Syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims & Mains | How To Study For UPSC CSE PDF Download

Civil Services Exam (IAS Exam), the most coveted exam of all, is conducted by UPSC every year to recruit candidates to various services & posts in the Government of India.
Stages of UPSC CSE Examination:
UPSC CSE is a three-stage exam consisting of:
1. Civil Services Preliminary Examination (objective type) for the selection of candidates for the Main Examination. UPSC Prelims syllabus focuses on general and societal awareness tested by objective-type (MCQ) questions.
2. Civil Services Main Examination for the selection of candidates for interview for various services & posts as mentioned in the official notification. UPSC Mains syllabus: On the other hand, the UPSC Mains syllabus is much more comprehensive as this stage comprises nine theory papers.
3. Civil Services Interview for the selection of candidates for various services & posts as mentioned in the official notification
Official Notification of UPSC:Every year, the Union Public Service Commission releases a complete IAS Syllabus along with its official notification in February. Here's a link to recent year's official notification: UPSC CSE Official Notification 2025.
What is the Pattern of UPSC IAS Preliminary Exam?
The UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) Prelims exam is the first examination stage and is qualifying in nature. IAS Prelims consist of two papers of objective type carrying a maximum of 400 marks: General Studies and Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT).
Here's the detailed exam pattern of UPSC Prelims:
- Objective (MCQ) type papers: Both the question papers will be of the objective type (multiple choice questions), and each will be of two hours duration.
- Bilingual (Hindi & English): The question papers will be set both in Hindi and English.
- Qualifying Exam: The candidate has to score a minimum of 33% marks and marks above the cut-off as decided by UPSC. In addition, the UPSC Prelims exam is conducted to shortlist limited candidates for the Mains exam.
- Negative Marking Cases: There will be negative marking for incorrect answers as detailed below:
(i) There are four alternatives for the answers to every question. For each question the candidate has given a wrong answer, one-third (0.33) of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as a penalty.
(ii) If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers happens to be correct, and there will be the same penalty as above for that question.
(iii) If a question is left blank, i.e., the candidate does not answer, there will be no penalty.
Here's the conclusion of the exam pattern of UPSC Prelims:

Syllabus of General Studies Paper-I
The General Studies test is the first paper of the preliminary examination of the UPSC Exam.
This test is intended to test the general awareness of the candidate in a wide range of subjects.
Here is the detailed syllabus of all the subjects:
1. Indian Polity:
Official Syllabus of Indian Polity & Governance includes:
- Constitution
- Political System
- Panchayati Raj
- Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- You can also refer to the detailed Syllabus, Booklist & Strategy to study Indian Polity for UPSC - CSE Prelims
2. Geography:
Official Syllabus of Indian and World Geography includes:
- Physical, Social & Economic Geography of India and the World.
- You can also refer to the detailed Syllabus, Booklist & Strategy to study Geography for UPSC - CSE Prelims.
3. History:
Official Syllabus of History is:
- History of India and Indian National Movement
- You can also refer to the detailed Syllabus, Booklist & Strategy to study History for UPSC - CSE Prelims
4. Indian Economy:
Official Syllabus of Economics & Social Development includes:
- Sustainable Development
- Poverty
- Inclusion
- Demographics
- Social Sector Initiatives, etc.
- You can also refer to the detailed Syllabus, Booklist & Strategy to study Indian Economy for UPSC - CSE Prelims

Official Syllabus of Science and Technology & Environment and Ecology includes:
- General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity, and climate change that do not require subject specialization.
- General Science
- You can also refer to the detailed Syllabus, Booklist & Strategy to study Science & Technology for UPSC-CSE Prelims
6. Current Affairs:
- Current events of national and international importance.
- You can refer to the document: How to Study Current Affairs for UPSC Preparation with EduRev App
Syllabus of General Studies Paper-II (CSAT)
This UPSC Prelims syllabus for CSAT intends to assess the candidate’s aptitude in solving.
It comprises of 80 questions from the following topics carrying a maximum of 200 marks to be solved in 2 hours.
- Comprehension.
- Interpersonal skills including communication skills.
- Logical reasoning & analytical ability.
- Decision-making & problem-solving.
- General mental ability.
- Basic numeracy (numbers & their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) (Class X level), Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency, etc. – Class X level)
- You can improve and test your aptitude via this course of CSAT for UPSC.
Important Points to be noted for UPSC CSAT Exam:
- The preliminary examination is only meant for screening a candidate for the subsequent stages of the exam.
- The marks obtained in the Prelims will not be added up while arriving at the final rank list.
- Paper-II of the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination will be a qualifying paper with minimum qualifying marks fixed at 33%.
- The questions will be of multiple-choice, objective type.
- The candidate must appear in the Papers of Civil Services (Prelim) Examination for evaluation. Therefore, a candidate will be disqualified if not in the Civil Services (Prelim) Examination papers.
(All the courses on EduRev are curated by the mentors of Anudeep Durishetty AIR 1 2017)
Syllabus of UPSC Mains
The Main exam, which assesses candidates' in-depth understanding of the topic, is the second step of the Civil Services Examination.UPSC Mains exam consists of nine papers that are held over 4-5 days. Out of these, only seven papers are merit-oriented. The other two papers, including the Compulsory Indian Language paper and Compulsory English paper, are qualifying in nature. Here’s a brief about UPSC Mains Paper: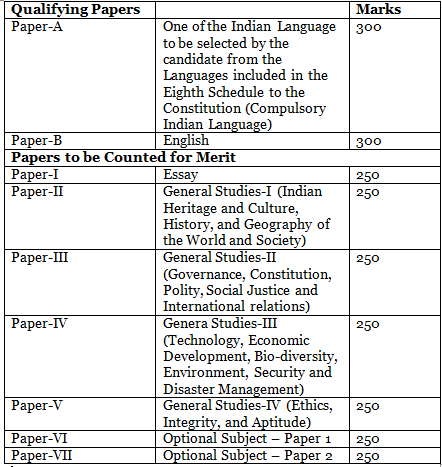
- The Mains examination constitutes the 2nd phase of the Civil Services Examination. Only after successfully qualifying in the prelims exam would the candidates be allowed to write the IAS Mains.
- The Mains exam tests the candidate’s academic talent in depth and their ability to present their understanding according to the question’s requirements in a time-bound manner.
- The UPSC Mains exam consists of 9 papers, out of which two are qualifying papers of 300 marks each.
Two qualifying papers for UPSC Mains
(i) Any Indian Language Paper
(ii) English Language Paper
- Candidates may choose any one of the optional subjects from amongst the list of subjects given:
Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science, Anthropology, Botany, Chemistry, Civil Engineering, Commerce and Accountancy, Economics, Electrical Engineering, Geography, Geology, History, Law, Management, Mathematics, Mechanical Engineering, Medical Science, Philosophy, Physics, Political Science and International Relations, Psychology, Public Administration, Sociology, Statistics, & Zoology. - Literature of any one of the following languages:
Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil Telugu, Urdu, and English.
The papers on Essay, General Studies, and Optional Subject of only such candidates who attain 25% marks in both the language papers as a minimum qualifying standard in these qualifying papers will be taken cognizance of for evaluation.
If a candidate does not qualify in these language papers, then the marks obtained by such candidates will not be considered or counted.
Syllabus for any Indian Languages in UPSC Mains
- Comprehension of given passages.
- Precis Writing.
- Usage and Vocabulary.
- Short Essays.
- Translation from English to the Indian Language and vice-versa.
Syllabus for English Language in UPSC Mains
- Comprehension of given passages.
- Precis Writing.
- Usage and Vocabulary.
- Short Essays.
Important Points to be noted:
- The papers on Indian Languages and English will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard and qualifying nature. Therefore, the marks obtained in these papers will not be counted for ranking.
- The candidates will have to answer the English and Indian Languages papers in English and the respective Indian language (except where the translation is involved).
Syllabus for Paper-I: Essay
Candidates may be required to write essays on multiple topics. They will be expected to keep close to the essay’s subject to arrange their ideas orderly and write concisely. Credit will be given for effective and exact expression.
You can learn and practice from EduRev’s course for Paper-I: Essay for MAINS- UPSC, PCS & Other Competitive exams Practice Essays for UPSC Mains course on EduRev
Practice Essays for UPSC Mains course on EduRev
Syllabus for Paper-II: General Studies-I (Indian Heritage and Culture, History, and Geography of the World and Society)
- Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature & Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until significant events, personalities, and issues.
- The Freedom Struggle - its various stages and significant contributors /contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post-independence consolidation and reorganization within the country.
- History of the World will include events from the 18th century, such as the Industrial Revolution, World Wars, redrawing of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization, political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism, etc., - their forms and effects on the society. You can cover World History for UPSC Mains from here
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India. Role of women and women's organizations, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems, and remedies. Effects of globalization on Indian society - Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism.
- Salient features of the world's physical geography.
- Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India); Important Geophysical phenomena, such as earthquakes, tsunami, volcanic activity, cyclones, etc., geographical features and their location - changes in critical geographical features (including waterbodies and ice-caps) and flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
You can cover the syllabus of UPSC Mains Geography from here
Syllabus for Paper-III: General Studies-II (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations)
- Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions, and basic structure.
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges about the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels, and challenges therein.
- Separation of powers between various organs, dispute redressal mechanisms, and institutions.
- Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries, Parliament and State Legislatures - structure, functioning, business conduct, powers & privileges and issues arising from these.
- Structure, organization, and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary, Ministries, and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- Salient features of the Representation of People's Act.
- Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions, and responsibilities of different Constitutional Bodies.
- Statutory, regulatory, and various quasi-judicial bodies, Government policies and interventions for development in multiple sectors, and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Development processes and the development industry - the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Center and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions, and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
- Issues related to development and management of Social Sector/Services in Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Issues related to poverty and hunger.
- Important aspects of governance, transparency, and accountability, e-governance - applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability, and institutional and other measures.
- Role of Civil Services in a democracy.
- India and its neighborhood - relations. Bilateral, regional, and global groupings and agreements involving India and affecting India's interests Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India's interests, Indian diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies, and fora- their structure, mandate.
This course covers International Relations, Social Issues, and other issues asked in UPSC Mains.
Syllabus for Paper-IV: General Studies-III (Technology, Economic Development, Biodiversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management)
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development, and employment. Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
- Government Budgeting, Major crops cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport, and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints;
- E-technology in aid of farmers, Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices;
- Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing.
- Food processing and related industries in India- scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management.
- Land reforms in India. Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy, and their impact on industrial growth.
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways, etc.
- Investment models. Science and technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life Achievement of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Awareness in IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology, and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment Disaster and disaster management.
- Linkages between development and spread of extremism.
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks, the role of media and social networking sites in internal security, basics of cyber security, money-laundering, and prevention.
You can cover the syllabus of UPSC Mains Internal Security & Disaster Management from here - Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate
Syllabus for Paper-V: General Studies-IV (Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitude)
This paper will include questions to test the candidates' attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life, and his problem-solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilize the case study approach to determine these aspects.
You can learn and practice from EduRev’s Course for Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude course on EduRev
Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude course on EduRev
This paper will include questions to test the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered:
- Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, Determinants and Consequences of Ethics in - Human Actions; Dimensions of Ethics; Ethics - in Private and Public Relationships. Human Values - Lessons from the Lives and Teachings of Great Leaders, Reformers and Administrators; Role of Family Society and Educational Institutions in Inculcating Values.
- Attitude: Content, Structure, Function; its Influence and Relation with Thought and Behaviour; Moral and Political Attitudes; Social Influence and Persuasion.
- Aptitude and Foundational Values for Civil Service, Integrity, Impartiality and Non-partisanship, Objectivity, Dedication to Public Service, Empathy, Tolerance and Compassion towards the weaker-sections.
- Emotional Intelligence-Concepts, and their Utilities and Application in Administration and Governance.
- Contributions of Moral Thinkers and Philosophers from India and World.
- Public/Civil Service Values and Ethics in Public Administration: Status and Problems; Ethical Concerns and Dilemmas in Government and Private Institutions; Laws, Rules, Regulations and Conscience as Sources of Ethical Guidance; Accountability and Ethical Governance; Strengthening of Ethical and Moral Values in Governance; Ethical Issues in International Relations and Funding; Corporate Governance.
- Probity in Governance: Concept of Public Service; Philosophical Basis of Governance and Probity; Information Sharing and Transparency in Government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work Culture, Quality of Service Delivery, Utilization of Public Funds, Challenges of Corruption.
- Case Studies on above issues.
What is the Syllabus for UPSC Optional Subjects (Paper VI, VII)?
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Agriculture
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Anthropology
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Botany
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Chemistry
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Commerce and Accountancy
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Civil Engineering
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Economics
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Electrical Engineering
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Geography
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Geology
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: History
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Law
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Management
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Maths
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Mechanical Engineering
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Medical Science
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Philosophy
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Physics
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Political Science and International Relations
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Psychology
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Public Administration
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Sociology
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Statistics
- UPSC Optional Subject Syllabus: Zoology
EduRev also offers courses for optional subjects Sociology & PSIR in collaboration with Sleepy Classes. AIR 5 2018 Srushti Deshmukh was a student of Sleepy Classes & studied Sociology from them.
This course covers Sociology for UPSC Mains Optional.
You can cover PSIR Optional for UPSC Mains from here
You can cover History Optional for UPSC Mains from here.
You can cover Geography Optional for UPSC Mains from here.
After Completion of all the exams the last step of the UPSC Exam is the Interview Process.
- A Board will interview the candidate, who will have a record of his or her career in front of them. He or she will be quizzed on topics of general interest.
- The purpose of the interview is for a Board of competent and neutral observers to assess the candidate's personal fitness for a career in public service.
- The interview is truly a test of not just his or her academic abilities, but also his or her social characteristics and interest in current events.
- Mental alertness, critical abilities of absorption, clear and logical presentation, a balance of judgement, diversity and depth of interest, aptitude for social cohesiveness, and leadership are some of the attributes to be rated on.
FAQs related to UPSC Prelims and Mains Syllabus
Q1: How many papers are there in UPSC prelims?
UPSC CSE Prelims consists of two papers namely General Studies I and CSAT (General Studies Paper-II). While CSAT is qualifying in nature, the marks obtained in the General Studies paper determine your selection for UPSC Mains. It means your score in the General Studies Paper will be considered for the Prelims cutoff.
Q2: How is the Prelims cut-off calculated?
The merit list is prepared according to the number of vacancies in every category for a particular year. For example, if there are 900 vacancies for the OBC category in a year, the mark of the last candidate in the OBC list (of 900) would be the cut-off for that category.
Q3: What is the weight required for an IAS officer?
There is no height, weight and chest girth minimum requirement as such for candidates for the IAS, unlike the technical services. However, if the candidates' measurements are disproportionate as regarded by the medical board, the candidates can be hospitalized for investigation and chest X-ray can be taken.
|
3 videos|27 docs
|

















