All Exams >
Biotechnology Engineering (BT) >
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Biochemistry for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam
If the value of ΔH and ΔS are positive, which of the following statements will be true.- a)Process will be spontaneous at any given temperature.
- b)Process will be spontaneous at high temperature only
- c)Process will never be spontaneous
- d)Process will be spontaneous at low temperature only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the value of ΔH and ΔS are positive, which of the following statements will be true.
a)
Process will be spontaneous at any given temperature.
b)
Process will be spontaneous at high temperature only
c)
Process will never be spontaneous
d)
Process will be spontaneous at low temperature only
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Option (a) is correct as according to Gibb's free energy equation ΔG = ΔH - TΔS.
Now if. ΔH = —ve (as given in option (a)) (at low temperature) and ΔS = +ve.
then ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
option (b) is correct if
ΔH = +ve (as given in option (b)) and ΔS = +ve. Also if ΔS > ΔH (conditional), then ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
Option (c) is correct
If ΔS = —ve (as given in option (c)) and ΔH = -ve. Also ΔH > ΔS (conditional) then. ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
Now if. ΔH = —ve (as given in option (a)) (at low temperature) and ΔS = +ve.
then ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
option (b) is correct if
ΔH = +ve (as given in option (b)) and ΔS = +ve. Also if ΔS > ΔH (conditional), then ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
Option (c) is correct
If ΔS = —ve (as given in option (c)) and ΔH = -ve. Also ΔH > ΔS (conditional) then. ΔG = -ve (spontaneous)
What is true about the Gibbs free energy change at equilibrium?- a)The value of ΔG° is zero at equilibrium
- b)The value of ΔG is zero at equilibrium
- c)The value of ΔG° is minimum at equilibrium
- d)Both b and c are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about the Gibbs free energy change at equilibrium?
a)
The value of ΔG° is zero at equilibrium
b)
The value of ΔG is zero at equilibrium
c)
The value of ΔG° is minimum at equilibrium
d)
Both b and c are correct
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The value of Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is zero at equilibrium as the direction of reaction is neither forward nor backward at equilibrium. However, the value of standard Gibbs fr ee energy change (ΔG°) cannot be zero at equilibrium unless the value of equilibrium constant is one (that will be a special case). However at equilibrium ΔG° is minimum
(We define ΔG° (pronounced “delta G naught prime*’) as the fr ee energy change of a reaction under “standard conditions" which are defined as:
(We define ΔG° (pronounced “delta G naught prime*’) as the fr ee energy change of a reaction under “standard conditions" which are defined as:
- All reactants and products are at an initial concentration of 1.0M
- Pressure of 1.0 atm
- Temperature is 25°C
Which of the following is true about DNA variants- a)B DNA has 34 Angstrom rise per turn
- b)Z DNA has two base pairs as repeating units
- c)A DNA is formed in excess of humidity
- d)A DNA has 2’ endo sugar puckering
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about DNA variants
a)
B DNA has 34 Angstrom rise per turn
b)
Z DNA has two base pairs as repeating units
c)
A DNA is formed in excess of humidity
d)
A DNA has 2’ endo sugar puckering
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Option (a) is correct. B DNA has 10.5 base pairs per helical turn and helix rise per base pair in B DNA is 3.4 Aº. Therefore rise per turn in B DNA will be 34 Å.
Option (b) is correct.
Z DNA is formed by DNA sequences in which pyrimidines alternate with purines especially alternating C and G. Hence Z DNA has GC as repeating unit.
Option (c) and (d) are incorrect as B DNA is formed in excess of humidity (92%). A DNA has 3’ endo sugar puckering.
Option (b) is correct.
Z DNA is formed by DNA sequences in which pyrimidines alternate with purines especially alternating C and G. Hence Z DNA has GC as repeating unit.
Option (c) and (d) are incorrect as B DNA is formed in excess of humidity (92%). A DNA has 3’ endo sugar puckering.
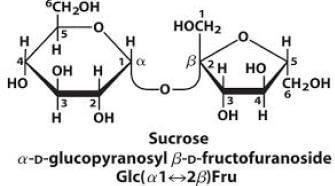
Sucrose, also known as table sugar is one of the most commonly used carbohydrate as a sweetener. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose. The kind of linkage that is found in sucrose is- a)1 → 2 Glycosidic linkage
- b)1 → 3 Glycosidic linkage
- c)1 → 4 Glycosidic linkage
- d)1 → 6 Glycosidic linkage
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sucrose, also known as table sugar is one of the most commonly used carbohydrate as a sweetener. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose. The kind of linkage that is found in sucrose is
a)
1 → 2 Glycosidic linkage
b)
1 → 3 Glycosidic linkage
c)
1 → 4 Glycosidic linkage
d)
1 → 6 Glycosidic linkage
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The glucose and fructose in sucrose are linked by glucose 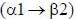 fructose linkage.
fructose linkage.
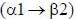 fructose linkage.
fructose linkage.
Which of the following options consist of combination of inhibitors which inhibit the same target.- a)Amytal, rotenone, carbon monoxide
- b)Antimycin, carbon monoxide, atractyloside
- c)Antimycin, rotenone, malonate
- d)Carbon monoxide, cyanide ion, azide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options consist of combination of inhibitors which inhibit the same target.
a)
Amytal, rotenone, carbon monoxide
b)
Antimycin, carbon monoxide, atractyloside
c)
Antimycin, rotenone, malonate
d)
Carbon monoxide, cyanide ion, azide
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |

The number of ATP needed for the preparatory phase of glycolysis for glycolytic breakdown of 12 glucose molecule is_______________ [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '24'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ATP needed for the preparatory phase of glycolysis for glycolytic breakdown of 12 glucose molecule is_______________ [Answer in integer]
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
For one molecule of glucose, there is requirement of two ATP molecules in preparatory phase, therefore for 12 molecules of glucose, 24 ATP will be required.
The net optical rotation of a solution containing 20% sucrose hydrolyzed into glucose and fructose during the process of sugar inversion is _____________
Given – Optical activity of Glucose = + 52.7, Fructose = –92.0 and Sucrose = + 66.7).
Correct answer is between '45.4,45.6'. Can you explain this answer?
The net optical rotation of a solution containing 20% sucrose hydrolyzed into glucose and fructose during the process of sugar inversion is _____________
Given – Optical activity of Glucose = + 52.7, Fructose = –92.0 and Sucrose = + 66.7).
Given – Optical activity of Glucose = + 52.7, Fructose = –92.0 and Sucrose = + 66.7).
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
In order to calculate the net optical activity add the contribution of each component
(20% sucrose was hydrolyzed means – 20% glucose, 20% fructose and 80 % sucrose)
0.2 x 52.7 – 92 x .2 + 0.8 x 66.7 = 45.5
(20% sucrose was hydrolyzed means – 20% glucose, 20% fructose and 80 % sucrose)
0.2 x 52.7 – 92 x .2 + 0.8 x 66.7 = 45.5
Which of the following carbohydrates would be the most abundant in the diet of strict vegetarians?- a)Amylose
- b)Lactose
- c)Cellulose
- d)Maltose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates would be the most abundant in the diet of strict vegetarians?
a)
Amylose
b)
Lactose
c)
Cellulose
d)
Maltose

|
Milan Majumdar answered |
Cellulose, the most abundant compound known, is the structural fiber of plants and bacterial walls. It is a polysaccharide consisting of chains of glucose residues linked by β 1 → 4 bonds. Since humans do not have intestinal hydrolases that attack β 1 → 4 linkages, cellulose cannot be digested but forms an important source of “bulk" in the diet. Lactose is a disaccharide of glucose and galactose found in milk. Amylose is an unbranched polymer of glucose residues in α-1.4 linkages. Glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose with both α-1.4 and α-1, 6 linkages. Maltose is a disaccharide of glucose, which is usually the breakdown pro duct of amylose.
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starch - a)Alpha D glucose
- b)Beta D glucose
- c)Alpha L glucose
- d)Beta L glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starch
a)
Alpha D glucose
b)
Beta D glucose
c)
Alpha L glucose
d)
Beta L glucose
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Starch is made up of repeating units of alpha D glucose. In aqueous solution, glucose occurs predominantly as cyclic (ring) structure in which the carbonyl group of glucose forms a covalent bond with oxygen of hydroxyl group at C-5 position of the same glucose molecule, resulting in formation of hemiacetal winch contains an additional asymmetric carbon atom. Thus cyclic form of glucose can exist in two stereoisomeric forms called α and β. Therefore, anomers are isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon atom

Number of ATP generated by beta oxidation of palmitic acid in peroxisomes.- a)106
- b)104
- c)20
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of ATP generated by beta oxidation of palmitic acid in peroxisomes.
a)
106
b)
104
c)
20
d)
Zero
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
In peroxisomes, beta oxidation do not produce any ATP due to the fact that FADH is not coupled to ATP generation.
This sugar is extracted from the roots of Dahelia and many other tuberous plants and useful in the determination of Glomerular filteration rate of kidneys. - a)Trehalose
- b)Vervascose
- c)Inulin
- d)Gentibiose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
This sugar is extracted from the roots of Dahelia and many other tuberous plants and useful in the determination of Glomerular filteration rate of kidneys.
a)
Trehalose
b)
Vervascose
c)
Inulin
d)
Gentibiose
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Inulin is useful as an indicator of GFR because the kidneys handle it in a unique way. Unlike most other substances in the blood, inulin is neither reabsorbed into the blood after filtration nor secreted through peritubular capillaries.
The number of hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule that has 500 base pairs and whose 20% of the total bases are Guanosine is __________________ [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '1200'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule that has 500 base pairs and whose 20% of the total bases are Guanosine is __________________ [Answer in integer]

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
Provided that there are 500 base pairs, which means 1000 bases, and if 20% are G, i.e. 200 are G hence, C will also be 200. Remaining 600 will be A and T (300 A and 300 T), so total number of AT pairs = 300 and total GC pairs = 200. Each AT pair has two hydrogen bonds and Each GC pair has 3 hydrogen bonds. So, total number of hydrogen bonds will be (300 x 2) + (200 x 3) = 1200.
Which of the following nitrogen bases has the highest number of nitrogen atoms - a)Adenine
- b)Cytosine
- c)Uracil
- d)Thymine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following nitrogen bases has the highest number of nitrogen atoms
a)
Adenine
b)
Cytosine
c)
Uracil
d)
Thymine

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Adenine has the highest number of nitrogen atoms. Its chemical name is 6-amino purine. A purine ring has 4 nitrogen atoms and additionally there is one amino group. Hence, total 5 nitrogen atoms. While cytosine has 3 nitrogen atoms, uracil and thymine have 2 nitrogen atoms each. The number of nitrogen atoms in Guanine is also 5 (not given in option).


Which of the following molecules produces highest energy on breakdown of its high energy bond- a)ATP
- b)Acetyl CoA
- c)PEP
- d)ADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules produces highest energy on breakdown of its high energy bond
a)
ATP
b)
Acetyl CoA
c)
PEP
d)
ADP

|
Sravya Mehta answered |
ATP produces high amount of energy, yet it is not the highest free energy molecule. The free energy of ATP hydrolysis is – 30 kJ per mole, while PEP has much higher energy of breakdown i.e. ~ 54 kJ per mole.
Which of the following sugars is a non- reducing sugar- a)Sucrose
- b)Trehalose
- c)Glucose
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following sugars is a non- reducing sugar
a)
Sucrose
b)
Trehalose
c)
Glucose
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
A reducing sugar is capable of acting as a reducing agent, because it has free aldehyde or a free ketone group. Sucrose and trehalose both don’t have free aldehyde and ketone group, so they are non-reducing.
Which of the following is a disaccharide.- a)Inulin
- b)Raffinose
- c)Trehalose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a disaccharide.
a)
Inulin
b)
Raffinose
c)
Trehalose
d)
Cellulose

|
Bhavana Pillai answered |
Trehalose, is a disachharides that is made up of α -D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 1)-α -D-glucopyranoside units. While inulin is polysaccharides, raffinose is trisaccharide and cellulose is polysaccharides.

Osazone are formed by a chemical reaction between carbohydrates containing a free aldehyde or keto group and- a)Phenyl hydrazine
- b)Sulphuric acid
- c)Mercaptoethanol
- d)Hydroxylamine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Osazone are formed by a chemical reaction between carbohydrates containing a free aldehyde or keto group and
a)
Phenyl hydrazine
b)
Sulphuric acid
c)
Mercaptoethanol
d)
Hydroxylamine

|
Om Desai answered |
Carbohydrates reaction with phenyl hydrazine leads to the formation of Osazone.
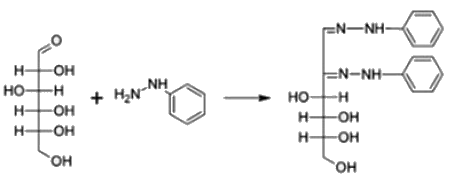
All reducing sugars form osazones. Glucose is a reducing sugar hence it forms osazone. Sucrose does not form osazone crystals because it is a non-reducing sugar as it has no free carbonyl group. Sucrose is made
up of glucose and fructose. The linkage in sucrose is Glucose

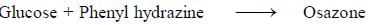
All reducing sugars form osazones. Glucose is a reducing sugar hence it forms osazone. Sucrose does not form osazone crystals because it is a non-reducing sugar as it has no free carbonyl group. Sucrose is made
up of glucose and fructose. The linkage in sucrose is Glucose
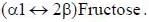
Which of the following combinations represent the correct set of charge on different phospholipids [PC: phosphotidylcholine; PS: Phosphotidylserine, PE: Phosphotidylethanolamine, CL: cardiolipin]- a)PC : 1 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: 0
- b)PC : -1 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 1 ; CL: -2
- c)PC : 0 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: -2
- d)PC : 0 ; PS: -1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: -2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following combinations represent the correct set of charge on different phospholipids [PC: phosphotidylcholine; PS: Phosphotidylserine, PE: Phosphotidylethanolamine, CL: cardiolipin]
a)
PC : 1 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: 0
b)
PC : -1 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 1 ; CL: -2
c)
PC : 0 ; PS: 1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: -2
d)
PC : 0 ; PS: -1 ; PE: 0 ; CL: -2

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
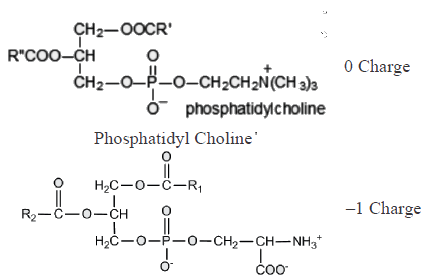
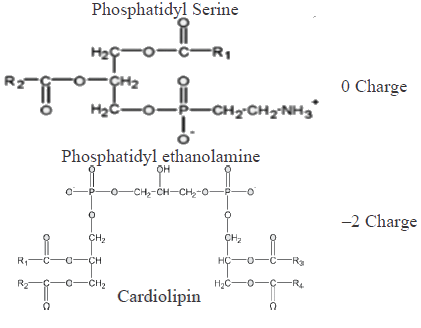
Which of the following amino acids cannot be converted to glucose.- a)Aspartate
- b)Glutamate
- c)Lysine
- d)Alanine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acids cannot be converted to glucose.
a)
Aspartate
b)
Glutamate
c)
Lysine
d)
Alanine

|
Sparsh Menon answered |
Amino acids which can be converted to glucose are called glucogenic amino acids and amino acids which cannot be converted to glucose are called ketogenic amino acids. Aspartate on deamination can produce oxaloacetic acid, while glutamate on deamination can produce alpha-ketogluterate, both of which are TCA cycle intermediates and can be converted to glucose. Lysine is ketogenic in nature. Lysine and leucine are the only amino acids which are exclusively ketogenic in nature.
Lecithin and cephalins are the alternate names for
- a)Phosphotidylcholine and phosphotidylionositol respectively
- b)phophatidylethanolamine and phosphotidylserine respectively
- c)Phosphotidylserine and phosphotidylionositol respectively
- d)Phosphotidylserine and Phosphotidylcholine respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lecithin and cephalins are the alternate names for
a)
Phosphotidylcholine and phosphotidylionositol respectively
b)
phophatidylethanolamine and phosphotidylserine respectively
c)
Phosphotidylserine and phosphotidylionositol respectively
d)
Phosphotidylserine and Phosphotidylcholine respectively

|
Bhavana Dasgupta answered |
Lecithin and cephalin are glycerophospholipids.The are abundant in brain and nerve tissues. Lecithin contains choline and cephalin contains serine. Lecithin is a mixture of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol. Cephalin is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidyl serine.
The pI for a polyelectrolyte that contains three carboxyl groups and three amino groups whose pKa values are 4.0, 4.6, 6.3, 7.7, 8.9, and 10.2 is _______________
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
The pI for a polyelectrolyte that contains three carboxyl groups and three amino groups whose pKa values are 4.0, 4.6, 6.3, 7.7, 8.9, and 10.2 is _______________

|
Jay Nambiar answered |
Example the pI is a pH midway between the 3rd and 4th pKa values: pI = (6.3 + 7.7)/2 = 7.0. To confirm this conclusion, imagine how the net charge on the molecule will change as the solution is adjusted from strongly acidic to strongly basic pH. As the carboxylate groups and subsequently the ammonium groups begin to ionize, the net charge will change successively as follows: +3, +2, +1, 0, “1, “2, “3.
A 250 mg sample of pure oil requires 47.5 mg of KOH for complete saponification. The average MW of the triglycerides in the olive oil is________. (Answer in integer)
Correct answer is '884'. Can you explain this answer?
A 250 mg sample of pure oil requires 47.5 mg of KOH for complete saponification. The average MW of the triglycerides in the olive oil is________. (Answer in integer)

|
Palak Singh answered |
Amount of KOH required = 47.5 x 10-3/ 56g mole = 8.482 x 10-4 moles
It takes 3 moles of KOH for each mole of triglyceride
Amount of triglyceride present = 8.482 x 10-4/3 = 2.828 x 10-4moles
No. of moles = wt/MW or MW = wt/no. of moles
MW = 250 x 10-5/2.827 x 104 = 884
It takes 3 moles of KOH for each mole of triglyceride
Amount of triglyceride present = 8.482 x 10-4/3 = 2.828 x 10-4moles
No. of moles = wt/MW or MW = wt/no. of moles
MW = 250 x 10-5/2.827 x 104 = 884
The net charge on the following peptide at pH 1 is _________________.
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
The net charge on the following peptide at pH 1 is _________________.

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
At pH 1 the charge distribution on the peptide will be as follows:
NH3+-Ala-Asp-Asn-Ile-Pro-Gln-Thr-Agr-COOH
Note that every peptide is written from amino to carboxy terminal, and at a very low pH such as 1 every side chain and main chain ionizable groups will be protonated. Hence net change will be decided by amino groups, as the sequence contain one basic amino acid (arginine) and only alanine contain free amino group, so the charge is due to positively charged amino group.
NH3+-Ala-Asp-Asn-Ile-Pro-Gln-Thr-Agr-COOH
Note that every peptide is written from amino to carboxy terminal, and at a very low pH such as 1 every side chain and main chain ionizable groups will be protonated. Hence net change will be decided by amino groups, as the sequence contain one basic amino acid (arginine) and only alanine contain free amino group, so the charge is due to positively charged amino group.
It is given that B DNA has 1000 base pairs and each turn is at 10 bp. Also the DNA has twenty negative supercoils in it. The linking number of this B DNA is ______________[Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '80'. Can you explain this answer?
It is given that B DNA has 1000 base pairs and each turn is at 10 bp. Also the DNA has twenty negative supercoils in it. The linking number of this B DNA is ______________[Answer in integer]

|
Pragati Sharma answered |
Linking number is sum of twist and writhe. Lk = Tw + Wr
Twist = number of times one strand crosses other i.e. total number of base pairs/bp per turn
i.e 1000/10 = 100 = Lk
Writhe = –20 (negative sign for negative supercoil, positive sign for positive supercoil)
So, linking number = 100 – 20 = 80.
Twist = number of times one strand crosses other i.e. total number of base pairs/bp per turn
i.e 1000/10 = 100 = Lk
Writhe = –20 (negative sign for negative supercoil, positive sign for positive supercoil)
So, linking number = 100 – 20 = 80.
The olive oil was reacted with iodine. The average MW of triglycerides present in the olive oil is 884 g. Exactly 578 mg of I2 were absorbed by 680 mg of the oil. On an average, the number of double bonds that are present in a molecule of triglyceride are _______ (Answer in integer)
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The olive oil was reacted with iodine. The average MW of triglycerides present in the olive oil is 884 g. Exactly 578 mg of I2 were absorbed by 680 mg of the oil. On an average, the number of double bonds that are present in a molecule of triglyceride are _______ (Answer in integer)

|
Maitri Sen answered |
0.578 g of I2/0.680 g oil = Wt I2/894 g oil
Wt I2 absorbed = (884)(0.578)/(0.680) = 751.4 g I2 per mole of oil
MW of I2 = (2) (126.9) = 253.8
751.4 g I2 / 253.8 g/mole = 2.96 moles I2/mole of oil
Thus on average there are three double bond per molecule of triglyceride.
Wt I2 absorbed = (884)(0.578)/(0.680) = 751.4 g I2 per mole of oil
MW of I2 = (2) (126.9) = 253.8
751.4 g I2 / 253.8 g/mole = 2.96 moles I2/mole of oil
Thus on average there are three double bond per molecule of triglyceride.
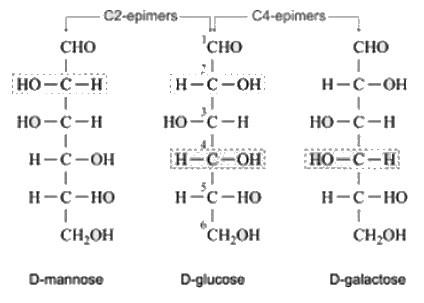
Which of the following is the correct combination of C-2 epimer and C-4 epimer of Glucose respectively.- a)Galactose, mannose
- b)Mannose, galactose
- c)Vervascose, mannose
- d)Idose, galactose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct combination of C-2 epimer and C-4 epimer of Glucose respectively.
a)
Galactose, mannose
b)
Mannose, galactose
c)
Vervascose, mannose
d)
Idose, galactose

|
Anushka Basak answered |
Epimers are the pair of carbohydrates that have difference in the rotation of atoms across single carbon atom. If they differ across 2nd carbon atoms, molecules are named as C-2 Epimers. If they differ across 4th carbon atoms, molecules are named as C-4 Epimers.

Which of the following amino acid is not needed for nucleotide biosynthesis- a)Histidine
- b)Glycine
- c)Glutamine
- d)Aspartate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acid is not needed for nucleotide biosynthesis
a)
Histidine
b)
Glycine
c)
Glutamine
d)
Aspartate

|
Shail Ghoshal answered |
Glycine, glutamine and aspartate provide one or more atoms to the nucleotide backbone (especially purines), however, histidine does not contribute to nucleotide biosynthesis.
In a radioactive labelling based tracer technique carbon 1 of glucose was labelled and products were evaluated, which of the following statements are true.- a)Only 50% of the pyruvate molecules will have radioactivity
- b)All the pyruvate molecules will be labelled
- c)Carbon dioxide released during the formation of acetyl CoA will be radiolabelled.
- d)Radioactivity will also be observed in the acetyl coA
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a radioactive labelling based tracer technique carbon 1 of glucose was labelled and products were evaluated, which of the following statements are true.
a)
Only 50% of the pyruvate molecules will have radioactivity
b)
All the pyruvate molecules will be labelled
c)
Carbon dioxide released during the formation of acetyl CoA will be radiolabelled.
d)
Radioactivity will also be observed in the acetyl coA

|
Madhavan Iyer answered |
Carbon 1 or the glucose is retained in 50% of the pyruvate molecules. While C3 and C4 make carbon dioxide. Therefore only 50% of the pyruvate will have radioactivity and it will also be observed in acetyl CoA, but not in carbon dioxide.
The number of base pairs in the B-DNA molecule of size 6.8 nm is _____________ [Answer in integer]
(Consider 10 bp per turn in B-DNA)
Correct answer is '20'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of base pairs in the B-DNA molecule of size 6.8 nm is _____________ [Answer in integer]
(Consider 10 bp per turn in B-DNA)
(Consider 10 bp per turn in B-DNA)

|
Varun Yadav answered |
No. of bp per turn = 10
Rise per base pair = 3.4Å
Rise per turn = 3.4Å x 10 = 34Å
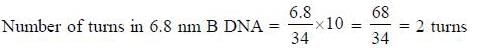
1 turn = 10 base pairs
2 turns = 20 base pairs
Rise per base pair = 3.4Å
Rise per turn = 3.4Å x 10 = 34Å
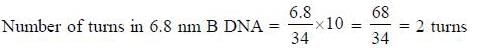
1 turn = 10 base pairs
2 turns = 20 base pairs
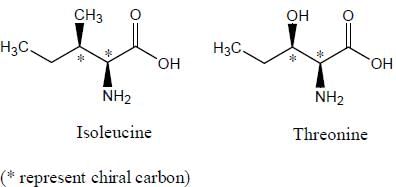
Which of the following amino acids will have Diastereomers.- a)Isoleucine
- b)Threonine
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acids will have Diastereomers.
a)
Isoleucine
b)
Threonine
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
None

|
Aashna Shah answered |
Stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers.
Diastereomers are present only in those molecules which have more than one chiral carbon atoms, and isoleucine as well as threonine both have two chiral centers. Since both threonine and isoleucine have two chiral centres each, maximum number of stereoisomers in each case will be 2n = 22 = 4 (n is the number of chiral centres).
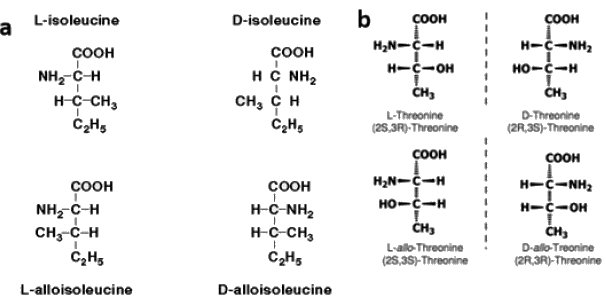
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers.
Diastereomers are present only in those molecules which have more than one chiral carbon atoms, and isoleucine as well as threonine both have two chiral centers. Since both threonine and isoleucine have two chiral centres each, maximum number of stereoisomers in each case will be 2n = 22 = 4 (n is the number of chiral centres).


If a DNA molecule was transferred from biological buffer to a low humidity condition (less than 50% humidity) The most likely transition in the biomolecule would be- a)A DNA to B DNA
- b)A DNA to Z DNA
- c)B DNA to A DNA
- d)Z DNA to A DNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a DNA molecule was transferred from biological buffer to a low humidity condition (less than 50% humidity) The most likely transition in the biomolecule would be
a)
A DNA to B DNA
b)
A DNA to Z DNA
c)
B DNA to A DNA
d)
Z DNA to A DNA

|
Amar Chawla answered |
On reducing the humidity below 50% the naturally occurring B-DNA has propensity to form A DNA conformation. B-DNA needs around 30% water by weight, to maintain its native conformation in the crystalline state. Partial dehydration converts B DNA to A-DNA (A DNA has a shallow, wide minor groove and a narrow, deeper major groove). The transition for this transformation occurs at about 20 water molecules per base pair, with its midpoint at about 15 water molecules per base pair (at about 85% relative humidity). The B-DNA possesses a spanning water network, and it is the loss of its continuity together with the competition between hydration and direct cation coupling to the free oxygen atoms in the phosphate groups that give rise to the transition to A-DNA. This dehydration induced structural transition decreases the free energy required for A-DNA deformation and twisting, which is usefully employed by encouraging supercoiling but eventually leads to denaturation. Further dehydration results in the least hydrated D-DNA (favored by excess counter-ions that shield the DNA phosphate charges), which has a very narrow minor groove with a string of alternating water and counter-ions distributed along its edge
Which of the following type of secondary conformation is in the same quadrant of the ramachandran plot- a)Right handed Alpha helix
- b)310 helix
- c)Beta sheets
- d)Left handed alpha helix
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of secondary conformation is in the same quadrant of the ramachandran plot
a)
Right handed Alpha helix
b)
310 helix
c)
Beta sheets
d)
Left handed alpha helix

|
Anushka Basak answered |
Only right handed alpha helix and 310 helix lie in the same quadrant

Ramachandran Plot

Ramachandran Plot
If the number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a sugar are 3, the total number of stereoisomers will be 8. Let us assume that one of the structure is named as pintose, then the number of Diasteromers pintose will have are_________________
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
If the number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a sugar are 3, the total number of stereoisomers will be 8. Let us assume that one of the structure is named as pintose, then the number of Diasteromers pintose will have are_________________

|
Raghav Rane answered |
The number of stereoisomers will be 8 (number of stereoisomers = 2n where n is number of chiral centres). So each molecule will have one enantiomer while remaining will be the Diasteromers. So in this case pintose will have one enantiomer and remaining 6 molecules will be its Diasteromers.
The number of ATP generated from oxidation of one molecule of glucose from TCA cycle is- a)10
- b)12
- c)20
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ATP generated from oxidation of one molecule of glucose from TCA cycle is
a)
10
b)
12
c)
20
d)
8

|
Raghav Rane answered |
One molecule of glucose gives 2 molecules of pyruvate and 2 molecules of pyruvate are further converted into 2 molecules of acetyl CoA. For every molecule of acetyl CoA that enters TCA cycle, 10 ATP are produced because each TCA cycle produces 3NADH, 1FADH and 1GTP [1 NADH = 2.5 ATP and 1FADH = 1.5 ATP]. So 2 molecules of acetyl CoA [produced from one molecule of glucose] will give 10 ATP × 2 = 20 ATP through citric acid cycle.
The isoelectric point of lysine which has pKb 9.06, pKa 2.16 and pKR as 10.54 is ____________[Answer upto two decimal places]
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
- e)
Correct answer is '9.8'. Can you explain this answer?
The isoelectric point of lysine which has pKb 9.06, pKa 2.16 and pKR as 10.54 is ____________[Answer upto two decimal places]
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Isoelectric point: In proteins the isoelectric point (pI) is defined as the pH at which a protein has no net charge.
In case of a basic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKR and is equal to the average of pKb and pKR(10.54+9.06)/2 = 9.77 = ~ 9.8.
In case of an acidic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKa and pKR and is equal to the average of pKa and pKR.
In case of a neutral amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKa and is equal to the average of pKa and pKb.
In case of a basic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKR and is equal to the average of pKb and pKR(10.54+9.06)/2 = 9.77 = ~ 9.8.
In case of an acidic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKa and pKR and is equal to the average of pKa and pKR.
In case of a neutral amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKa and is equal to the average of pKa and pKb.
Total number of known amino acids in biological systems is- a)20
- b)21
- c)22
- d)More than 900
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of known amino acids in biological systems is
a)
20
b)
21
c)
22
d)
More than 900

|
Juhi Sen answered |
There are various groups of amino acids:
• 20 standard amino acids
• 22 proteinogenic amino acids
• Over 80 amino acids created abiotically in high concentrations
• About 900 are produced by natural pathways
• Over 118 engineered amino acids have been placed into protein
• 20 standard amino acids
• 22 proteinogenic amino acids
• Over 80 amino acids created abiotically in high concentrations
• About 900 are produced by natural pathways
• Over 118 engineered amino acids have been placed into protein
Which of the following technique was used for the determination of structure of DNA by Willkins, Watson and Crick?- a)X-ray crystallography
- b)NMR
- c)Surface plasmon resonance
- d)Transmission electron microscopy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following technique was used for the determination of structure of DNA by Willkins, Watson and Crick?
a)
X-ray crystallography
b)
NMR
c)
Surface plasmon resonance
d)
Transmission electron microscopy

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Nucleic acid structure cannot be determined using transmission electron microscopy or surface plasmon resonance. Both NMR and X-ray crystallography can be used to determine the structure of nucleic acids (or other biomolecules), but Wilkins, Watson and crick determined the structure of DNA using X-ray crystallography.
Platelet activation factor found in heart is one of fastest acting biomolecule, with extremely fast rate kinetics. Biochemically PAF is- a)Phospholipid
- b)Sphingolipid
- c)Protein
- d)Plasmalogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Platelet activation factor found in heart is one of fastest acting biomolecule, with extremely fast rate kinetics. Biochemically PAF is
a)
Phospholipid
b)
Sphingolipid
c)
Protein
d)
Plasmalogen

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
It is plasmalogen with ether linkage at C1 and glycerol at C2.Platelet-activating factor, also known as PAF, PAF-acether or AGEPC (acetyl-glyceryl-ether-phosphorylcholine), is a potent phospholipid activator and mediator of many leukocyte functions, platelet aggregation and degranulation, inflammation, and anaphylaxis.
Base pair stacking is a type of stabilizing interaction in the DNA double helix. The exact nature of this interaction is- a)Pi – pi interactions
- b)Hydrophobic interactions
- c)Covalent interactions
- d)Vander Walls interactions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Base pair stacking is a type of stabilizing interaction in the DNA double helix. The exact nature of this interaction is
a)
Pi – pi interactions
b)
Hydrophobic interactions
c)
Covalent interactions
d)
Vander Walls interactions

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
The base pair stacking interaction are the interaction between pi bonds of the adjacent base pairs.The stability of the DNA double helix depends on a fine balance of interactions including hydrogen bonds between bases, hydrogen bonds between bases and surrounding water molecules, and base-stacking interactions between adjacent bases. Inter-strand hydrogen bonding is clearly important in driving the formation of DNA double strands, but it is by no means the only contributing factor. The individual bases form strong stacking interactions which are major contributors to double strand stability, as base stacking is much more prevalent in double strands than in single strands. Base-stacking interactions are hydrophobic and electrostatic in nature, and depend on the aromaticity of the bases and their dipole moments. Base-stacking interactions in nucleic acid double strands are partly inter-strand and partly intra-strand in nature. However, it is probably more informative to consider base pairs rather than individual bases as discrete units in order to visualize the stabilising effects of base stacking.The degree of stabilization afforded by base stacking depends on the DNA sequence. Some combinations of base pairs form more stable interactions than others, so nearest neighbour base-stacking interactions are important determinants of DNA double strand stability.
Base-stacking interactions increase with increasing salt concentration, as high salt concentrations mask the destabilizing charge repulsion between the two negatively charged phosphodiester backbones. DNA double strand stability therefore increases with increasing salt concentration. Divalent cations such as Mg2+ are more stabilising than Na+ ions, and some metal ions bind to specific loci on the DNA duplex.
Base-stacking interactions increase with increasing salt concentration, as high salt concentrations mask the destabilizing charge repulsion between the two negatively charged phosphodiester backbones. DNA double strand stability therefore increases with increasing salt concentration. Divalent cations such as Mg2+ are more stabilising than Na+ ions, and some metal ions bind to specific loci on the DNA duplex.
Which of the following is not true for energy currency of the cell- a)ATP is known as energy currency of cell
- b)It is produced in mitochondria and cytoplasm
- c)It is the molecule with highest Gibbs free energy of hydrolysis
- d)It has three high energy bonds
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true for energy currency of the cell
a)
ATP is known as energy currency of cell
b)
It is produced in mitochondria and cytoplasm
c)
It is the molecule with highest Gibbs free energy of hydrolysis
d)
It has three high energy bonds

|
Pragati Sharma answered |
PEP has the highest Gibb’s energy of hydrolysis and ATP has two high energy bonds.




The number of ATP generated from the complete beta oxidation of C20 fatty acid is _______ [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '136'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ATP generated from the complete beta oxidation of C20 fatty acid is _______ [Answer in integer]

|
Kiran Pillai answered |
C20 fatty acid will produce 10 molecules of acetyl CoA after undergoing 9 oxidation cycle.
No. of acetyl CoA = 20/2 = 10
10 ATP are produced for every acetyl CoA that enters citric acid cycle. Therefore, 10 acetyl CoA will produce 10×10 = 100 ATP
No. of oxidation cycles = 9
1 oxidation cycle produces 1 NADH and 1 FADH each, therefore, the number of NADH and FADH produced from 9 oxidation cycles are as follows:-
NADH = 9
FADH = 9
Net ATP = 10 x10 (10 ATP per Acetyl CoA) + 9 x 2.5 (2.5 ATP per NADH) + 9 x 1.5 (1.5 ATP per FADH molecule) = 136 ATP
No. of acetyl CoA = 20/2 = 10
10 ATP are produced for every acetyl CoA that enters citric acid cycle. Therefore, 10 acetyl CoA will produce 10×10 = 100 ATP
No. of oxidation cycles = 9
1 oxidation cycle produces 1 NADH and 1 FADH each, therefore, the number of NADH and FADH produced from 9 oxidation cycles are as follows:-
NADH = 9
FADH = 9
Net ATP = 10 x10 (10 ATP per Acetyl CoA) + 9 x 2.5 (2.5 ATP per NADH) + 9 x 1.5 (1.5 ATP per FADH molecule) = 136 ATP
Which of the following enzymes involved in transamination reaction are often used for liver function tests- a)Aspartate transaminase
- b)Polynucleotide transferase
- c)Lactate dehydrogenase
- d)Glutamine oxidase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following enzymes involved in transamination reaction are often used for liver function tests
a)
Aspartate transaminase
b)
Polynucleotide transferase
c)
Lactate dehydrogenase
d)
Glutamine oxidase

|
Saikat Ghoshal answered |
Alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase (sGPT and sGOT) are commonly used serum biomarkers for hepatic health.
SGPT (Alanine amino transferase): There is high concentration of SGPT in the liver. This enzyme is present in the cytosolic and mitochondrial forms in the liver. SGPT enzyme is specific for the liver cell necrosis. In case of liver cell necrosis, first cytosolic SGPT is released and then mitochondrial SGPT is released into circulation. There is always a low level of SGPT in the blood under normal conditions. However, the levels of SGPT increase in case of liver disease.
SGOT (Asparate amino transferase) : This enzyme is found in high concentration in liver, heart and skeletal muscles. SGOT is released into circulation in liver diseases. The amount of SGOT is directly related to the number of cells injured.
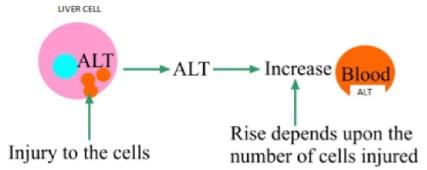
SGPT (Alanine amino transferase): There is high concentration of SGPT in the liver. This enzyme is present in the cytosolic and mitochondrial forms in the liver. SGPT enzyme is specific for the liver cell necrosis. In case of liver cell necrosis, first cytosolic SGPT is released and then mitochondrial SGPT is released into circulation. There is always a low level of SGPT in the blood under normal conditions. However, the levels of SGPT increase in case of liver disease.
SGOT (Asparate amino transferase) : This enzyme is found in high concentration in liver, heart and skeletal muscles. SGOT is released into circulation in liver diseases. The amount of SGOT is directly related to the number of cells injured.

The number of ATP generated from complete oxidative phosphorylation of two moles of acetyl CoA molecules is ______________ [Answer in integer]
Correct answer is '20'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ATP generated from complete oxidative phosphorylation of two moles of acetyl CoA molecules is ______________ [Answer in integer]

|
Abhijeet Majumdar answered |
Each mole of acetyl CoA undergoes a cycle of citric acid pathway and during each citric acid pathway, ten ATPs are generated, so the number of ATP molecules per mole of acetyl CoA will be 10 and for 2 moles of acetyl CoA, the number of moles of ATP would be 20
A new amino acid was found on the surface of moon with no ionizable side chain and pKa value 1.8 and pKb value 9.5. The isoelectric point of this new amino acid is _____________ [Answer upto two decimal places]
Correct answer is between '5.64,5.66'. Can you explain this answer?
A new amino acid was found on the surface of moon with no ionizable side chain and pKa value 1.8 and pKb value 9.5. The isoelectric point of this new amino acid is _____________ [Answer upto two decimal places]

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Isoelectric point in case of no ionizable side chain is the average of pKa and pKb, (1.8+9.5)/2 = 5.65
During a mutarotation experiment, the net optical activity at any given time point was observed as +100o. The absolute optical activity of alpha anomer is +112.2º and beta anomer is +18.7º. The percentage of alpha anomers at that time will be ___________
Correct answer is between '86.7,87.1'. Can you explain this answer?
During a mutarotation experiment, the net optical activity at any given time point was observed as +100o. The absolute optical activity of alpha anomer is +112.2º and beta anomer is +18.7º. The percentage of alpha anomers at that time will be ___________

|
Athul Menon answered |
Let us assume that the percentage of alpha anomer is x, so the percentage of beta anomer will be
100-x. The net optical activity will be the result of individual contribution of each anomer.
i.e. 112.2(x/100) + 18.7 (100-x/100) = 100
112x - 18.7 x = 10000 – 1870
X = 86.9
100-x. The net optical activity will be the result of individual contribution of each anomer.
i.e. 112.2(x/100) + 18.7 (100-x/100) = 100
112x - 18.7 x = 10000 – 1870
X = 86.9
On an average, in an adult human of 70 kg, around 10 kg is fat reserve. It is given that the calorific value of fat is 9 kcal/g and that of glucose is 4 kcal/g. The approximate weight (in kg) of the same human being, if he would have had no fat but stored glucose to generate equivalent energy will be_________ (answer upto one decimal place)
Correct answer is between '82.4,82.6'. Can you explain this answer?
On an average, in an adult human of 70 kg, around 10 kg is fat reserve. It is given that the calorific value of fat is 9 kcal/g and that of glucose is 4 kcal/g. The approximate weight (in kg) of the same human being, if he would have had no fat but stored glucose to generate equivalent energy will be_________ (answer upto one decimal place)

|
Dipanjan Sharma answered |
Out of 70 Kg 10 kg is fat , so remaining wt = 60 kg
Energy produced by 10 kg fat = 10,000 x 9 kcal=90,000Kcal
Amount of glucose needed to produce same amount of energy = 90,000/4 = 22,250 g or 22.5 kg
Hence total weight of the person with same level of energy reserve as glucose will be
60 + 22.5 = 82.5 kg
Energy produced by 10 kg fat = 10,000 x 9 kcal=90,000Kcal
Amount of glucose needed to produce same amount of energy = 90,000/4 = 22,250 g or 22.5 kg
Hence total weight of the person with same level of energy reserve as glucose will be
60 + 22.5 = 82.5 kg
Which of the following information is not derived from first law of thermodynamics - a)Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed
- b)The total change in internal energy is equal to heat involved and work done in a process
- c)During a process of energy conversion some energy is lost as heat
- d)The randomness of the universe is always increasing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following information is not derived from first law of thermodynamics
a)
Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed
b)
The total change in internal energy is equal to heat involved and work done in a process
c)
During a process of energy conversion some energy is lost as heat
d)
The randomness of the universe is always increasing

|
Sahana Roy answered |
Randomness of the universe is always increasing. This is stated in second law of thermodynamics
The Gibbs free energy change for conversion of compound X to Compound Y is 20 kJ mol–1 and it is a non spontaneous reaction.
Also hydrolysis of ATP is a coupled reaction and provides –30 kJ/mol energy on hydrolysis.
From the information given above, the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction
Compound X + ATP —> Compound Y + ADP is__________ (in kJ mol-1) (answer in integer)
Correct answer is '-10'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gibbs free energy change for conversion of compound X to Compound Y is 20 kJ mol–1 and it is a non spontaneous reaction.
Also hydrolysis of ATP is a coupled reaction and provides –30 kJ/mol energy on hydrolysis.
From the information given above, the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction
Compound X + ATP —> Compound Y + ADP is__________ (in kJ mol-1) (answer in integer)
Also hydrolysis of ATP is a coupled reaction and provides –30 kJ/mol energy on hydrolysis.
From the information given above, the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction
Compound X + ATP —> Compound Y + ADP is__________ (in kJ mol-1) (answer in integer)

|
Siddharth Banerjee answered |
X→Y ; ΔG = 20 kJ mol-1 ... (1)
ATP →ADP + pi; ΔG = —30 kJ mot-1 ... (2)
Add reaction (1) and (2)
X + ATP → Y + ADP + p1 ΔG = 20 — 30 = —10 kJ mol-1
In order to calculate the net Gibbs energy of a reaction, if the Gibbs energy of two separate reactions are given, add or substract the two given reactions in such a way that you obtain the desired reaction. In the same way energies are also added or subtracted.
ATP →ADP + pi; ΔG = —30 kJ mot-1 ... (2)
Add reaction (1) and (2)
X + ATP → Y + ADP + p1 ΔG = 20 — 30 = —10 kJ mol-1
In order to calculate the net Gibbs energy of a reaction, if the Gibbs energy of two separate reactions are given, add or substract the two given reactions in such a way that you obtain the desired reaction. In the same way energies are also added or subtracted.
If an amino acid with neutral side chain has pKa value of 3.4 and pKb value of 9.6 at which of the following pH the amino acid will migrate towards anode- a)6
- b)7.4
- c)2.3
- d)3.4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an amino acid with neutral side chain has pKa value of 3.4 and pKb value of 9.6 at which of the following pH the amino acid will migrate towards anode
a)
6
b)
7.4
c)
2.3
d)
3.4

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
The isoelectric point here is the average of pKa and pKb which is (3.4+9.6)/2 = 6.5.
Every amino acid is negatively charged at pH above its pI and move towards Anode (+). So at pH 7.4 the overall charge on amino acid will be negative and it will move towards Anode. Only pH 7.4 is above the isoelectric part of amino acid (isoelectric point = 6.5)
Every amino acid is negatively charged at pH above its pI and move towards Anode (+). So at pH 7.4 the overall charge on amino acid will be negative and it will move towards Anode. Only pH 7.4 is above the isoelectric part of amino acid (isoelectric point = 6.5)
Chapter doubts & questions for Biochemistry - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 2025 is part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biochemistry - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026
7 docs|34 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









