All Exams >
Year 10 >
Science for Year 10 >
All Questions
All questions of DNA & Genes for Year 10 Exam
Select the incorrect statement.- a)Lean and thin parents may have fat progeny.
- b)Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution
- c)Frequency of certain genes in a population changes after several generations
- d)Reduction in weight of the organism due to starvation is genetically controlled
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement.
a)
Lean and thin parents may have fat progeny.
b)
Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution
c)
Frequency of certain genes in a population changes after several generations
d)
Reduction in weight of the organism due to starvation is genetically controlled
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Weight of body depends on diet and habits. If somebody is not eating he will definitely lose weight as the body fat will be used for production of energy once glycogen reserve finishes.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following statement is not correct regarding variation in species?- a)Depending on the nature of variation, different individuals have different kind of advantages
- b)Selection of variants depend on environmental factors
- c)Variation is basis of evolutionary process
- d)All variation in species have equal chances of survival in the environment
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not correct regarding variation in species?
a)
Depending on the nature of variation, different individuals have different kind of advantages
b)
Selection of variants depend on environmental factors
c)
Variation is basis of evolutionary process
d)
All variation in species have equal chances of survival in the environment
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Only those variation which are useful and have advantage get selected.
Mendel formulated the law of purity of gametes on the basis of :-- a)test cross
- b)dihybrid corss
- c)back cross
- d)monohybrid cross
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mendel formulated the law of purity of gametes on the basis of :-
a)
test cross
b)
dihybrid corss
c)
back cross
d)
monohybrid cross

|
Smriti Tripathi answered |
Through this cross he found about the two major types of traits that are Dominant traits(traits that can be seen in an organism) and reccessive traits(traits that cannot be seen under the dominance of dominant traits but are present in organisms). The result he got by this cross shows the purity of the gametes.
The contrasting pairs of factors in Mendelian crosses are called :-- a)alloloci
- b)paramorphs
- c)allelomorphs
- d)multiple alleles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The contrasting pairs of factors in Mendelian crosses are called :-
a)
alloloci
b)
paramorphs
c)
allelomorphs
d)
multiple alleles
|
|
Abhi Prajapati answered |
¶The contrasting pairs of factors in Mendelian crosses are called allelomorphs. Alleles or allelomorphs are the different forms of a gene, having the same locus on homologous chromosomes and are subject to mendelian (alternative) inheritance¶.
HOPE'S IT'S HELPFUL FOR YOU :-)
New species may be formed if
(i) mating does not take place.
(ii) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells.
(iii) there is no change in genetic material.
(iv) chromosome number changes in gametes.- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
New species may be formed if
(i) mating does not take place.
(ii) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells.
(iii) there is no change in genetic material.
(iv) chromosome number changes in gametes.
(i) mating does not take place.
(ii) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells.
(iii) there is no change in genetic material.
(iv) chromosome number changes in gametes.
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
New species may be formed if DNA undergoes significant change in germ cells. Changes in DNA will be inherited by the germ cells. Germ cells which when passes to the next generation will be inherited in the subsequent generations.
Change in the chromosome number makes a change in the gametes which leads to change in the gene pool and causes variation.
Gregor Mendel was born in :-- a)Austria
- b)Russia
- c)Czechoslovakia
- d)United Kingdom
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gregor Mendel was born in :-
a)
Austria
b)
Russia
c)
Czechoslovakia
d)
United Kingdom

|
Smriti Tripathi answered |
There is no explaination for this...
A basket of vegetables contains carrot, potato, radish and tomato. Which of them represent the correct homologous structures?- a)Carrot and potato
- b)Carrot and tomato
- c)Radish and carrot
- d)Radish and potato
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A basket of vegetables contains carrot, potato, radish and tomato. Which of them represent the correct homologous structures?
a)
Carrot and potato
b)
Carrot and tomato
c)
Radish and carrot
d)
Radish and potato

|
Sonika Attitdejaatni answered |
Homologous structures are those that are related by common ancestry. The common ancestry is reflected in a common structural plan. These structures might be adapted to suit different functional roles. Of the given options, potato is a storage stem, tomato is a fruit (in fact, it is a berry), radish and carrots are roots. Since both radish and carrots are roots, they have similar structural plans and are homologous.
So, the correct option is C
Differences between organisms in a species are described as variation. Which of the following would you describe as continuous variation?- a)Hair colour
- b)Eye colour
- c)Weight
- d)Sex
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Differences between organisms in a species are described as variation. Which of the following would you describe as continuous variation?
a)
Hair colour
b)
Eye colour
c)
Weight
d)
Sex
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Continuous variation can be defined as the variations in the phenotypic traits in which a series of types are distributed on a continuum rather than separate groups. For example body weight.
The terms 'genotype' and 'phenotype' were introduced by :-- a)Bateson
- b)Darwin
- c)Johannsen
- d)Mendel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The terms 'genotype' and 'phenotype' were introduced by :-
a)
Bateson
b)
Darwin
c)
Johannsen
d)
Mendel
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Johannsen introduced the concepts genotype and phenotype in 1909 in his textbook on heredity research, titled Elemente der exakten Ereblichkeitslehre (The Elements of an Exact Theory of Heredity).
The normal number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained when the germ cells:- a)take all maternal and paternal chromosomes
- b)divide by the process of mitosis
- c)divide by mitosis and take all maternal and paternal chromosome
- d)take one chromosome from each pair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The normal number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained when the germ cells:
a)
take all maternal and paternal chromosomes
b)
divide by the process of mitosis
c)
divide by mitosis and take all maternal and paternal chromosome
d)
take one chromosome from each pair
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
The number of chromosomes in each generation are maintained due to meiosis. The meiosis is a kind of reductive division. When gametes are formed by meiosis, the number of chromosomes are halved. Hence each gamete will have only one pair of chromosome.
Later the haploid gamete will fuse with the complementary haploid gamete and form Diploid Zygote(2n). Hence the number of chromosomes are maintained.
For more details you can view my old answers regarding S-phase, certain stages of meiosis etc. If still you have doubts, you can ask anytime or you can refer Molecular cell biology by Bruce Alberts.
The reason why pea plants were suitable than dogs for Mendel's experiments :-- a)Dogs have many genetic traits
- b)Pea plants can be self fertilized
- c)There are no pedigree records of dogs
- d)The pea plants favour cross-fertilization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reason why pea plants were suitable than dogs for Mendel's experiments :-
a)
Dogs have many genetic traits
b)
Pea plants can be self fertilized
c)
There are no pedigree records of dogs
d)
The pea plants favour cross-fertilization
|
|
Kuldeep Raj answered |

The traits which are expressed in first filial (F1) generation are known as which traits.- a)inherited
- b)dominant
- c)recessive
- d)acquired
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The traits which are expressed in first filial (F1) generation are known as which traits.
a)
inherited
b)
dominant
c)
recessive
d)
acquired
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Blending Theory of Inheritance - offspring of two parents "blend" the traits of both parents
Particulate Theory of Inheritance - traits are inherited as "particles", offspring receive a "particle" from each parent.
Analysis:
- The F1 generation always displayed one trait (he later called this the dominant trait)
- The F1 generation must have within it the trait from the original parents - the white trait
- The F2 generation displayed the hidden trait, 1/4 of the F2 generation had it (he later called this hidden trait the recessive trait)
- Each individual has two "factors" that determine what external appearance the offspring will have. (We now call these factors genes or alleles)
From the options given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited?
- a)Colour of eye
- b)Colour of skin
- c)Size of body
- d)Nature of hair
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
From the options given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited?
a)
Colour of eye
b)
Colour of skin
c)
Size of body
d)
Nature of hair

|
Sushant Sen answered |
Since the size of body can vary person to person according to lifestyle and diet and is not same from generation to generation.For e.g., A fat boy can have a slim father or mother or both.
Skin complexion or skin color is an inherited characteristic. Hair is a trait that is passed down through generations so it is an inherited characteristic.
Skin complexion or skin color is an inherited characteristic. Hair is a trait that is passed down through generations so it is an inherited characteristic.
The earlobe variants found in human population are
(i) free
(ii) curved
(iii) round
(iv) attached- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The earlobe variants found in human population are
(i) free
(ii) curved
(iii) round
(iv) attached
(i) free
(ii) curved
(iii) round
(iv) attached
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The earlobe variants found in human population are free and attached.
EXPLANATION:-
All the human beings have two types of earlobes.
One of such earlobes are the attached earlobes which are attached to the skin of human being near his or her ear . 2nd earlobes are the earlobes which are not so attached rather they are hanged freely
EXPLANATION:-
All the human beings have two types of earlobes.
One of such earlobes are the attached earlobes which are attached to the skin of human being near his or her ear . 2nd earlobes are the earlobes which are not so attached rather they are hanged freely
The main reason of Mendel's successs in discovering the principles of inheritance was :-- a)He considered each character separately
- b)He was lucky not to encounter linkage problem
- c)The plant was pure breeding
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main reason of Mendel's successs in discovering the principles of inheritance was :-
a)
He considered each character separately
b)
He was lucky not to encounter linkage problem
c)
The plant was pure breeding
d)
All the above
|
|
HÊÅRT HÂCKÊR answered |
Main reasons for the success of Gregor Mendel:
1. Mendel concentrated in one or few characters at a time.
2. He made controlled crosses and kept careful numerical records of the results.
3. He suggested 'factors' as a cause of characters.
4. The experimental material Pisum sativum was a wise choice.
1. Mendel concentrated in one or few characters at a time.
2. He made controlled crosses and kept careful numerical records of the results.
3. He suggested 'factors' as a cause of characters.
4. The experimental material Pisum sativum was a wise choice.
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a- a)Boy
- b)Girl
- c) X-chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
- d)Either boy or girl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a
a)
Boy
b)
Girl
c)
X-chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
d)
Either boy or girl

|
Sushant Sen answered |
Explanation: Humans follow XX- XY mechanism of sex determination.
Select the correct statement.- a)Thom of Bougainvillea and potato are homologous
- b)Wing of a bird and wing of bat are homologous
- c)Apple and Banana are analogous
- d)Carrot and sweet potato are analogous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement.
a)
Thom of Bougainvillea and potato are homologous
b)
Wing of a bird and wing of bat are homologous
c)
Apple and Banana are analogous
d)
Carrot and sweet potato are analogous
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
(a) Homologous structures are the organs which are similar in basic structure and have a common origin but perform different functions.
(i) They have same basic structure but are used for different functions i.e. swimming and flying respectively. So they are homologous.
(ii) Tuber of potato is a stem modification while the tuber of sweet potato is a root modification. But their function is same i.e food storage, so they are analogous.
(iii) Eyes of octopus and mammals have different basic structures but their function is same so they are analogous.
(iv) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita are both stem modifications but their functions are different i.e. protection and climbing respectively. So they are homologous.
(b) This type of evolution is called divergent evolution because the origin of homologous organs are same but they diverged into different directions to perform different functions.
(i) They have same basic structure but are used for different functions i.e. swimming and flying respectively. So they are homologous.
(ii) Tuber of potato is a stem modification while the tuber of sweet potato is a root modification. But their function is same i.e food storage, so they are analogous.
(iii) Eyes of octopus and mammals have different basic structures but their function is same so they are analogous.
(iv) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita are both stem modifications but their functions are different i.e. protection and climbing respectively. So they are homologous.
(b) This type of evolution is called divergent evolution because the origin of homologous organs are same but they diverged into different directions to perform different functions.
How many types of gametes will be produced in F2 generation of a monohybrid cross of Mendel :-- a)3
- b)4
- c)8
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many types of gametes will be produced in F2 generation of a monohybrid cross of Mendel :-
a)
3
b)
4
c)
8
d)
16
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Each dihybrid plant produces 4 gamete types of equal frequency. In the offspring F2 showed 4 different phenotypes : the round and yellow traits did not stay linked to each other.
Wild cabbage has evolved into new varieties fike cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower by- a)genetic drift
- b)natural selection
- c)reproductive isolation
- d)artificial selection
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Wild cabbage has evolved into new varieties fike cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower by
a)
genetic drift
b)
natural selection
c)
reproductive isolation
d)
artificial selection
|
|
Kuldeep Raj answered |
Correct answer is Option (d) Artificial selection. Because, it does not occurs naturally. It is man made for to lead his life easily.
Artificial selection is the process of selecting desired (more wanted) trait, when breed (to cross) with other plants/animals to get desired (more wanted) traits.
Examples:- Obtaining of Dogs from Wolves, Obtaining of Kohlrabi Cauliflower, Broccoli, Cabbage, Red cabbage, Kale from Wild cabbage.
Option a, b, and c occurs naturally by leaving the option d as it is a man made process.
Hence, Option d is correct friend...
Which of the following is an example of genetic variation ?- a)One person has a scar, but his friend does not
- b)One person is older than another
- c)Reeta eats meat, but her sister Geeta is a vegetarian
- d)Two children have different eye colours
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of genetic variation ?
a)
One person has a scar, but his friend does not
b)
One person is older than another
c)
Reeta eats meat, but her sister Geeta is a vegetarian
d)
Two children have different eye colours
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Different eye colour is a genetic variation.
Genetic material is exchanged during- a)budding
- b)sexual reproduction
- c)asexual reproduction
- d)mitosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic material is exchanged during
a)
budding
b)
sexual reproduction
c)
asexual reproduction
d)
mitosis
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
During formation of gametes meiosis occurs resulting in exchange of genes by the process of crossing over.
Natural selection is called ‘survival of the fittest'.Which of the following statements best describes an organism?- a)How strong it is compared to other individuals of the same species
- b)How much food and resources it is able to gather for its offspring
- c)The ability to adapt to the environment in the niche it occupies
- d)The number of fertile offspring it has
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Natural selection is called ‘survival of the fittest'.Which of the following statements best describes an organism?
a)
How strong it is compared to other individuals of the same species
b)
How much food and resources it is able to gather for its offspring
c)
The ability to adapt to the environment in the niche it occupies
d)
The number of fertile offspring it has
|
|
Swati Malkani answered |
Option C..
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?- a)For every molecule of fat there is a gene
- b)For production of every enzyme there is a gene
- c)For every protein there is a gene
- d)For insulin hormone there is a gene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
a)
For every molecule of fat there is a gene
b)
For production of every enzyme there is a gene
c)
For every protein there is a gene
d)
For insulin hormone there is a gene
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The information coded in DNA (genes) is for only polypeptides (proteins). Insulin hormone is peptide and all enzyme are also proteins.
A trait in an organism is influenced by- a) Paternal DNA only
- b) Maternal DNA only
- c)Both maternal and paternal DNA
- d)Neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A trait in an organism is influenced by
a)
Paternal DNA only
b)
Maternal DNA only
c)
Both maternal and paternal DNA
d)
Neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA

|
Anisha Mukherjee answered |
Explanation: An organism develops from zygote which in turn is product of fusion of male and female gamete.
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?- a)Genetic drift does not require the presence of variation
- b)Genetic drift never occurs in nature, natural selection does
- c)Genetic drift does not involve competition between members of a species
- d)There is no difference
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the difference between genetic drift and change due to natural selection?
a)
Genetic drift does not require the presence of variation
b)
Genetic drift never occurs in nature, natural selection does
c)
Genetic drift does not involve competition between members of a species
d)
There is no difference
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Both natural selection and genetic drift are mechanisms for evolution. The key distinction is that in genetic drift allele frequencies change by chance, whereas in natural selection allele frequencies change by differential reproductive success and genetic drift does not involve competition between members of species.
Some dinosaurs had feathers but they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In terms of evolution it means- a)reptiles have evolved from birds
- b)feathers of both are analogous structures
- c)there is no evolutionary connection between reptile and birds
- d)birds have evolved from reptiles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some dinosaurs had feathers but they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In terms of evolution it means
a)
reptiles have evolved from birds
b)
feathers of both are analogous structures
c)
there is no evolutionary connection between reptile and birds
d)
birds have evolved from reptiles

|
Mahesh Basu answered |
In the context of evolution, the use of feathers by birds for flying means that birds have evolved from reptiles. Dinosaurs had feathers but could not fly using them. Birds, later adapted the feathers for flight. Since, dinosaurs were reptiles, this means that birds have evolved from them.
The more characteristics two species have in common :- a)More closely they are related and more recently they had a common ancestors
- b)More distantly they are related and more recently they have common ancestors
- c)More closely they are related and more distantly they have common ancestors
- d)More distantly they are related and more distantly they have common ancestors
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The more characteristics two species have in common :
a)
More closely they are related and more recently they had a common ancestors
b)
More distantly they are related and more recently they have common ancestors
c)
More closely they are related and more distantly they have common ancestors
d)
More distantly they are related and more distantly they have common ancestors
|
|
Swati Malkani answered |
More closely they are related and more recently they had a common ancestors.
Mendel published the results of his experiments in the year :-- a)1568
- b)1773
- c)1866
- d)1921
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mendel published the results of his experiments in the year :-
a)
1568
b)
1773
c)
1866
d)
1921
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Mendel's presentations were published as "Experiments on Plant Hybridization" in the Proceedings of the Nature Research Society of Brünn in 1866.
The fossil remains of Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between- a)reptiles and mammals
- b)reptiles and bird
- c)fish and amphibian
- d)amphibian and reptile
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The fossil remains of Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between
a)
reptiles and mammals
b)
reptiles and bird
c)
fish and amphibian
d)
amphibian and reptile

|
Sonika Attitdejaatni answered |
Answer
Archeopteryx is a connecting link between non - avians, and dinosaurs. We can say that they are bird-like reptiles. Their fossils have revealed that they possess the characteristics of both, reptiles and birds. So, they are said to be a connecting link between reptiles and birds.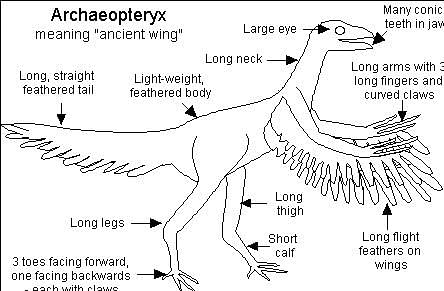
They have wings and feathers like birds, and claws and teeth like reptiles. So, option B "Reptiles and birds" is the correct option.

If yellow seeded wrinkled pea plant (YYrr) is crossed with green seeded round pea plant (yyRR), the seeds produced in F1 generation are- a)yellow and round
- b)green and round
- c)wrinkled and green
- d)wrinkled and yellow
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If yellow seeded wrinkled pea plant (YYrr) is crossed with green seeded round pea plant (yyRR), the seeds produced in F1 generation are
a)
yellow and round
b)
green and round
c)
wrinkled and green
d)
wrinkled and yellow
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
If a round, green seeded pea plant is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, the seeds produced in F1 generation are round and yellow.
Which of the following act as an information source for making proteins in a cell?- a)DNA
- b)Lipids
- c)RNA
- d)Carbohydrates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following act as an information source for making proteins in a cell?
a)
DNA
b)
Lipids
c)
RNA
d)
Carbohydrates
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The DNA in the nucleus of a cell is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins will be made. The basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell and they need to get separated from each other. DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus, and then the DNA copies separate, each with its own cellular apparatus.
Select the correct statement.
- a)Wing of a bird and wing of a bat are analogous
- b)Sweet potato and potato are analogous
- c)Tendril of a pea plant and phylloclade of Opuntia are analogous
- d)Radish and Ginger are analogous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement.
a)
Wing of a bird and wing of a bat are analogous
b)
Sweet potato and potato are analogous
c)
Tendril of a pea plant and phylloclade of Opuntia are analogous
d)
Radish and Ginger are analogous
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
1. Wing of a bird and wing of a bat are analogous.
Analogous structures are those that have evolved independently to serve a similar function but do not share a common ancestor. The wings of birds and bats are similar in function (both are used for flying), but they have evolved independently in these different groups of animals.
A pea plant shows the genetic makeup TtRr. How will the plant appear externally?- a)Tall with wrinkled seeds
- b)Dwarf with round seeds
- c)Dwarf with wrinkled seeds
- d)Tall with round seeds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A pea plant shows the genetic makeup TtRr. How will the plant appear externally?
a)
Tall with wrinkled seeds
b)
Dwarf with round seeds
c)
Dwarf with wrinkled seeds
d)
Tall with round seeds
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Tall with round seeds
Since tallness of plant and round shape of seeds are dominant characters, these will be expressed in F2 generation.
To study the natural phenomenon of inheritance, Mendel selected the pea plants. Which of the following properties were suitable for their studies?
(i) Plants would easily self pollinate or cross pollinate in nature.
(ii) Plants were easily grown in garden soil with a considerably shorter generation time.
(iii) Pea plants do not require the true-breeding for hybridisation experiments.
(iv) Many parts of the plant such as pod, seed, flower, cotyledons showed distinct phenotypes.- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
To study the natural phenomenon of inheritance, Mendel selected the pea plants. Which of the following properties were suitable for their studies?
(i) Plants would easily self pollinate or cross pollinate in nature.
(ii) Plants were easily grown in garden soil with a considerably shorter generation time.
(iii) Pea plants do not require the true-breeding for hybridisation experiments.
(iv) Many parts of the plant such as pod, seed, flower, cotyledons showed distinct phenotypes.
(i) Plants would easily self pollinate or cross pollinate in nature.
(ii) Plants were easily grown in garden soil with a considerably shorter generation time.
(iii) Pea plants do not require the true-breeding for hybridisation experiments.
(iv) Many parts of the plant such as pod, seed, flower, cotyledons showed distinct phenotypes.
a)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Plant is easily grown in garden soil so it can be easily used for experiment.
Mendels experiment is to prove that pure tall and pure dwarf give different types of progency. So, he have to take a plant which have distinct phenotype. Therefore he used pea.
Mendels experiment is to prove that pure tall and pure dwarf give different types of progency. So, he have to take a plant which have distinct phenotype. Therefore he used pea.
Your mother bought carrot, potato, radish and brinjal. Which of them represent the correct homologus structures ?- a)Radish and potato
- b)Radish and carrot
- c)Carrot and brinjal
- d)Carrot and potato
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Your mother bought carrot, potato, radish and brinjal. Which of them represent the correct homologus structures ?
a)
Radish and potato
b)
Radish and carrot
c)
Carrot and brinjal
d)
Carrot and potato
|
|
Nitin shetty answered |
Both are modifications of root while potato is a stem modification and brinjal is a fruit.
Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygene. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc (light colour), in F2-generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent- a)One fourth
- b)Less than 5 percent
- c)One third
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygene. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc (light colour), in F2-generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent
a)
One fourth
b)
Less than 5 percent
c)
One third
d)
None of these
|
|
Learnever Education answered |
Polygene results in quantitative inheritance which is characterized by occurrence of intermediate forms between the parental type. In case of crossing between AABBCC (dark colour) and aabbcc (light colour), in F2 generation seven phenotypes will obtain with ratio of 1 : 6 : 15 : 20 : 15 : 6 : 1. The total number of progeny is 64, out of which only two will be likely resemble with either parents. Hence, their proportion in F2 generation would be 3.12 ie, less than 5%.
If a heterozygous tall palnt is crossed with a homozygous dwarf palnt, the proportion of dwarf progeny will:-- a)50%
- b)75%
- c)100%
- d)25%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a heterozygous tall palnt is crossed with a homozygous dwarf palnt, the proportion of dwarf progeny will:-
a)
50%
b)
75%
c)
100%
d)
25%
|
|
Rohan pandey answered |
A) 50%
Explanation:
A heterozygous tall plant has the genotype Tt (T for the tall allele and t for the dwarf allele). A homozygous dwarf plant has the genotype tt. When these two plants are crossed, the possible genotypes of the progeny can be determined using a Punnett square.
Tt (heterozygous tall plant)
T | t
---------
t | Tt | tt
t | Tt | tt
As we can see, there are 4 possible outcomes: 2 Tt (tall) and 2 tt (dwarf). So, the proportion of dwarf progeny (tt) is 2 out of the 4 possibilities, which is equal to 50%.
Explanation:
A heterozygous tall plant has the genotype Tt (T for the tall allele and t for the dwarf allele). A homozygous dwarf plant has the genotype tt. When these two plants are crossed, the possible genotypes of the progeny can be determined using a Punnett square.
Tt (heterozygous tall plant)
T | t
---------
t | Tt | tt
t | Tt | tt
As we can see, there are 4 possible outcomes: 2 Tt (tall) and 2 tt (dwarf). So, the proportion of dwarf progeny (tt) is 2 out of the 4 possibilities, which is equal to 50%.
Which of the following contributed to the success of Mendel :-- a)His knowledge of biology
- b)Qualitative analysis of data
- c)Observation of distinct inherited traits
- d)consideration of one character at a time
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following contributed to the success of Mendel :-
a)
His knowledge of biology
b)
Qualitative analysis of data
c)
Observation of distinct inherited traits
d)
consideration of one character at a time
|
|
Rhea singhania answered |
Mendel's success in discovering the laws of inheritance can be attributed to several factors, but the most important one is his approach to experimentation. His approach was unique and different from the contemporary methods of experimentation.
Consideration of one character at a time:
Mendel focused on studying one trait at a time, rather than studying multiple traits simultaneously. This allowed him to maintain a clear focus on the traits he was studying and avoid confusion caused by multiple traits. He chose to study pea plants, which have seven distinct traits that can be easily identified and studied. By choosing to study one trait at a time, Mendel was able to identify patterns of inheritance that were not noticeable before.
Qualitative analysis of data:
Mendel used a qualitative analysis of data, which means he focused on identifying the presence or absence of a trait rather than measuring the quantity of the trait. This approach allowed him to identify clear and distinct patterns of inheritance. He counted the number of offspring with a particular trait and used statistical analysis to determine the ratios of dominant and recessive traits in the offspring.
Observation of distinct inherited traits:
Mendel observed seven distinct inherited traits in pea plants, including seed color, seed shape, flower color, and plant height. He carefully observed the traits and recorded his findings. This allowed him to identify patterns of inheritance that were not noticeable before.
His Knowledge of biology:
Mendel had a good understanding of biology, which helped him to interpret his findings and draw conclusions about patterns of inheritance. He was familiar with the concepts of genetics, heredity, and variation. This knowledge allowed him to design experiments that were effective in studying inherited traits.
In conclusion, Mendel's success can be attributed to his focus on studying one trait at a time, qualitative analysis of data, observation of distinct inherited traits, and his knowledge of biology. These factors allowed him to discover the laws of inheritance, which revolutionized the field of genetics.
Consideration of one character at a time:
Mendel focused on studying one trait at a time, rather than studying multiple traits simultaneously. This allowed him to maintain a clear focus on the traits he was studying and avoid confusion caused by multiple traits. He chose to study pea plants, which have seven distinct traits that can be easily identified and studied. By choosing to study one trait at a time, Mendel was able to identify patterns of inheritance that were not noticeable before.
Qualitative analysis of data:
Mendel used a qualitative analysis of data, which means he focused on identifying the presence or absence of a trait rather than measuring the quantity of the trait. This approach allowed him to identify clear and distinct patterns of inheritance. He counted the number of offspring with a particular trait and used statistical analysis to determine the ratios of dominant and recessive traits in the offspring.
Observation of distinct inherited traits:
Mendel observed seven distinct inherited traits in pea plants, including seed color, seed shape, flower color, and plant height. He carefully observed the traits and recorded his findings. This allowed him to identify patterns of inheritance that were not noticeable before.
His Knowledge of biology:
Mendel had a good understanding of biology, which helped him to interpret his findings and draw conclusions about patterns of inheritance. He was familiar with the concepts of genetics, heredity, and variation. This knowledge allowed him to design experiments that were effective in studying inherited traits.
In conclusion, Mendel's success can be attributed to his focus on studying one trait at a time, qualitative analysis of data, observation of distinct inherited traits, and his knowledge of biology. These factors allowed him to discover the laws of inheritance, which revolutionized the field of genetics.
Which concept was not included in Charles Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection?- a)Struggle for existence
- b)Punctuated equilibrium
- c)Survival of the fittest
- d)Overproduction of offspring
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which concept was not included in Charles Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection?
a)
Struggle for existence
b)
Punctuated equilibrium
c)
Survival of the fittest
d)
Overproduction of offspring
|
|
Anurag Singh answered |
He take a probability of out comes offspring
If a plant is heterozygous for tallness, the F2 generation has both tall and dwarf plants. This proves the principle of :-- a)dominance
- b)segregation
- c)independent assortment
- d)incomplete dominance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a plant is heterozygous for tallness, the F2 generation has both tall and dwarf plants. This proves the principle of :-
a)
dominance
b)
segregation
c)
independent assortment
d)
incomplete dominance

|
Uday Iyer answered |
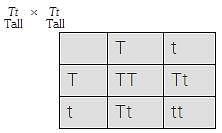
In F2 -3 tall : 1 dwarf This is the law of segregation. 1 Homozygous tall 1 Homozygous dwarf 2 Heterozygous tall.
Alleles of a gene are found on :-- a)same chromosome
- b)any chromosomes
- c)homologous chromosomes
- d)nonhomologous chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Alleles of a gene are found on :-
a)
same chromosome
b)
any chromosomes
c)
homologous chromosomes
d)
nonhomologous chromosomes

|
Aditi Choudhury answered |
An allele is a two form of a gene which carries the contrasting characters. In a diploid organism, one that has two copies of each chromosome, two alleles make up the individual's genotype. Two allelic genes are located on two homologous chromosomes.
When a gene exists in more than one form, the different forms are termed :-- a)alleles
- b)heterozygotes
- c)genotypes
- d)complementary genes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a gene exists in more than one form, the different forms are termed :-
a)
alleles
b)
heterozygotes
c)
genotypes
d)
complementary genes

|
Saxena Aastha answered |
An allele is one of at least two alternative forms of a particular gene.
so correct option is A
Sex of a child is determined by- a)diet of mother
- b)cytoplasm of egg
- c)type of sperm fertilising the egg
- d)health of mother
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sex of a child is determined by
a)
diet of mother
b)
cytoplasm of egg
c)
type of sperm fertilising the egg
d)
health of mother
|
|
Ritika Pandey answered |
Men determine the sex of a child depending on whether their sperm is carrying X or Y chromosomes.
An X chromosome combines with mother's X chromosome to make a baby girl ( XX) and a Y chromosomes will combine with mother's to make a boy ( XY).
An X chromosome combines with mother's X chromosome to make a baby girl ( XX) and a Y chromosomes will combine with mother's to make a boy ( XY).
Mendel crossed a pure white flowered recessive pea plant with a dominant pure red flowered plant. The first generation of hybrids from the cross should show :-- a)50% white flowers and 50% red flowers
- b)all red flowered plants
- c)75% red flowered and 25% red flowered plants
- d)all white flowered plants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mendel crossed a pure white flowered recessive pea plant with a dominant pure red flowered plant. The first generation of hybrids from the cross should show :-
a)
50% white flowers and 50% red flowers
b)
all red flowered plants
c)
75% red flowered and 25% red flowered plants
d)
all white flowered plants

|
Janhavi Chakraborty answered |
All red flowered plants; according to Mendel's law of dominance.
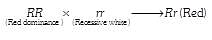
If a couple has three daughters, what are the chances that the fourth child will be a son ?- a)100%
- b)75%
- c)50%
- d)0%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a couple has three daughters, what are the chances that the fourth child will be a son ?
a)
100%
b)
75%
c)
50%
d)
0%
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Almost everyone has around a 50% chance of having a boy and a 50% chance of having a girl. What we can say is that dad's sperm determines whether a baby will be a boy or a girl. About half of his sperm will make a boy and half a girl. The sex of the baby depends on which sperm gets to the egg first.
Chapter doubts & questions for DNA & Genes - Science for Year 10 2024 is part of Year 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Year 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Year 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of DNA & Genes - Science for Year 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Year 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Year 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Year 10
30 videos|121 docs|28 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup