the British intention behind the INC's formation.
- Statement II serves as a correct explanation for Statement I, highlighting the colonial strategy to prevent unrest.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- This reflects the nuanced understanding of colonial strategies and the emergence of nationalist movements in India.
Assertion (A): The early nationalists failed to draw the masses into the freedom movement.Reason (R): They focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, believing in British justice and goodwill.In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The early nationalists failed to draw the masses into the freedom movement.
Reason (R): They focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, believing in British justice and goodwill.
In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Nishanth Goyal answered |
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Analysis:
Assertion (A): The early nationalists failed to draw the masses into the freedom movement.
- The assertion is true as the early nationalists, who focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, did not effectively mobilize the masses for the freedom movement.
Reason (R): They focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, believing in British justice and goodwill.
- The reason is also true as the early nationalists primarily believed in negotiating with the British through petitions and seeking reforms within the existing system, rather than engaging in mass mobilization and agitation.
Explanation:
- The assertion and reason are related as the reason provides an explanation for why the early nationalists failed to involve the masses in the freedom movement. By relying on petitions and expecting British justice and goodwill, they did not adopt more radical or mass-oriented approaches that could have sparked a larger movement.
Conclusion:
- In this context, option 'A' is correct as both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason indeed provides the correct explanation for the assertion. The early nationalists' focus on petitions and constitutional reforms, while overlooking mass mobilization, hindered their ability to draw the masses into the freedom movement.
Assertion (A): The early nationalists failed to draw the masses into the freedom movement.
- The assertion is true as the early nationalists, who focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, did not effectively mobilize the masses for the freedom movement.
Reason (R): They focused on petitions and constitutional reforms, believing in British justice and goodwill.
- The reason is also true as the early nationalists primarily believed in negotiating with the British through petitions and seeking reforms within the existing system, rather than engaging in mass mobilization and agitation.
Explanation:
- The assertion and reason are related as the reason provides an explanation for why the early nationalists failed to involve the masses in the freedom movement. By relying on petitions and expecting British justice and goodwill, they did not adopt more radical or mass-oriented approaches that could have sparked a larger movement.
Conclusion:
- In this context, option 'A' is correct as both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason indeed provides the correct explanation for the assertion. The early nationalists' focus on petitions and constitutional reforms, while overlooking mass mobilization, hindered their ability to draw the masses into the freedom movement.
Assertion (A): The early nationalists were successful in creating a broad public opinion against British rule.Reason (R): They highlighted the economic exploitation of India through the drain theory and criticized British economic policies.In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The early nationalists were successful in creating a broad public opinion against British rule.
Reason (R): They highlighted the economic exploitation of India through the drain theory and criticized British economic policies.
In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Shounak Malik answered |
Explanation:
Early Nationalists and Creation of Public Opinion:
- The early nationalists in India were successful in creating a broad public opinion against British rule by highlighting the various injustices and exploitative practices of the British colonial administration.
- They worked towards awakening the masses and garnering support for the freedom struggle through various means such as newspapers, pamphlets, public speeches, and social reform movements.
Drain Theory and Criticism of British Economic Policies:
- One of the key strategies employed by the early nationalists was to highlight the economic exploitation of India by the British through the drain theory.
- The drain theory outlined how the British were siphoning off resources from India to Britain, leading to economic stagnation and poverty in India.
- Additionally, the early nationalists criticized British economic policies that were detrimental to the Indian economy, such as high tariffs and discriminatory trade practices.
Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true in this context.
- The early nationalists indeed succeeded in creating a broad public opinion against British rule by focusing on various aspects of exploitation, including economic exploitation through the drain theory and criticism of British economic policies.
- Therefore, Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A) as the highlighting of economic exploitation played a significant role in shaping public opinion against British rule.
Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Early Nationalists and Creation of Public Opinion:
- The early nationalists in India were successful in creating a broad public opinion against British rule by highlighting the various injustices and exploitative practices of the British colonial administration.
- They worked towards awakening the masses and garnering support for the freedom struggle through various means such as newspapers, pamphlets, public speeches, and social reform movements.
Drain Theory and Criticism of British Economic Policies:
- One of the key strategies employed by the early nationalists was to highlight the economic exploitation of India by the British through the drain theory.
- The drain theory outlined how the British were siphoning off resources from India to Britain, leading to economic stagnation and poverty in India.
- Additionally, the early nationalists criticized British economic policies that were detrimental to the Indian economy, such as high tariffs and discriminatory trade practices.
Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true in this context.
- The early nationalists indeed succeeded in creating a broad public opinion against British rule by focusing on various aspects of exploitation, including economic exploitation through the drain theory and criticism of British economic policies.
- Therefore, Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A) as the highlighting of economic exploitation played a significant role in shaping public opinion against British rule.
Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer.
Consider the following pairs:
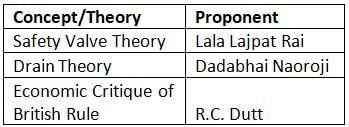
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)All three pairs
- d)None of the pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
All three pairs
d)
None of the pairs

|
K.L Institute answered |
- Lala Lajpat Rai was among the nationalist leaders who supported the 'safety valve' theory regarding the founding of the INC.
- Dadabhai Naoroji introduced the Drain Theory to highlight the economic exploitation of India by Britain.
- R.C. Dutt provided a detailed economic critique of British rule, particularly focusing on its impact on India's economy and agriculture.
Consider the following statements: - The British Indian Government was supportive of the Indian National Congress in its early years, seeing it as a means to channel nationalist sentiments.
- The government attempted to divide nationalist ranks by fostering divisions based on religion, using a 'carrot and stick' approach.
How many of the statements given above are correct?- a)Only 1
- b)Only 2
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
- The British Indian Government was supportive of the Indian National Congress in its early years, seeing it as a means to channel nationalist sentiments.
- The government attempted to divide nationalist ranks by fostering divisions based on religion, using a 'carrot and stick' approach.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only 1
b)
Only 2
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
None

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
Incorrect Statement Explanation:
The British Indian Government was not supportive of the Indian National Congress in its early years. In fact, the government viewed the Indian National Congress with suspicion and as a threat to British colonial rule in India. The Congress was seen as a platform for Indian nationalist sentiments and demands for self-governance, which went against British interests.
Correct Statement Explanation:
The British Indian Government did attempt to divide nationalist ranks by fostering divisions based on religion. This was a tactic used to weaken the Indian National Congress and the broader nationalist movement. The government employed a "carrot and stick" approach, offering incentives to certain religious or ethnic groups while using repression and coercion against others. This strategy aimed to create disunity and prevent a united front against British rule.
The British Indian Government was not supportive of the Indian National Congress in its early years. In fact, the government viewed the Indian National Congress with suspicion and as a threat to British colonial rule in India. The Congress was seen as a platform for Indian nationalist sentiments and demands for self-governance, which went against British interests.
Correct Statement Explanation:
The British Indian Government did attempt to divide nationalist ranks by fostering divisions based on religion. This was a tactic used to weaken the Indian National Congress and the broader nationalist movement. The government employed a "carrot and stick" approach, offering incentives to certain religious or ethnic groups while using repression and coercion against others. This strategy aimed to create disunity and prevent a united front against British rule.
Consider the following statements: - The early nationalists introduced the "drain theory" to articulate how wealth was being extracted from India to Britain.
- The Indian Councils Act of 1892 significantly increased the powers of legislative councils in India, especially in financial matters.
How many of the statements given above are correct?- a)Only 1
- b)Only 2
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
- The early nationalists introduced the "drain theory" to articulate how wealth was being extracted from India to Britain.
- The Indian Councils Act of 1892 significantly increased the powers of legislative councils in India, especially in financial matters.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a)
Only 1
b)
Only 2
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
None

|
Shounak Malik answered |
Explanation:
Statement 1: The early nationalists did introduce the "drain theory" to explain how wealth was being extracted from India to Britain. This theory highlighted the economic exploitation by the British colonial rulers and gained popularity among Indian nationalists during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Therefore, this statement is correct.
Statement 2: The Indian Councils Act of 1892 did not significantly increase the powers of legislative councils in India, especially in financial matters. It was a relatively minor piece of legislation that made limited changes to the composition and functioning of the legislative councils. The real increase in powers came with subsequent acts like the Indian Councils Act of 1909 and the Government of India Act of 1919. Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
Therefore, only statement 1 is correct, and the correct answer is option 'A' (Only 1).
Statement 1: The early nationalists did introduce the "drain theory" to explain how wealth was being extracted from India to Britain. This theory highlighted the economic exploitation by the British colonial rulers and gained popularity among Indian nationalists during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Therefore, this statement is correct.
Statement 2: The Indian Councils Act of 1892 did not significantly increase the powers of legislative councils in India, especially in financial matters. It was a relatively minor piece of legislation that made limited changes to the composition and functioning of the legislative councils. The real increase in powers came with subsequent acts like the Indian Councils Act of 1909 and the Government of India Act of 1919. Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
Therefore, only statement 1 is correct, and the correct answer is option 'A' (Only 1).
Which of the following statements are correct about Moderate Nationalists? 1. The early nationalists, led by Dada Naoroji and RC Dutt put forwarded the drain theory to explain British exploitation in India 2. The moderates were failed to create an all India public opinion against the British rule in India Choose from the following options.- a)1 Only
- b)2 Only
- c)Both of them
- d)Neither of them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct about Moderate Nationalists?
1. The early nationalists, led by Dada Naoroji and RC Dutt put forwarded the drain theory to explain British exploitation in India
2. The moderates were failed to create an all India public opinion against the British rule in India
Choose from the following options.
a)
1 Only
b)
2 Only
c)
Both of them
d)
Neither of them
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
- The early nationalists, led by Dadabhai Naoroji, R.C. Dutt, Dinshaw Wacha and others, carefully analyzed the political economy of British rule in India and put forward the "drain theory" to explain British exploitation of India.
- They opposed transforming a basically self-sufficient Indian economy into a colonial economy (i.e., a supplier of raw materials and foodstuff, an importer of finished goods and a field of investment for British capital).
- Thus, the Moderates created an all-India public opinion that British rule in India was the major cause of India's poverty and economic backwardness.
In 1851, Landholders society and the Bengal British India society merged into the- a) British Indian Association
- b) Indian Association of Kolkata
- c) The East India Association
- d) Indian National Association
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1851, Landholders society and the Bengal British India society merged into the
a)
British Indian Association
b)
Indian Association of Kolkata
c)
The East India Association
d)
Indian National Association

|
Valor Academy answered |
- The Zamindari Association, more popularly known as the 'Landholders' Society', was founded to safeguard the landlords' interests.
- Although limited in its objectives, the Landholders' Society marked the beginning of organised political activity and use of methods of constitutional agitation for the redressal of grievances.
- The Bengal British India Society was founded in 1843 with the object of the collection and dissemination of information relating to the actual condition of the people of British India... and to employ such other means of peaceful and lawful character as may appear calculated to secure the welfare, extend the just rights and advance the interests of all classes of our fellow-subjects".
Assertion (A): The Indian Councils Act of 1892 was criticized by nationalist leaders.Reason (R): It significantly increased the representation and powers of Indians in the legislative councils.In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The Indian Councils Act of 1892 was criticized by nationalist leaders.
Reason (R): It significantly increased the representation and powers of Indians in the legislative councils.
In the context of the above, which one of the following is correct?
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Neha Khanna answered |
Explanation:
Indian Councils Act of 1892:
- The Indian Councils Act of 1892, also known as the Morley-Minto Reforms, was introduced by the British government in India.
- It aimed to increase Indian representation in the legislative councils and give Indians a larger role in the governance of the country.
Criticism by Nationalist Leaders:
- Nationalist leaders criticized the Indian Councils Act of 1892 for various reasons.
- They felt that the reforms were not sufficient and did not meet the demands of the Indian people for greater participation in the legislative process.
- Nationalist leaders believed that the Act did not go far enough in granting Indians equal representation and decision-making power in the legislative councils.
- They argued that the Act maintained significant British control over the legislative process and did not adequately address the aspirations of the Indian population for self-governance.
Assertion and Reason Analysis:
- The assertion that the Indian Councils Act of 1892 was criticized by nationalist leaders is true.
- The reason given, that it significantly increased the representation and powers of Indians in the legislative councils, is false.
- In reality, while the Act did increase Indian representation to some extent, nationalist leaders felt that it fell short of their expectations and demands for greater empowerment and self-governance.
Therefore, option 'C' is the correct choice as the Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
Indian Councils Act of 1892:
- The Indian Councils Act of 1892, also known as the Morley-Minto Reforms, was introduced by the British government in India.
- It aimed to increase Indian representation in the legislative councils and give Indians a larger role in the governance of the country.
Criticism by Nationalist Leaders:
- Nationalist leaders criticized the Indian Councils Act of 1892 for various reasons.
- They felt that the reforms were not sufficient and did not meet the demands of the Indian people for greater participation in the legislative process.
- Nationalist leaders believed that the Act did not go far enough in granting Indians equal representation and decision-making power in the legislative councils.
- They argued that the Act maintained significant British control over the legislative process and did not adequately address the aspirations of the Indian population for self-governance.
Assertion and Reason Analysis:
- The assertion that the Indian Councils Act of 1892 was criticized by nationalist leaders is true.
- The reason given, that it significantly increased the representation and powers of Indians in the legislative councils, is false.
- In reality, while the Act did increase Indian representation to some extent, nationalist leaders felt that it fell short of their expectations and demands for greater empowerment and self-governance.
Therefore, option 'C' is the correct choice as the Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
- Statement I: The aim of the Indian National Congress during its initial years was to establish a platform for all Indians to unite and articulate their political and economic demands.
- Statement II: The formation of the INC was primarily a response to the British economic policies that were seen as detrimental to the economic interests of Indians.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
- Statement I: The aim of the Indian National Congress during its initial years was to establish a platform for all Indians to unite and articulate their political and economic demands.
- Statement II: The formation of the INC was primarily a response to the British economic policies that were seen as detrimental to the economic interests of Indians.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Jaideep Roy answered |
Explanation:
Statement I:
- The aim of the Indian National Congress during its initial years was indeed to establish a platform for all Indians to unite and articulate their political and economic demands.
- The INC was founded in 1885 by A.O. Hume, Dadabhai Naoroji, Dinshaw Wacha, and others with the goal of promoting a common platform for Indians to voice their concerns and grievances.
- The INC played a crucial role in bringing together people from diverse backgrounds and regions to work towards common goals such as self-governance and social reform.
Statement II:
- The formation of the INC was indeed a response to the British economic policies that were seen as detrimental to the economic interests of Indians.
- The INC emerged at a time when Indians were facing economic exploitation under British colonial rule, such as high taxes, discriminatory tariffs, and lack of economic opportunities.
- By advocating for economic reforms and representing the interests of Indians, the INC aimed to address these economic challenges and promote Indian economic development.
Therefore, both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I as the formation of the INC had broader goals beyond just responding to British economic policies.
Statement I:
- The aim of the Indian National Congress during its initial years was indeed to establish a platform for all Indians to unite and articulate their political and economic demands.
- The INC was founded in 1885 by A.O. Hume, Dadabhai Naoroji, Dinshaw Wacha, and others with the goal of promoting a common platform for Indians to voice their concerns and grievances.
- The INC played a crucial role in bringing together people from diverse backgrounds and regions to work towards common goals such as self-governance and social reform.
Statement II:
- The formation of the INC was indeed a response to the British economic policies that were seen as detrimental to the economic interests of Indians.
- The INC emerged at a time when Indians were facing economic exploitation under British colonial rule, such as high taxes, discriminatory tariffs, and lack of economic opportunities.
- By advocating for economic reforms and representing the interests of Indians, the INC aimed to address these economic challenges and promote Indian economic development.
Therefore, both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I as the formation of the INC had broader goals beyond just responding to British economic policies.
Chapter doubts & questions for The Struggle Begins - History for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The Struggle Begins - History for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
History for State PSC Exams
125 videos|772 docs|270 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup