All Exams >
Grade 9 >
History for Grade 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Nazism and the Rise of Hitler for Grade 9 Exam
Who among the given were called "November Criminals" ? - a)Bolsheviks
- b)Jews
- c)Nazis
- d)Socialists, Catholics and Democrats
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bolsheviks
b)
Jews
c)
Nazis
d)
Socialists, Catholics and Democrats
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
The first world war had a devastating impact on the entire Europe both psychology and financially. From a continent of creditors, Europe turned into one of debtors. unfortunately the infant Weimar republic was being made to pay for the sin of the old empire. The republic carried the burden of war guilt and national humiliation and way financially crippled by being forced to pay compensation. Those who supported the weimar republic, mainly socialist, Catholic and democrats, became easy target in the conservative nationalist circle. They were mockingly called November criminals.
Which of the following was the immediate factor for the Great Depression (1929-1932) ? - a)Collapse of Wall Street Exchange
- b)Financial Impact of World War I
- c)Fall in US exports
- d)Collapse of banks
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Collapse of Wall Street Exchange
b)
Financial Impact of World War I
c)
Fall in US exports
d)
Collapse of banks
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 was the greatest stock market crash in the history of the United States. It happened in the New York Stock Exchangeon Tuesday October 29, 1929, now known as Black Tuesday. Bank failures followed, resulting in businesses closing, which started the Great Depression.
What was Jungvolk ? - a)Nazi youth group for children below 14 years
- b)Nazi youth group for children above 14 years
- c)It was the other name for Youth League
- d)It referred to the undesirable German children
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What was Jungvolk ?
a)
Nazi youth group for children below 14 years
b)
Nazi youth group for children above 14 years
c)
It was the other name for Youth League
d)
It referred to the undesirable German children
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The Deutsches Jung volk in der Hitler judged was a separate section for boys aged 10 to 14 of the Hitler youth organization in Nazi Germany.
Which of the following can best define Nazism?
- a)Extermination of Jews
- b)Hitler's determination to make Germany a great nation
- c)A system, a structure of ideas about the world and politics
- d)Hitler's ambition of conquering the world
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can best define Nazism?
a)
Extermination of Jews
b)
Hitler's determination to make Germany a great nation
c)
A system, a structure of ideas about the world and politics
d)
Hitler's ambition of conquering the world
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Nazism is best defined as a system, a structure of ideas about the world and politics. Nazism, also known as National Socialism, was the ideology of the Nazi Party in Germany that led to and sustained World War II. It was an extreme form of fascism that incorporated fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, and totalitarianism. Other aspects such as Hitler's determination to make Germany a great nation, the extermination of Jews, and ambition of conquering the world were components or consequences of this ideology, but not comprehensive definitions of Nazism itself.
What was not a factor in the rise of Hitler ?
- a)Birth of Weimer Republic
- b)Nazi propoganda and Hitler's charismatic leadership
- c)Years of Depression and Economic crisis
- d)Death of the President Hindenburg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What was not a factor in the rise of Hitler ?
a)
Birth of Weimer Republic
b)
Nazi propoganda and Hitler's charismatic leadership
c)
Years of Depression and Economic crisis
d)
Death of the President Hindenburg
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
- The rise of Hitler to power was influenced by multiple factors:
- Birth of Weimar Republic: Created political instability and dissatisfaction among Germans.
- Nazi Propaganda and Hitler's Leadership: Used to gain mass support and manipulate the public.
- Years of Depression and Economic Crisis: Weakened the economy and increased desperation among the populace.
- Death of President Hindenburg was not a factor in Hitler's rise but rather a key event that solidified his power, allowing him to become Führer.
- Birth of Weimar Republic: Created political instability and dissatisfaction among Germans.
- Nazi Propaganda and Hitler's Leadership: Used to gain mass support and manipulate the public.
- Years of Depression and Economic Crisis: Weakened the economy and increased desperation among the populace.
- Death of President Hindenburg was not a factor in Hitler's rise but rather a key event that solidified his power, allowing him to become Führer.
In what ways did the First World War leave a deep imprint on European society and polity ?- a)Soldiers were put above civilians, trench-life was glorified
- b)Politicians and publicists laid stress on men to be aggressive and masculine
- c)Aggressive war propaganda and national honour were given the most support and Conservative dictatorships were welcomed
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In what ways did the First World War leave a deep imprint on European society and polity ?
a)
Soldiers were put above civilians, trench-life was glorified
b)
Politicians and publicists laid stress on men to be aggressive and masculine
c)
Aggressive war propaganda and national honour were given the most support and Conservative dictatorships were welcomed
d)
All the above
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The First World War left a deep imprint on European society and polity.
Soldiers came to be placed above civilians.Politicians and publicists laid great success on the need for men to be aggressive, strong and masculine.The media glorified trench life but actually soldiers lived miserable lives in these trenches, trapped with rats feeding on corpses.They faced poisonous gas and enemy shelling, and witnessed their ranks reduce rapidly.Aggressive war propaganda and national honour occupied centre stage in the public sphere, while popular support grew for conservative dictatorships that had recently come into being.
Soldiers came to be placed above civilians.Politicians and publicists laid great success on the need for men to be aggressive, strong and masculine.The media glorified trench life but actually soldiers lived miserable lives in these trenches, trapped with rats feeding on corpses.They faced poisonous gas and enemy shelling, and witnessed their ranks reduce rapidly.Aggressive war propaganda and national honour occupied centre stage in the public sphere, while popular support grew for conservative dictatorships that had recently come into being.
Which of the following was not a feature of the new Nazi style of politics ? - a)Massive rallies
- b)Ritualised applause
- c)Red banners with Swastika
- d)Not so powerful speeches of Hitler
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Massive rallies
b)
Ritualised applause
c)
Red banners with Swastika
d)
Not so powerful speeches of Hitler
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Three features of the new style of politics:
I) placed a lot of emphasis on rituals, propagand, spectacles to mobilise people.
ii) rallies and public meeting held were held to support for hitler and instill a sense of unity among people.
iii)red banners with swastika nazi salute rounds of applause after speeches were part of spectacle of power.
World War II began with German invasion of ?- a)Poland
- b)Belgium
- c)Austria
- d)Czechoslovakia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Poland
b)
Belgium
c)
Austria
d)
Czechoslovakia
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
The German-Soviet Pact of August 1939, which stated that Poland was to be partitioned between the two powers, enabled Germany to attack Poland without the fear of Soviet intervention. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. The Polish army was defeated within weeks of the invasion.
When did Hitler try to seize control of Bavaria and capture Berlin?- a)1919
- b)1929
- c) 1923
- d)1933
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When did Hitler try to seize control of Bavaria and capture Berlin?
a)
1919
b)
1929
c)
1923
d)
1933

|
Oviya Senthil answered |
In 1923 Hitler plan to seize control of Mahavira and mast Berlin to capture the power but he failed in that plan and it right for presence and was arrested and later released without any issue
The following statements are about Hitler’s early life. Which of them is incorrect?- a)Hitler was born in 1889 in Austria and spent his youth in poverty
- b)He joined the army during World War I and earned accolades for bravery
- c)He was totally unaffected by German defeat in the war and only thought of improving his career
- d)In 1919 he joined a small group called the German Workers' Party, which later was known
as the Nazi Party.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following statements are about Hitler’s early life. Which of them is incorrect?
a)
Hitler was born in 1889 in Austria and spent his youth in poverty
b)
He joined the army during World War I and earned accolades for bravery
c)
He was totally unaffected by German defeat in the war and only thought of improving his career
d)
In 1919 he joined a small group called the German Workers' Party, which later was known
as the Nazi Party.
as the Nazi Party.
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The German defeat horrified him. The Treaty of Versailles made him furious. He joined the German Workers Party and renamed it National Socialist German Workers’ Party. This later came to be known as the Nazi Party.
According to the Nazis, which people were to be regarded as desirable?
- a)Pure and healthy Nordic Aryans
- b)German soldiers who helped in territorial expansion.
- c)German police of different types.
- d)All the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the Nazis, which people were to be regarded as desirable?
a)
Pure and healthy Nordic Aryans
b)
German soldiers who helped in territorial expansion.
c)
German police of different types.
d)
All the above.
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Nazis wanted only a society of ‘pure and healthy Nordic Aryans’. They alone were considered ‘desirable’. Only they were seen as worthy of prospering and multiplying against all others who were classed as ‘undesirable’. This meant that even those Germans who were seen as impure or abnormal had no right to exist.
Which of the following statements is false about soldiers in the World War I?- a)The soldiers, in reality, led miserable lives in trenches, survived with feeding on the copras
- b)They faced poisonous gas and enemy shelling and loss of comrades
- c)All soldiers were ready to die for their country’s honour and personal glory
- d)Aggressive propaganda glorified war
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false about soldiers in the World War I?
a)
The soldiers, in reality, led miserable lives in trenches, survived with feeding on the copras
b)
They faced poisonous gas and enemy shelling and loss of comrades
c)
All soldiers were ready to die for their country’s honour and personal glory
d)
Aggressive propaganda glorified war
|
|
Zeba Isani answered |
C
The International War Tribunal was set up in ?- a)Vienna
- b)Munich
- c)Nuremberg
- d)Auschwitz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Vienna
b)
Munich
c)
Nuremberg
d)
Auschwitz
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The four major Allied powers—France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States—set up the International Military Tribunal (IMT) in Nuremberg, Germany, to prosecute and punish “the major war criminals of the European Axis.”
What is the name of the world’s biggest stock exchange located in the USA? - a)World trade centre
- b)Wall street Exchange
- c)World Exchange market
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the name of the world’s biggest stock exchange located in the USA?
a)
World trade centre
b)
Wall street Exchange
c)
World Exchange market
d)
None of these
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
B is the correct option.Wall Street is a street located in the lower Manhattan section of New York City that is the home of the New York Stock Exchange or NYSE. The New York Stock Exchange is the largest stock exchange in the world, with an equity market capitalization over 25 trillion U.S. dollars in April 2020.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:The crisis in the economy, policy and society formed the background to Hitler's rise to power. Born in 1889 in Austria, Hitler spent his youth in poverty. When the First World War broke out, he enrolled for the army, acted as a messenger in the front, became a corporal, and earned medals for bravery. The German defeat horrified him and the Versailles Treaty made him furious. In 1919; he joined a small group called the German Workers' Party. He subsequently took over the organisation and renamed it the National Socialist German Workers' Party. This Party came to be known as the Nazi Party.In 1923, Hitler planned to seize control of Bavaria, march to Berlin and capture power. He failed, was arrested, tried for treason, and later released. The Nazis could not effectively mobilise popular support till the early 1930s. It was during the Great Depression that Nazism became a mass movement. As we have seen, after 1929, banks collapsed and businesses shut down, workers lost their jobs and the middle classes were threatened with destitution. In such a situation Nazi Propaganda stirred hopes of a better future. In 1928, the Nazi Party got no more than 2.6 per cent votes in the Reichstag – The German Parliament. By 1932, it had become the largest Party with 37 per cent votes.Q. When did Hitler join the German Workers' Party?- a)In 1914
- b)In 1919
- c)In 1916
- d)In 1918
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
The crisis in the economy, policy and society formed the background to Hitler's rise to power. Born in 1889 in Austria, Hitler spent his youth in poverty. When the First World War broke out, he enrolled for the army, acted as a messenger in the front, became a corporal, and earned medals for bravery. The German defeat horrified him and the Versailles Treaty made him furious. In 1919; he joined a small group called the German Workers' Party. He subsequently took over the organisation and renamed it the National Socialist German Workers' Party. This Party came to be known as the Nazi Party.
In 1923, Hitler planned to seize control of Bavaria, march to Berlin and capture power. He failed, was arrested, tried for treason, and later released. The Nazis could not effectively mobilise popular support till the early 1930s. It was during the Great Depression that Nazism became a mass movement. As we have seen, after 1929, banks collapsed and businesses shut down, workers lost their jobs and the middle classes were threatened with destitution. In such a situation Nazi Propaganda stirred hopes of a better future. In 1928, the Nazi Party got no more than 2.6 per cent votes in the Reichstag – The German Parliament. By 1932, it had become the largest Party with 37 per cent votes.
Q. When did Hitler join the German Workers' Party?
a)
In 1914
b)
In 1919
c)
In 1916
d)
In 1918
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
Frustrated by Germany's defeat in the war, which left the nation economically depressed and politically unstable, Hitler joined a fledgling organization called the German Workers' Party in 1919.
The National Assembly met at Weimer and decided to establish- a)a democratic constitution with a federal structure
- b)a communist form of government
- c)a powerful monarchy
- d)a military state
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The National Assembly met at Weimer and decided to establish
a)
a democratic constitution with a federal structure
b)
a communist form of government
c)
a powerful monarchy
d)
a military state
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The Weimar National Assembly (German: Weimarer Nationalversammlung) was the constitutional convention and de facto parliament of Germany from 6 February 1919 to 6 June 1920. The assembly drew up the new constitution which was in force from 1919 to 1933, technically remaining in effect even until the end of Nazi rule in 1945. It convened in Weimar, Thuringia and is the reason for this period in German history becoming known as the Weimar Republic.
With the end of the First World War and the start of the November Revolution, Chancellor Max of Baden announced the abdication of the German Emperor Wilhelm II on 9 November 1918. He also appointed Friedrich Ebert as his own successor as Chancellor. The Council of the People's Deputies, a provisional government consisting of three delegates from the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and three from the Independent Social Democratic Party (USPD), took over the executive power on the following day and called for a National Congress of Councils on 16 to 21 December to convene in Berlin. This Reichsrätekongress set elections for a national assembly to take place on 19 January 1919.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:In May 1945, Germany surrendered to the Allies. Anticipating what was coming, Hitler, his propaganda minister Goebbels and his entire family committed suicide collectively in his Berlin bunker in April. At the end of the war, an International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg was set up to prosecute Nazi War Criminals for Crimes against Peace, for War Crimes and Crimes Against Humanity. Germany's conduct during the war, especially those actions which came to be called Crimes Against Humanity, raised serious moral and ethical questions and invited worldwide condemnation. What were these acts?Under the shadow of the Second World War, Germany had waged a Genocidal war, which resulted in the mass murder of selected groups of innocent civilians of Europe. The number of people killed included 6 million Jews, 200,000 Gypsies, 1 million Polish Civilians, 70,000 Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled, besides innumerable political opponents. Nazis devised an unprecedented means of killing people, that is, by gassing them in various killing centres like Auschwitz. The Nuremberg Tribunal sentenced only eleven leading Nazis to death. Many others were imprisoned for life. The retribution did come, yet the punishment of the Nazis was far short of the brutality and extent of their crimes. The Allies did not want to be as harsh on defeated Germany as they had been after the First World War.Q. When did Germany surrender to the Allies?- a)In July 1945
- b)In May 1945
- c)In March 1945
- d)In June 1945
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
In May 1945, Germany surrendered to the Allies. Anticipating what was coming, Hitler, his propaganda minister Goebbels and his entire family committed suicide collectively in his Berlin bunker in April. At the end of the war, an International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg was set up to prosecute Nazi War Criminals for Crimes against Peace, for War Crimes and Crimes Against Humanity. Germany's conduct during the war, especially those actions which came to be called Crimes Against Humanity, raised serious moral and ethical questions and invited worldwide condemnation. What were these acts?
Under the shadow of the Second World War, Germany had waged a Genocidal war, which resulted in the mass murder of selected groups of innocent civilians of Europe. The number of people killed included 6 million Jews, 200,000 Gypsies, 1 million Polish Civilians, 70,000 Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled, besides innumerable political opponents. Nazis devised an unprecedented means of killing people, that is, by gassing them in various killing centres like Auschwitz. The Nuremberg Tribunal sentenced only eleven leading Nazis to death. Many others were imprisoned for life. The retribution did come, yet the punishment of the Nazis was far short of the brutality and extent of their crimes. The Allies did not want to be as harsh on defeated Germany as they had been after the First World War.
Q. When did Germany surrender to the Allies?
a)
In July 1945
b)
In May 1945
c)
In March 1945
d)
In June 1945
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
German armed forces surrendered unconditionally in the west on May 7 and in the east on May 9, 1945. Victory in Europe Day (V-E Day) was proclaimed on May 8, 1945, amid celebrations in Washington, London, Moscow, and Paris.
The Treaty of Versailles (1920) signed at the end of World War I, was harsh and humiliating for Germany, because- a)Germany lost its overseas colonies, and 13 percent of its territories
- b)It lost 75% of its iron and 26% of its coal to France, Poland, Denmark and Lithuania, was forced to pay compensation of 6 billion pounds
- c)The western powers demilitarised Germany and they occupied resource-rich Rhineland in the 1920s
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Treaty of Versailles (1920) signed at the end of World War I, was harsh and humiliating for Germany, because
a)
Germany lost its overseas colonies, and 13 percent of its territories
b)
It lost 75% of its iron and 26% of its coal to France, Poland, Denmark and Lithuania, was forced to pay compensation of 6 billion pounds
c)
The western powers demilitarised Germany and they occupied resource-rich Rhineland in the 1920s
d)
All the above
|
|
Roshni Shah answered |
It was harsh and humiliating because Germany lost its overseas colonies, a tenth of its population, 13% of its territories, 75% of its iron and 26% of its coal to France, Poland, Denmark, and Lithuania.
The Allied powers demilitarised Germany to weaken its powers.
The War Guilt Clause held Germany responsible for the war damages that the Allied countries had to suffer.
Germany was forced to pay a compensation of 6 billion.
The Allied armies also occupied the resource-rich Rhineland for much of the 1920s.
Many Germans held the Weimar Republic responsible for not only the defeat in the war but the disgrace at Versailles.
The Allied powers demilitarised Germany to weaken its powers.
The War Guilt Clause held Germany responsible for the war damages that the Allied countries had to suffer.
Germany was forced to pay a compensation of 6 billion.
The Allied armies also occupied the resource-rich Rhineland for much of the 1920s.
Many Germans held the Weimar Republic responsible for not only the defeat in the war but the disgrace at Versailles.
Which of the following was a special surveillance and security force created by Hitler ?- a)Regular police force in green uniform and stormtroopers
- b)Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads)
- c)Criminal police (SD), the security service
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was a special surveillance and security force created by Hitler ?
a)
Regular police force in green uniform and stormtroopers
b)
Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads)
c)
Criminal police (SD), the security service
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Prasad Chatterjee answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - both (b) and (c).
Explanation:
The special surveillance and security force created by Hitler included both the Gestapo (secret state police) and the SS (the protection squads), as well as the Criminal Police (SD) and the Security Service.
1. Gestapo (secret state police):
The Gestapo was the official secret state police of Nazi Germany. It was established in 1933 and operated until the end of World War II in 1945. The primary purpose of the Gestapo was to identify and suppress any opposition or resistance to Hitler's regime. The Gestapo had extensive powers to arrest, interrogate, and imprison individuals suspected of treason, espionage, or any other activities deemed threatening to the Nazi regime.
2. SS (the protection squads):
The SS, or Schutzstaffel, was initially created as Hitler's personal bodyguard unit. However, it expanded its role and became one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. The SS was responsible for various tasks, including internal security, intelligence gathering, and maintaining control over concentration camps and the Holocaust. They played a major role in implementing Hitler's policies and carrying out acts of violence and repression.
3. Criminal Police (SD):
The Criminal Police, or SD (Sicherheitsdienst), was the intelligence agency of the SS. It was responsible for collecting information, conducting investigations, and monitoring potential threats to the Nazi regime. The SD played a crucial role in identifying and eliminating political opponents and gathering intelligence on various groups and individuals.
4. Security Service:
The Security Service, or Sicherheitsdienst, was also a part of the SS. It was responsible for gathering intelligence, conducting surveillance, and carrying out counterintelligence activities. The Security Service played a significant role in maintaining internal security and suppressing any form of dissent or opposition.
In summary, Hitler created a special surveillance and security force that included the Gestapo, the SS, the Criminal Police (SD), and the Security Service. These organizations were instrumental in maintaining Hitler's control, suppressing opposition, and carrying out acts of violence and repression during the Nazi regime.
Explanation:
The special surveillance and security force created by Hitler included both the Gestapo (secret state police) and the SS (the protection squads), as well as the Criminal Police (SD) and the Security Service.
1. Gestapo (secret state police):
The Gestapo was the official secret state police of Nazi Germany. It was established in 1933 and operated until the end of World War II in 1945. The primary purpose of the Gestapo was to identify and suppress any opposition or resistance to Hitler's regime. The Gestapo had extensive powers to arrest, interrogate, and imprison individuals suspected of treason, espionage, or any other activities deemed threatening to the Nazi regime.
2. SS (the protection squads):
The SS, or Schutzstaffel, was initially created as Hitler's personal bodyguard unit. However, it expanded its role and became one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. The SS was responsible for various tasks, including internal security, intelligence gathering, and maintaining control over concentration camps and the Holocaust. They played a major role in implementing Hitler's policies and carrying out acts of violence and repression.
3. Criminal Police (SD):
The Criminal Police, or SD (Sicherheitsdienst), was the intelligence agency of the SS. It was responsible for collecting information, conducting investigations, and monitoring potential threats to the Nazi regime. The SD played a crucial role in identifying and eliminating political opponents and gathering intelligence on various groups and individuals.
4. Security Service:
The Security Service, or Sicherheitsdienst, was also a part of the SS. It was responsible for gathering intelligence, conducting surveillance, and carrying out counterintelligence activities. The Security Service played a significant role in maintaining internal security and suppressing any form of dissent or opposition.
In summary, Hitler created a special surveillance and security force that included the Gestapo, the SS, the Criminal Police (SD), and the Security Service. These organizations were instrumental in maintaining Hitler's control, suppressing opposition, and carrying out acts of violence and repression during the Nazi regime.
What was the response of the Germans to the new Weimar Republic?- a)They held the new Weimar Republic responsible for Germany’s defeat and the disgrace at Versailles
- b)The republic carried the burden of war guilt and national humiliation
- c)It became the target of attacks in the conservative national circles
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the response of the Germans to the new Weimar Republic?
a)
They held the new Weimar Republic responsible for Germany’s defeat and the disgrace at Versailles
b)
The republic carried the burden of war guilt and national humiliation
c)
It became the target of attacks in the conservative national circles
d)
All the above
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Germany emerged from World War I with huge debts incurred to finance a costly war for almost five years. The treasury was empty, the currency was losing value, and Germany needed to pay its war debts and the huge reparations bill imposed on it by the Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended the war.
The separately marked areas for Jews were called as _______.Correct answer is 'Ghettos'. Can you explain this answer?
The separately marked areas for Jews were called as _______.
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Jews were the worst sufferers in Nazi-Germany. They survived mainly through trade and money-lending. They lived in separately marked areas called ghettos. They were often persecuted through periodic organised violence, and expulsion from the land.
The German parliament was known as:- a)National Parliament
- b)German Legislature
- c)Reichstag
- d)Estates General
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The German parliament was known as:
a)
National Parliament
b)
German Legislature
c)
Reichstag
d)
Estates General
|
|
Priyal Reddy answered |
The German parliament was known as the Reichstag. This legislative body was established in 1871, following the unification of Germany under the leadership of Chancellor Otto von Bismarck. The Reichstag was responsible for passing laws and approving the national budget, and its members were elected through a system of proportional representation.
History of the Reichstag
The Reichstag was first convened in 1871, and it continued to play a central role in German politics until its dissolution in 1933. During this time, the Reichstag faced a number of challenges and crises, including the rise of the Nazi Party in the 1920s and 1930s.
One of the most significant events in the history of the Reichstag was the Reichstag Fire of 1933, which was used by the Nazis as a pretext to seize power and establish a dictatorship. Following the fire, the Nazis suspended civil liberties and began to systematically persecute their political opponents.
Re-establishment of the Reichstag
After the fall of the Nazi regime in 1945, the Reichstag was re-established as the parliament of West Germany. Following the reunification of Germany in 1990, the Reichstag became the parliament of the unified German state.
Today, the Reichstag is known as the Bundestag, and it is located in Berlin. The Bundestag is responsible for representing the interests of the German people and passing laws that affect the country as a whole. Its members are elected through a system of proportional representation, and the Bundestag is considered to be one of the most powerful parliaments in Europe.
History of the Reichstag
The Reichstag was first convened in 1871, and it continued to play a central role in German politics until its dissolution in 1933. During this time, the Reichstag faced a number of challenges and crises, including the rise of the Nazi Party in the 1920s and 1930s.
One of the most significant events in the history of the Reichstag was the Reichstag Fire of 1933, which was used by the Nazis as a pretext to seize power and establish a dictatorship. Following the fire, the Nazis suspended civil liberties and began to systematically persecute their political opponents.
Re-establishment of the Reichstag
After the fall of the Nazi regime in 1945, the Reichstag was re-established as the parliament of West Germany. Following the reunification of Germany in 1990, the Reichstag became the parliament of the unified German state.
Today, the Reichstag is known as the Bundestag, and it is located in Berlin. The Bundestag is responsible for representing the interests of the German people and passing laws that affect the country as a whole. Its members are elected through a system of proportional representation, and the Bundestag is considered to be one of the most powerful parliaments in Europe.
Arrange the following events in chronological order:(1) Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles.(2) Establishment of the Weimar Republic.(3) The Economic Depression occurs in the USA.(4) Adolf Hitler was born in Austria.- a)1 – 2 – 4 – 3
- b)4 – 3 – 2 – 1
- c)4 – 2 – 1 – 3
- d)1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following events in chronological order:
(1) Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles.
(2) Establishment of the Weimar Republic.
(3) The Economic Depression occurs in the USA.
(4) Adolf Hitler was born in Austria.
a)
1 – 2 – 4 – 3
b)
4 – 3 – 2 – 1
c)
4 – 2 – 1 – 3
d)
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
|
|
Sagnik Menon answered |
The correct chronological order of the events is:
(4) Adolf Hitler was born in Austria.
(2) Establishment of the Weimar Republic.
(1) Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles.
(3) The Economic Depression occurs in the USA.
Explanation:
Adolf Hitler was born in Austria:
Adolf Hitler, the future dictator of Germany, was born in Braunau am Inn, Austria, on April 20, 1889.
Establishment of the Weimar Republic:
After the end of World War I, the German Empire was replaced by the Weimar Republic. The Weimar Republic was established on August 11, 1919, following the signing of the Treaty of Versailles.
Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles:
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919. It was a peace treaty that officially ended World War I. As part of the treaty, Germany was held responsible for the war and was subjected to severe economic and territorial penalties.
The Economic Depression occurs in the USA:
The Great Depression, an economic crisis that affected many countries around the world, including Germany, began in the United States in October 1929. It was characterized by a severe decline in economic activity, high unemployment rates, and financial instability.
In summary, Adolf Hitler was born before any of the other events took place. The Weimar Republic was established after World War I, and Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles as part of the peace settlement. The Great Depression occurred several years later in the United States. Therefore, the correct chronological order is 4-2-1-3.
(4) Adolf Hitler was born in Austria.
(2) Establishment of the Weimar Republic.
(1) Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles.
(3) The Economic Depression occurs in the USA.
Explanation:
Adolf Hitler was born in Austria:
Adolf Hitler, the future dictator of Germany, was born in Braunau am Inn, Austria, on April 20, 1889.
Establishment of the Weimar Republic:
After the end of World War I, the German Empire was replaced by the Weimar Republic. The Weimar Republic was established on August 11, 1919, following the signing of the Treaty of Versailles.
Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles:
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919. It was a peace treaty that officially ended World War I. As part of the treaty, Germany was held responsible for the war and was subjected to severe economic and territorial penalties.
The Economic Depression occurs in the USA:
The Great Depression, an economic crisis that affected many countries around the world, including Germany, began in the United States in October 1929. It was characterized by a severe decline in economic activity, high unemployment rates, and financial instability.
In summary, Adolf Hitler was born before any of the other events took place. The Weimar Republic was established after World War I, and Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles as part of the peace settlement. The Great Depression occurred several years later in the United States. Therefore, the correct chronological order is 4-2-1-3.
German defeat in World War I ?- a)led to the establishment of the Weimer Republic
- b)adoption of declaration of rights of man and citizens
- c)establishment of Nazi rule
- d)restoration of monarchy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
led to the establishment of the Weimer Republic
b)
adoption of declaration of rights of man and citizens
c)
establishment of Nazi rule
d)
restoration of monarchy
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
In November 1918, with internal revolution, a stalemated war, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire suing for peace, Austria-Hungary falling apart from multiple ethnic tensions, and pressure from the German high command, the Kaiser and all German ruling princes abdicated. On 9 November 1918, the Social Democrat Philipp Scheidemann proclaimed a Republic, in cooperation with the business and middle classes, not the revolting workers. The new government led by the German Social Democrats called for and received an armistice on 11 November 1918; in practice it was a surrender, and the Allies kept up the food blockade to guarantee an upper hand. The war was over; the history books closed on the German Empire. It was succeeded by the democratic, yet flawed, Weimar Republic.
Seven million soldiers and sailors were quickly demobilized, and they became a conservative voice that drowned out the radical left in cities such as Kiel and Berlin. The radicals formed the Spartakusbund and later the Communist Party of Germany.
Germany lost the war because it was decisively defeated by a stronger military power; it was out of soldiers and ideas, and was losing ground every day by October 1918. Nevertheless, it was still in France when the war ended on Nov. 11 giving die-hard nationalists the chance to blame the civilians back home for betraying the army and surrendering. This was the false "Stab-in-the-back legend" that soured German politics in the 1920s and caused a distrust of democracy and the Weimar government
Germany’s ‘genocidal war’ was against which of the following people ?- a)Jews and political opponents
- b)Gypsies and Polish civilians
- c)Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Germany’s ‘genocidal war’ was against which of the following people ?
a)
Jews and political opponents
b)
Gypsies and Polish civilians
c)
Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled
d)
All the above
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
Germany's 'genocidal war' was against which of the following people?
The correct answer is option D: All of the above.
Explanation:
During World War II, Germany under Nazi rule carried out a genocidal war against multiple groups of people. The following groups were systematically targeted:
- Jews and political opponents: The Nazi regime implemented a policy of anti-Semitism, leading to the persecution, discrimination, and ultimately the genocide of six million Jews. They were considered a threat to the Aryan race and were subjected to mass murder in concentration camps and extermination camps like Auschwitz.
- Gypsies and Polish civilians: The Romani people, commonly known as Gypsies, were also targeted for extermination by the Nazis. They were subjected to forced labor, sterilization, and mass murder in concentration camps. Additionally, the Germans targeted Polish civilians, particularly intellectuals, resistance fighters, and anyone perceived as a threat to German occupation.
- Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled: The Nazi regime implemented a eugenics program that aimed to eliminate individuals with disabilities. Thousands of mentally and physically disabled Germans were forcibly sterilized, euthanized, or subjected to medical experiments.
Therefore, Germany's 'genocidal war' during World War II targeted Jews, political opponents, Gypsies, Polish civilians, and Germans with disabilities. The correct answer is option D: All of the above.
The correct answer is option D: All of the above.
Explanation:
During World War II, Germany under Nazi rule carried out a genocidal war against multiple groups of people. The following groups were systematically targeted:
- Jews and political opponents: The Nazi regime implemented a policy of anti-Semitism, leading to the persecution, discrimination, and ultimately the genocide of six million Jews. They were considered a threat to the Aryan race and were subjected to mass murder in concentration camps and extermination camps like Auschwitz.
- Gypsies and Polish civilians: The Romani people, commonly known as Gypsies, were also targeted for extermination by the Nazis. They were subjected to forced labor, sterilization, and mass murder in concentration camps. Additionally, the Germans targeted Polish civilians, particularly intellectuals, resistance fighters, and anyone perceived as a threat to German occupation.
- Germans who were considered mentally and physically disabled: The Nazi regime implemented a eugenics program that aimed to eliminate individuals with disabilities. Thousands of mentally and physically disabled Germans were forcibly sterilized, euthanized, or subjected to medical experiments.
Therefore, Germany's 'genocidal war' during World War II targeted Jews, political opponents, Gypsies, Polish civilians, and Germans with disabilities. The correct answer is option D: All of the above.
State whether True or False:The Jewish population was largely discriminated against under the rule of Hitler.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether True or False:
The Jewish population was largely discriminated against under the rule of Hitler.
a)
True
b)
False

|
prateek patil answered |
Yes check pg 50 of ncert u will find answer
it says he killed 6million jew near 70 percent of the population
it was because Weimar republic had almost all jew and he thought these jew cocroches signed Versailles treaty due to which his country suffered a lot
it says he killed 6million jew near 70 percent of the population
it was because Weimar republic had almost all jew and he thought these jew cocroches signed Versailles treaty due to which his country suffered a lot
What was the most important result of the Spartacus League uprising in Germany in 1918-19 ?- a)The Weimar Republic crushed the rebellion
- b)The Spartacists founded the Communist Party of Germany
- c)The Weimar government accepted the demands of the Spartacus League
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the most important result of the Spartacus League uprising in Germany in 1918-19 ?
a)
The Weimar Republic crushed the rebellion
b)
The Spartacists founded the Communist Party of Germany
c)
The Weimar government accepted the demands of the Spartacus League
d)
Both (a) and (b)

|
Debanshi Chopra answered |
The Spartacist League was a political party that opposed the Weimer Republic in Germany. They were in favour of a Soviet-style governance. However, they could not achieve the success as they were opposed by the Socialists, Democrats, Catholics and severely crushed by the Free Corps.
Assertion (A): The Nazi regime used carefully crafted language and media to propagate their ideologies.Reason (R): The Nazis avoided using direct terms like 'kill' or 'murder' in their official communications, employing euphemisms like 'special treatment' or 'final solution' instead.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The Nazi regime used carefully crafted language and media to propagate their ideologies.
Reason (R): The Nazis avoided using direct terms like 'kill' or 'murder' in their official communications, employing euphemisms like 'special treatment' or 'final solution' instead.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Let's Tute answered |
- The Assertion is true since the Nazi regime indeed utilized language and media meticulously to spread their ideologies.
- The Reason is also true as the Nazis refrained from direct terms like 'kill' or 'murder', opting for more euphemistic language.
- However, Reason does not directly explain why the Nazis used carefully crafted language and media; it provides a specific example of their use of euphemisms but does not fully account for the broader strategy of propaganda. Thus, Option B is correct: both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the direct explanation of the Assertion
State whether True or False:The Fascist Party was founded under the leadership of Adolf Hitler.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether True or False:
The Fascist Party was founded under the leadership of Adolf Hitler.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Aditi Sharma answered |
On July 29, 1921, Adolf Hitler becomes the leader of the National Socialist German Workers' (Nazi) Party. Under Hitler, the Nazi Party grew into a mass movement and ruled Germany as a totalitarian state from 1933 to 1945.
State whether True or False:The Nazi Ideology believed in equality.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether True or False:
The Nazi Ideology believed in equality.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
According to Nazi ideology there was no equality between people, but only racial hierarchy. The Nazis quickly began to implement their dream of creating an exclusive racial community of pure Germans by physically eliminating all those who were considered undesirable. They wanted a society of pure and healthy Nordic Aryans. Jews, Gypsies, blacks, Russian, Poles, even certain Germans and abnormal were considered undesirable.
Why did the Nuremburg Tribunal sentence only 11 Nazis to death for such a massive genocide?- a)Only these 11 Nazis were found guilty
- b)The Allies did not want to be harsh on the defeated Germany as they had been after World War I
- c)Germany promised never to repeat such an act
- d)Germany was ready to pay a huge compensation to the Allied countries for these killings
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why did the Nuremburg Tribunal sentence only 11 Nazis to death for such a massive genocide?
a)
Only these 11 Nazis were found guilty
b)
The Allies did not want to be harsh on the defeated Germany as they had been after World War I
c)
Germany promised never to repeat such an act
d)
Germany was ready to pay a huge compensation to the Allied countries for these killings
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
The correct answer is "B". Actually,they did not want to repeat the same mistakes that they did after the World War I. The world war II was a way through which the citizens of Nazi Germany sought to take revenge for their humiliation and disgrace caused by the treaty of versailles. In order to avoid such situations,Nuremberg Tribunal decided not to be harsh on them as they had been earlier. Maybe they felt guilty about it.
When was the Nazi Party formed?- a)1919
- b)1920
- c)1921
- d)1922
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When was the Nazi Party formed?
a)
1919
b)
1920
c)
1921
d)
1922
|
|
Mohit Malik answered |
The Nazi Party emerged from the German nationalist, racist and populist Freikorps paramilitary culture, which fought against the communist uprisings in post-World War I Germany in 1920.
Which of the following was the most feared security force of the Nazi State ? - a)Storm Troopers (SA)
- b)Protection Squads (SS)
- c)Gestapo
- d)Security Service
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Storm Troopers (SA)
b)
Protection Squads (SS)
c)
Gestapo
d)
Security Service
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
Besides the existing regular police and the SA or Storm Troopers, special surveillance and security forces like the Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads), criminal police and the Security Service (SD) were created to control and order society. Out of these, the Gestapo was the most feared security force of the Nazi state.
Who among the following topped the list of undesirables' ? - a)Blacks
- b)Jews
- c)Gypsies
- d)Nordic Aryans
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Blacks
b)
Jews
c)
Gypsies
d)
Nordic Aryans
|
|
Sonam rao answered |
Jews topped the list of undesirables. At first, the Nazis boycotted Jewish businesses for one day in April 1933. Then legislation excluded Jews from certain professions. The Nuremberg Laws created very detailed Nazi definitions of who was Jewish. Many people who never considered themselves Jewish suddenly became targets of Nazi persecution.
Which of the following statements is correct?- a)In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between Germany, Italy and Japan
- b)In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between England, France and Russia
- c)In September 1939 a Tripartite Pact was signed between England, France and U.S.A
- d)In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between USA, Russia and Japan
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct?
a)
In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between Germany, Italy and Japan
b)
In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between England, France and Russia
c)
In September 1939 a Tripartite Pact was signed between England, France and U.S.A
d)
In September 1940, a Tripartite Pact was signed between USA, Russia and Japan

|
Kruthi Shetty answered |
Option A is correct. Germany Italy and France were the axis powers and fought against allied powers in world war 2.
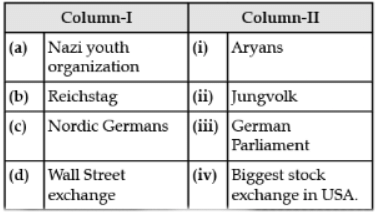
Choose the correct option from Column-I and Column-II: Correct answer is 'b'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is 'b'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct option from Column-I and Column-II:


|
Ishika Anand answered |
(a) It's wrong because war veterans Organisation was formed in 1919 not in 1940.
(b) It's right because Treaty of Versailles was signed in 1919 only.
(c) It's wrong because tripartite pact was just a pact signed between Germany, Italy and Japan and it does not give any power to president.
(d) It's wrong because it allowed the President to declare a state of emergency in Germany in times of national danger and to rule as a dictator for short periods of time not free corps.
I hope its helpful.
(b) It's right because Treaty of Versailles was signed in 1919 only.
(c) It's wrong because tripartite pact was just a pact signed between Germany, Italy and Japan and it does not give any power to president.
(d) It's wrong because it allowed the President to declare a state of emergency in Germany in times of national danger and to rule as a dictator for short periods of time not free corps.
I hope its helpful.
Which of the following is not a part of Nazi ideology?- a)Poles are a desirable section of society
- b)Jews were the most inferior and undesirable section of society
- c)Germans are the descendant of Pure Aryan race
- d)Society should be ruled by Nordic Aryans
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of Nazi ideology?
a)
Poles are a desirable section of society
b)
Jews were the most inferior and undesirable section of society
c)
Germans are the descendant of Pure Aryan race
d)
Society should be ruled by Nordic Aryans
|
|
Kalpana Meena answered |
(a) Poles are a desirable section of society.
This sentence is incorrect.
This sentence is incorrect.
Why did Helmuth’s father kill himself in the spring of 1945 ?- a)He was depressed by Germany’s defeat in Second World War
- b)He feared that common people would mishandle him and his family
- c)He feared revenge by the Allied Powers
- d)He wanted to die because of the crimes he had committed during Nazi rule
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why did Helmuth’s father kill himself in the spring of 1945 ?
a)
He was depressed by Germany’s defeat in Second World War
b)
He feared that common people would mishandle him and his family
c)
He feared revenge by the Allied Powers
d)
He wanted to die because of the crimes he had committed during Nazi rule
|
|
Barkha Deoband answered |
Helmuth's father feared that the Allied Powers will take revenge and the Nazis would meet the same fate as the Jews and the crippled
The National Assembly met at Weimar and established a ______ Constitution.Correct answer is 'Democratic'. Can you explain this answer?
The National Assembly met at Weimar and established a ______ Constitution.
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
The Weimar Republic was set up as a representative democracy which tried to give genuine power to all German adults. However, it had major flaws that contributed to its downfall in 1933-34.
State whether True or False:The Great Depression of 1929 contributed to the fall of the Weimar Republic.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether True or False:
The Great Depression of 1929 contributed to the fall of the Weimar Republic.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Rishika Nambiar answered |
The statement is true. The Great Depression of 1929 indeed contributed to the fall of the Weimar Republic. Here's a detailed explanation:
1. Economic Impact:
- The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic crisis that started in the United States in 1929 and quickly spread to other countries. Germany, being heavily dependent on foreign loans and exports, was deeply affected.
- The German economy, already weakened by the consequences of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles, suffered greatly during the Great Depression. Industrial production declined, unemployment soared, and businesses went bankrupt.
- The collapse of the global economy led to a sharp decrease in international trade, negatively impacting Germany's export-oriented economy. This further exacerbated the economic crisis within the country.
2. Political Instability:
- The economic hardships caused by the Great Depression fueled social unrest and political instability in Germany. The Weimar Republic, which had already been facing challenges since its establishment in 1919, was further weakened.
- The German people became disillusioned with the government's inability to address the economic crisis effectively. This led to a loss of confidence in the democratic system and opened the door for extremist political parties to gain support.
- The Nazi Party, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, capitalized on the discontent and promised to restore Germany's economy and national pride. The party's popularity grew significantly during the Great Depression.
3. Rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party:
- The economic turmoil and political instability created by the Great Depression provided fertile ground for the rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party.
- In the elections of 1930 and 1932, the Nazi Party gained a significant number of seats in the Reichstag, Germany's parliament. The party's message of nationalistic fervor, anti-Semitism, and promises of economic recovery resonated with many desperate Germans.
- In 1933, Hitler was appointed as the Chancellor of Germany, and his subsequent consolidation of power led to the downfall of the Weimar Republic, marking the end of democracy in Germany.
In conclusion, the Great Depression of 1929 played a crucial role in the fall of the Weimar Republic. The economic crisis caused by the depression weakened the German economy and created social and political unrest, paving the way for the rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party.
1. Economic Impact:
- The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic crisis that started in the United States in 1929 and quickly spread to other countries. Germany, being heavily dependent on foreign loans and exports, was deeply affected.
- The German economy, already weakened by the consequences of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles, suffered greatly during the Great Depression. Industrial production declined, unemployment soared, and businesses went bankrupt.
- The collapse of the global economy led to a sharp decrease in international trade, negatively impacting Germany's export-oriented economy. This further exacerbated the economic crisis within the country.
2. Political Instability:
- The economic hardships caused by the Great Depression fueled social unrest and political instability in Germany. The Weimar Republic, which had already been facing challenges since its establishment in 1919, was further weakened.
- The German people became disillusioned with the government's inability to address the economic crisis effectively. This led to a loss of confidence in the democratic system and opened the door for extremist political parties to gain support.
- The Nazi Party, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, capitalized on the discontent and promised to restore Germany's economy and national pride. The party's popularity grew significantly during the Great Depression.
3. Rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party:
- The economic turmoil and political instability created by the Great Depression provided fertile ground for the rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party.
- In the elections of 1930 and 1932, the Nazi Party gained a significant number of seats in the Reichstag, Germany's parliament. The party's message of nationalistic fervor, anti-Semitism, and promises of economic recovery resonated with many desperate Germans.
- In 1933, Hitler was appointed as the Chancellor of Germany, and his subsequent consolidation of power led to the downfall of the Weimar Republic, marking the end of democracy in Germany.
In conclusion, the Great Depression of 1929 played a crucial role in the fall of the Weimar Republic. The economic crisis caused by the depression weakened the German economy and created social and political unrest, paving the way for the rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:Political Radicalism and Economic CrisesPolitical Radicalisation was only heightened by the economic crisis of 1923. Germany had fought the war largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in Gold. This depleted gold reserves at a time resources were scarce. In 1923 Germany refused to pay, and the French occupied its leading Industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much printed money in circulation, the value of the German Mark fell. In April the US Dollar was equal to 24,000 Marks, in July 353,000 Marks, in August 4,621,000 Marks and at 98,860,000 Marks by December, the figure had run into trillions. As the value of the Mark collapsed, prices of goods soared. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicised evoking worldwide sympathy. This crisis came to be known as hyperinflation, a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.Q. Germany had fought the War largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in:- a)Gold
- b)Silver
- c)Currency
- d)Coal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Political Radicalism and Economic Crises
Political Radicalisation was only heightened by the economic crisis of 1923. Germany had fought the war largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in Gold. This depleted gold reserves at a time resources were scarce. In 1923 Germany refused to pay, and the French occupied its leading Industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much printed money in circulation, the value of the German Mark fell. In April the US Dollar was equal to 24,000 Marks, in July 353,000 Marks, in August 4,621,000 Marks and at 98,860,000 Marks by December, the figure had run into trillions. As the value of the Mark collapsed, prices of goods soared. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicised evoking worldwide sympathy. This crisis came to be known as hyperinflation, a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.
Q. Germany had fought the War largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in:
a)
Gold
b)
Silver
c)
Currency
d)
Coal
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Germany had fought the war largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in gold. This depleted gold reserves at a time resources were scarce. In 1923 Germany refused to pay and the French occupied its leading industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much currency in circulation, the value of the German mark fell. As the value of Mark collapsed, prices of goods soared.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:Political Radicalism and Economic CrisesPolitical Radicalisation was only heightened by the economic crisis of 1923. Germany had fought the war largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in Gold. This depleted gold reserves at a time resources were scarce. In 1923 Germany refused to pay, and the French occupied its leading Industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much printed money in circulation, the value of the German Mark fell. In April the US Dollar was equal to 24,000 Marks, in July 353,000 Marks, in August 4,621,000 Marks and at 98,860,000 Marks by December, the figure had run into trillions. As the value of the Mark collapsed, prices of goods soared. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicised evoking worldwide sympathy. This crisis came to be known as hyperinflation, a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.Q. What is the currency of Germany called?- a)Rupee
- b)Pound
- c)Dollar
- d)Mark
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Political Radicalism and Economic Crises
Political Radicalisation was only heightened by the economic crisis of 1923. Germany had fought the war largely on loans and had to pay war reparations in Gold. This depleted gold reserves at a time resources were scarce. In 1923 Germany refused to pay, and the French occupied its leading Industrial area, Ruhr, to claim their coal. Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much printed money in circulation, the value of the German Mark fell. In April the US Dollar was equal to 24,000 Marks, in July 353,000 Marks, in August 4,621,000 Marks and at 98,860,000 Marks by December, the figure had run into trillions. As the value of the Mark collapsed, prices of goods soared. The image of Germans carrying cartloads of currency notes to buy a loaf of bread was widely publicised evoking worldwide sympathy. This crisis came to be known as hyperinflation, a situation when prices rise phenomenally high.
Q. What is the currency of Germany called?
a)
Rupee
b)
Pound
c)
Dollar
d)
Mark
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Germany's currency is the Euro. Germany has been using the euro since 2002. The mark of the euro is € and the code is EUR. The country's currency before 2002 is Deutsche Mark.
When was the Treaty of veriailles signed ? - a)1917
- b)1918
- c)1919
- d)1920
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When was the Treaty of veriailles signed ?
a)
1917
b)
1918
c)
1919
d)
1920

|
Sumit Bidlan answered |
After the world war 1 (1914-1918) this treaty was signed ..
Chapter doubts & questions for Nazism and the Rise of Hitler - History for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Nazism and the Rise of Hitler - History for Grade 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
History for Grade 9
17 videos|70 docs|23 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily