All Exams >
NEET >
NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes for NEET Exam
Study the following statements regarding recombinant DNA technology and select the incorrect ones
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction- a)(i), (iii) and (vi)
- b)(i), (iii) and (v)
- c)(ii), (iii) and (v)
- d)(i), (iv) and (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements regarding recombinant DNA technology and select the incorrect ones
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction
a)
(i), (iii) and (vi)
b)
(i), (iii) and (v)
c)
(ii), (iii) and (v)
d)
(i), (iv) and (v)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Antibiotic resistance genes are selectable markers. Desirable genes are the ones which are introduced in the vector for getting desired protein product. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated according to their charge and size. After the formation of the product in a bioreactors, it undergoes through some processes before a finished product is ready for marketing. The processes include separation and purification of products which are collectively called as downstream processing.
After completion of the biosynthetic stage in the bioreactors, the product undergoes separation and purification processes, collectively termed as __________.- a)Transformation
- b)Electrophoresis
- c)Downstream processing
- d)Upstream processing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
After completion of the biosynthetic stage in the bioreactors, the product undergoes separation and purification processes, collectively termed as __________.
a)
Transformation
b)
Electrophoresis
c)
Downstream processing
d)
Upstream processing
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
After the formation of the product in bioreactors, it undergoes through some processes before a finished product is ready for marketing. The processes include separation and purification of products which is collectively called as downstream processing.
Plasmid used to construct the first recombinant DNA was isolated from which bacterium species?- a)Escherichia coli
- b)Salmonella typhimurium
- c)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- d)Thermus aquaticus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmid used to construct the first recombinant DNA was isolated from which bacterium species?
a)
Escherichia coli
b)
Salmonella typhimurium
c)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
d)
Thermus aquaticus
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The first recombinant DNA was constructed by Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer in 1972. They cut the piece of DNA from a plasmid carrying antibiotic resistance gene in the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium and linked it to the plasmid of Escherichia coil.
If a plasmid vector is digested with EcoRI at a single site, then- a)One sticky ends will be produced
- b)Two sticky ends will be produced
- c)Four sticky ends will be produced
- d)Six sticky ends will be produced
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a plasmid vector is digested with EcoRI at a single site, then
a)
One sticky ends will be produced
b)
Two sticky ends will be produced
c)
Four sticky ends will be produced
d)
Six sticky ends will be produced
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Plasmid is a circular DNA, if it is digested at a single site, one fragment will be produced with two sticky ends.
Read statements (i)-(iv). Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read statements (i)-(iv). Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (ii)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In 1997, Rosie, the tirst transgenic cow was engineered to produce milk enriched with a human protein called alpha-lactalbumin, making it nutritionally more balanced. Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sites.
______ a crown gall bacterium, is called as 'natural genetic engineer' of plants.- a)Escherichia coli
- b)Streptomyces albus
- c)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- d)Azotobacter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
______ a crown gall bacterium, is called as 'natural genetic engineer' of plants.
a)
Escherichia coli
b)
Streptomyces albus
c)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
d)
Azotobacter
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
A soil-inhabiting plant bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a pathogen of several dicot plants. It is able to transfer a piece of DNA known as 'T-DNA' into the plant cells. The T-DNA causes tumours, the tumours are called crown galls. Tumour formation is induced by Ti plasmid (Ti for tumour inducing). As gene transfer occurs without human effort, the bacterium is called natural genetic engineer of plants. Similarly retroviruses in animals including humans are able to change normal cells into cancerous cells.
The letter 'R' in EcoRI is derived from- a)the name of genus
- b)the name of strain
- c)the name of species
- d)the term 'restriction'
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The letter 'R' in EcoRI is derived from
a)
the name of genus
b)
the name of strain
c)
the name of species
d)
the term 'restriction'
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
In EcoRI, capital letter E comes from the genus Escherichia. The letters co are from the species coli. The letter R is from RY 13 (strain). The Roman number I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from the bacterium E.coli RY 13.
The term 'recombinant DNA' refers to- a)DNA of the host cell
- b)DNA with a piece of foreign DNA
- c)DNA with selectable marker
- d)DNA with more than one recognition sites
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 'recombinant DNA' refers to
a)
DNA of the host cell
b)
DNA with a piece of foreign DNA
c)
DNA with selectable marker
d)
DNA with more than one recognition sites
|
|
Rajat Parihar answered |
Construction of recombinant DNA, in which a foreign DNA fragment is inserted into a plasmid vector.
In recombinant DNA technology, the term vector refers to- a)the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments
- b)the sticky end of a DNA fragment
- c)a plasmid used to transfer DNA into a living cell
- d)a DNA fragment which carries only ori gene.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In recombinant DNA technology, the term vector refers to
a)
the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments
b)
the sticky end of a DNA fragment
c)
a plasmid used to transfer DNA into a living cell
d)
a DNA fragment which carries only ori gene.
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The DNA used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called vehicle DNA or cloning vector or gene carrier. When desired gene is introduced into a vector, recombinant DNA is formed. Vectors may be plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, phagemids, Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (Y ACs), Bacterial Artificial Chromosomes (BACs), transposons, viruses, etc.
Which of the following statement is not correct?
- a)Recombinant technologies are used to produce desirable proteins
- b)Agrobacterium is a genus of bacteria that causes tumours in plants
- c)Log phase does not show any significant increase in the number of cells whereas the lag phase shows rapid multiplication of cells
- d)Dolly, a sheep was the first animal to be cloned in 1997
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not correct?
a)
Recombinant technologies are used to produce desirable proteins
b)
Agrobacterium is a genus of bacteria that causes tumours in plants
c)
Log phase does not show any significant increase in the number of cells whereas the lag phase shows rapid multiplication of cells
d)
Dolly, a sheep was the first animal to be cloned in 1997
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The statement that is not correct is:
3. Log phase does not show any significant increase in the number of cells whereas the lag phase shows rapid multiplication of cells.
Here's why:
-
Log phase (or exponential phase) is actually characterized by a rapid and significant increase in the number of cells. During this phase, cells are dividing at an exponential rate.
-
Lag phase is the initial phase where cells are adapting to new conditions and preparing for growth. During this phase, there is little to no significant increase in cell number as the cells are not yet dividing rapidly.
To summarize, the log phase is when cell multiplication is most rapid, not the lag phase.
How many fragments will be generated if you digest a linear DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having four recognition sites on the DNA?- a)3
- b)6
- c)5
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many fragments will be generated if you digest a linear DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having four recognition sites on the DNA?
a)
3
b)
6
c)
5
d)
4
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
If DNA is linear then the number of fragments generated is (N+1), where N= number of recognition sites or sequences.
Hence the number of fragments generated is 5 if we digest a linear DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having four recognition sites on the DNA.
Hence the number of fragments generated is 5 if we digest a linear DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having four recognition sites on the DNA.
Which of the following is required for microinjection method of gene transfer?- a)Micro-particles
- b)Micro-pipettes
- c)Divalent cations
- d)UV radiations
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is required for microinjection method of gene transfer?
a)
Micro-particles
b)
Micro-pipettes
c)
Divalent cations
d)
UV radiations
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Micro-injection method is the direct or vectorless method of gene transfer, in which foreign DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of animal cell or plant cell by using micro-needles or micro-pipettes. It is used to transfer DNA in oocytes, eggs and embryo.
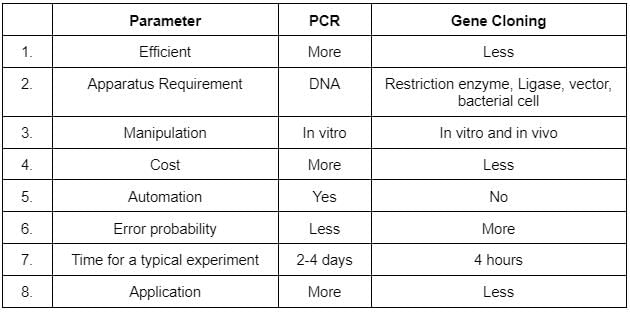
Given table gives an account of differences between PCR and gene cloning.. Which of the following points show the incorrect differences?
- a)1 and 3
- b)4 and 6
- c)4 and 7
- d)4, 7 and 8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given table gives an account of differences between PCR and gene cloning.. Which of the following points show the incorrect differences?


a)
1 and 3
b)
4 and 6
c)
4 and 7
d)
4, 7 and 8

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The correct option is C 4 and 7
The cost of gene cloning is far more than PCR because gene cloning requires many intricate steps. PCR takes less than 4 hours while gene cloning can take days.
The cost of gene cloning is far more than PCR because gene cloning requires many intricate steps. PCR takes less than 4 hours while gene cloning can take days.
Which of the following are the types of bioreactors?
(i) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(ii) Complex Stirred-tank bioreactor
(iii) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
(iv) Agitator stirred-tank bioreactor- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)Only (iii)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(i) and (ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the types of bioreactors?
(i) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(ii) Complex Stirred-tank bioreactor
(iii) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
(iv) Agitator stirred-tank bioreactor
(i) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(ii) Complex Stirred-tank bioreactor
(iii) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
(iv) Agitator stirred-tank bioreactor
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
Only (iii)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(i) and (ii) and (iv)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The most commonly used bioreactors are of stirring type. Stirring type bioreactors are simple stirred-tank bioreactor and sparged stirred-tank bioreactor.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The cloning vector is required to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
Statement 2: Presence of more than one recognition sites within a cloning vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the process of gene cloning.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The cloning vector is required to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
Statement 2: Presence of more than one recognition sites within a cloning vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the process of gene cloning.
Statement 1: The cloning vector is required to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
Statement 2: Presence of more than one recognition sites within a cloning vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the process of gene cloning.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
When cut by the same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments have the same kind of 'sticky-ends' produced, which can be joined together (end-to-end) using DNA ligase. Restriction enzymes are of two kinds - exonucleases and endonucleases. Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the j ends of the DNA whereas endonucleases make cuts at specific positions within the DNA. Presence of more than one recognition sites within the vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the gene cloning. Therefore, in order to link the alien DNA (or foreign DNA), the vector needs to have very few, preferably single, recognition/cloning sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
One of the key factors, which makes the plasmid the vector in genetic engineering is- a)Its resistance to antibiotics
- b)Its resistance to restriction enzymes
- c)Its ability to carry a foreign gene
- d)Its ability to cause infection in the host
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the key factors, which makes the plasmid the vector in genetic engineering is
a)
Its resistance to antibiotics
b)
Its resistance to restriction enzymes
c)
Its ability to carry a foreign gene
d)
Its ability to cause infection in the host
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeasts. Plasmids are usually not essential for normal cell growth and division, they often confer some traits to the host organism e.g., resistance to certain antibiotics. The plasmid that is used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called vehicle DNA or cloning vector or gene carrier.
If a recombinant DNA bearing gene for resistance to antibiotic ampicillin is transferred to E.coli cells, the host cells become transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If such bacteria are transferred on agar plates containing ampicillin, only transformants will grow and the non-transformed recipient cells will die. The ampicillin-resistant gene in this case is called as _______.- a)Selectable marker
- b)Recombinant protein
- c)Cloning site
- d)Chemical scalpels
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a recombinant DNA bearing gene for resistance to antibiotic ampicillin is transferred to E.coli cells, the host cells become transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If such bacteria are transferred on agar plates containing ampicillin, only transformants will grow and the non-transformed recipient cells will die. The ampicillin-resistant gene in this case is called as _______.
a)
Selectable marker
b)
Recombinant protein
c)
Cloning site
d)
Chemical scalpels
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The cloning vector requires the presence of a selectable marker, which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants. Normally, the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline or kanamycin, etc. are considered useful selectable markers for E. coli. The normal E.coli cells do not carry resistance against any of these antibiotics.
The term “competent” refers to- a)Increasing the competition between cells
- b)Making cells impermeable for DNA
- c)Increasing the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall
- d)Making cells permeable for divalent cations
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term “competent” refers to
a)
Increasing the competition between cells
b)
Making cells impermeable for DNA
c)
Increasing the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall
d)
Making cells permeable for divalent cations
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Transformation is a process by which a cell takes up naked DNA fragment from the environment, incorporates it into its own chromosomal DNA and finally expresses the trait controlled by the incoming DNA. Since DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, it can not pass through membranes, so the bacterial cells must be made competent to take up DNA. This is done by treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent cation, such as calcium (Ca2+) which increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
Enzyme' Taq polymerase' used in PCR, has been isolated from bacterium ________.- a)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- b)Thermus aquaticus
- c)Streptomyces albus
- d)Escherichia coli
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzyme' Taq polymerase' used in PCR, has been isolated from bacterium ________.
a)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
b)
Thermus aquaticus
c)
Streptomyces albus
d)
Escherichia coli
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The final step of PCR is extension, wherein TaqDNA polymerase (isolated from a thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus) synthesies the DNA region between the primers, using DNTPs (denoxynucleoside triphosphates) and Mg2+. The primers are extened towards each other so that the DNA segment lying between the two primers is copied. The optimum temperature for this polymerisation step is 72∘C. Taq polymerase remains active during high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA.
In biolistic method of gene transfer, the microparticles coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. These microparticles are made up of- a)Silver or Tungsten
- b)Arsenic or Silver
- c)Gold or Tungsten
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In biolistic method of gene transfer, the microparticles coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. These microparticles are made up of
a)
Silver or Tungsten
b)
Arsenic or Silver
c)
Gold or Tungsten
d)
None of these
|
|
Ashwini Malik answered |
Biolistic Method of Gene Transfer
The biolistic method, also known as the "gene gun" method, is a technique used to introduce foreign DNA into target cells. This process is particularly useful in plant biotechnology and genetic engineering.
Microparticles Used
- Microparticles in this method are typically made of Gold or Tungsten.
- These metals are chosen due to their high density and ability to penetrate cell walls effectively.
Process of Gene Transfer
- Coating with DNA: Foreign DNA is coated onto the surface of these microparticles.
- High Velocity Bombardment: The microparticles are then propelled at a very high velocity towards the target cells using a burst of helium gas or a similar mechanism.
- Cell Penetration: The high kinetic energy allows the microparticles to penetrate the cell membrane, delivering the DNA directly into the cell's cytoplasm.
Advantages of Using Gold or Tungsten
- Biocompatibility: Both gold and tungsten are biocompatible, reducing the chances of eliciting an immune response.
- Efficient Delivery: Their density allows for efficient delivery of the genetic material, increasing the likelihood of successful transformation.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to the question regarding the materials used for microparticles in the biolistic method of gene transfer is option C: Gold or Tungsten. These materials are specifically chosen for their properties that facilitate effective gene delivery into target cells.
The biolistic method, also known as the "gene gun" method, is a technique used to introduce foreign DNA into target cells. This process is particularly useful in plant biotechnology and genetic engineering.
Microparticles Used
- Microparticles in this method are typically made of Gold or Tungsten.
- These metals are chosen due to their high density and ability to penetrate cell walls effectively.
Process of Gene Transfer
- Coating with DNA: Foreign DNA is coated onto the surface of these microparticles.
- High Velocity Bombardment: The microparticles are then propelled at a very high velocity towards the target cells using a burst of helium gas or a similar mechanism.
- Cell Penetration: The high kinetic energy allows the microparticles to penetrate the cell membrane, delivering the DNA directly into the cell's cytoplasm.
Advantages of Using Gold or Tungsten
- Biocompatibility: Both gold and tungsten are biocompatible, reducing the chances of eliciting an immune response.
- Efficient Delivery: Their density allows for efficient delivery of the genetic material, increasing the likelihood of successful transformation.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer to the question regarding the materials used for microparticles in the biolistic method of gene transfer is option C: Gold or Tungsten. These materials are specifically chosen for their properties that facilitate effective gene delivery into target cells.
Which of the following processes/techniques can be included under biotechnology?
(i) In vitro fertilisation
(ii) Synthesis of a gene
(iii) Correcting a defective gene
(iv) Developing a DNA vaccine- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following processes/techniques can be included under biotechnology?
(i) In vitro fertilisation
(ii) Synthesis of a gene
(iii) Correcting a defective gene
(iv) Developing a DNA vaccine
(i) In vitro fertilisation
(ii) Synthesis of a gene
(iii) Correcting a defective gene
(iv) Developing a DNA vaccine
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Biotechnology deals with techniques of using live micro-organisms, plant or animal cells or their components or enzymes from organisms to produce products and processes (service) useful to human beings. In vitro fertilisation, synthesis of recombinant gene, correcting a defective gene and developing a DNA vaccine are all parts of biotechnology.
Primers are- a)Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA
- b)Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are not complementary to the regions of DNA
- c)Chemically synthesised, autonomously replicating circular DNA molecules
- d)Specific sequences present on recombinant DNA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Primers are
a)
Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA
b)
Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are not complementary to the regions of DNA
c)
Chemically synthesised, autonomously replicating circular DNA molecules
d)
Specific sequences present on recombinant DNA
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Primers are small, chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the sequences, present at 3' end of the template DNA. They hybridise to the target DNA region, one to each strand of the double helix. These primers are oriented with their ends facing each other allowing synthesis of the DNA towards one another.
The restriction enzyme responsible for the cleavage of following sequence is
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
- a)Eco RI
- b)Hind II
- c)Bam HI
- d)Alu I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The restriction enzyme responsible for the cleavage of following sequence is
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
a)
Eco RI
b)
Hind II
c)
Bam HI
d)
Alu I
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
HindII was the first discovered restriction endonuclease. It was isolated from Haemophilus influenzae. It produces blunt ends.
During isolation of genetic material, the chemical used to precipitate out the purified DNA is- a)Bromophenol blue
- b)Chilled ethanol
- c)Ethidium bromide
- d)Both A and C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During isolation of genetic material, the chemical used to precipitate out the purified DNA is
a)
Bromophenol blue
b)
Chilled ethanol
c)
Ethidium bromide
d)
Both A and C
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The purified DNA, after treatment with various enzymes, precipitates out after the addition of chilled ethanol.
This is viewed as a collection of fine threads in the suspension and is easily collected. The process is known as DNA spooling.
This is viewed as a collection of fine threads in the suspension and is easily collected. The process is known as DNA spooling.
Which of the following is not used to transfer the recombinant DNA into the host?- a)Micro-injection method
- b)Gene gun method
- c)Bioreactors
- d)Disarmed pathogen vectors
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not used to transfer the recombinant DNA into the host?
a)
Micro-injection method
b)
Gene gun method
c)
Bioreactors
d)
Disarmed pathogen vectors
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Bioreactors are considered as vessels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products by microbes, plant and animal cells or their enzymes. To produce large quantities of these products, bioreactors are used where large volumes (100-1000 litres) of culture can be processed. Bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for obtaining the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, vitamins, oxygen and salts.
The term 'chemical knife' refers to- a)Polymerases
- b)Endonucleases
- c)Ribonudeases
- d)Cellulases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 'chemical knife' refers to
a)
Polymerases
b)
Endonucleases
c)
Ribonudeases
d)
Cellulases
|
|
Diya Khanna answered |
Explanation:
The term "chemical knife" refers to endonucleases. Endonucleases are a group of enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a DNA or RNA molecule. They are called "chemical knives" because they can cut DNA or RNA at specific target sequences, similar to how a knife can cut through a specific point on an object.
Endonucleases:
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a DNA or RNA molecule. They are essential for various biological processes like DNA replication, repair, and recombination. Endonucleases can recognize specific nucleotide sequences and cleave the DNA or RNA at those sites.
Types of Endonucleases:
There are several types of endonucleases, including restriction endonucleases, homing endonucleases, and RNA endonucleases. Each type of endonuclease has its own specific function and target sequence.
- Restriction Endonucleases: These enzymes are commonly found in bacteria and are used as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA. They recognize specific sequences of DNA and cleave the DNA at those sites, preventing the foreign DNA from replicating.
- Homing Endonucleases: These enzymes are involved in genetic recombination and can recognize and cleave specific target sequences within DNA. They are often used in genetic engineering techniques to introduce new DNA sequences into an organism.
- RNA Endonucleases: These enzymes cleave RNA molecules at specific sites. They are involved in various processes, including RNA splicing, RNA degradation, and RNA maturation.
Applications of Endonucleases:
Endonucleases have several important applications in molecular biology and biotechnology:
- Genetic Engineering: Endonucleases are used to cleave DNA at specific sites, allowing for the insertion or removal of specific DNA sequences. This is commonly used in genetic engineering techniques like gene cloning and genome editing.
- Diagnostic Tools: Certain endonucleases are used as diagnostic tools to detect specific DNA sequences. For example, restriction endonucleases are often used in DNA fingerprinting techniques.
- Gene Therapy: Endonucleases like CRISPR-Cas9 are being used in gene therapy to correct genetic mutations by editing the DNA sequence.
In conclusion, the term "chemical knife" refers to endonucleases, which are enzymes that cleave DNA or RNA at specific target sequences. They have various applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
The term "chemical knife" refers to endonucleases. Endonucleases are a group of enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a DNA or RNA molecule. They are called "chemical knives" because they can cut DNA or RNA at specific target sequences, similar to how a knife can cut through a specific point on an object.
Endonucleases:
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a DNA or RNA molecule. They are essential for various biological processes like DNA replication, repair, and recombination. Endonucleases can recognize specific nucleotide sequences and cleave the DNA or RNA at those sites.
Types of Endonucleases:
There are several types of endonucleases, including restriction endonucleases, homing endonucleases, and RNA endonucleases. Each type of endonuclease has its own specific function and target sequence.
- Restriction Endonucleases: These enzymes are commonly found in bacteria and are used as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA. They recognize specific sequences of DNA and cleave the DNA at those sites, preventing the foreign DNA from replicating.
- Homing Endonucleases: These enzymes are involved in genetic recombination and can recognize and cleave specific target sequences within DNA. They are often used in genetic engineering techniques to introduce new DNA sequences into an organism.
- RNA Endonucleases: These enzymes cleave RNA molecules at specific sites. They are involved in various processes, including RNA splicing, RNA degradation, and RNA maturation.
Applications of Endonucleases:
Endonucleases have several important applications in molecular biology and biotechnology:
- Genetic Engineering: Endonucleases are used to cleave DNA at specific sites, allowing for the insertion or removal of specific DNA sequences. This is commonly used in genetic engineering techniques like gene cloning and genome editing.
- Diagnostic Tools: Certain endonucleases are used as diagnostic tools to detect specific DNA sequences. For example, restriction endonucleases are often used in DNA fingerprinting techniques.
- Gene Therapy: Endonucleases like CRISPR-Cas9 are being used in gene therapy to correct genetic mutations by editing the DNA sequence.
In conclusion, the term "chemical knife" refers to endonucleases, which are enzymes that cleave DNA or RNA at specific target sequences. They have various applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
Which of the following is not a cloning vector?- a)Cosmid
- b)pBR 322
- c)Sal l
- d)Phagemid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a cloning vector?
a)
Cosmid
b)
pBR 322
c)
Sal l
d)
Phagemid
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Sal l is a restriction enzyme isolated from Streptomyces albus.
The term 'molecular scissors' refers to- a)Recombinant DNA
- b)Restriction enzymes
- c)Taq polymerase
- d)Palindromic nucleotide sequences
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 'molecular scissors' refers to
a)
Recombinant DNA
b)
Restriction enzymes
c)
Taq polymerase
d)
Palindromic nucleotide sequences
|
|
Sounak Shah answered |
The term molecular scissors refers to Restriction enzymes.
Explanation:
Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, are enzymes that can recognize specific DNA sequences and cleave the DNA at those sequences. These enzymes act as "molecular scissors" by cutting the DNA into smaller fragments.
Function of Restriction Enzymes:
Restriction enzymes are naturally occurring enzymes found in bacteria and archaea. They play a crucial role in the defense mechanisms of these organisms by cutting foreign DNA, such as viral DNA, at specific recognition sites. This helps protect the organism from invasion by foreign genetic material.
Recognition Sites:
Restriction enzymes recognize specific DNA sequences called recognition sites or restriction sites. These recognition sites are usually palindromic, meaning they read the same forward and backward on complementary DNA strands. For example, the recognition site for the restriction enzyme EcoRI is 5'-GAATTC-3', which is palindromic.
Cutting the DNA:
Once the restriction enzyme recognizes its specific recognition site, it binds to the DNA at that site and makes a double-stranded cut. The cut can be blunt or staggered, depending on the type of restriction enzyme. Some enzymes create overhangs known as sticky ends, while others create blunt ends.
Applications:
Restriction enzymes are widely used in molecular biology and biotechnology. Their ability to cut DNA at specific sequences allows scientists to manipulate and study DNA in various ways. Some applications of restriction enzymes include:
1. DNA Fragmentation: Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA into smaller fragments, which can be further analyzed or used in other experiments.
2. DNA Cloning: Restriction enzymes are used to generate compatible ends on DNA fragments and vectors, allowing them to be ligated together during the cloning process.
3. Genetic Engineering: Restriction enzymes are used to insert or remove specific DNA sequences during the process of genetic engineering.
4. DNA Fingerprinting: Restriction enzymes are used in DNA fingerprinting techniques to generate unique DNA fragment patterns for identification purposes.
In summary, the term "molecular scissors" refers to restriction enzymes because they have the ability to recognize specific DNA sequences and cleave the DNA at those sequences. These enzymes play a crucial role in DNA manipulation and various applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
Explanation:
Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, are enzymes that can recognize specific DNA sequences and cleave the DNA at those sequences. These enzymes act as "molecular scissors" by cutting the DNA into smaller fragments.
Function of Restriction Enzymes:
Restriction enzymes are naturally occurring enzymes found in bacteria and archaea. They play a crucial role in the defense mechanisms of these organisms by cutting foreign DNA, such as viral DNA, at specific recognition sites. This helps protect the organism from invasion by foreign genetic material.
Recognition Sites:
Restriction enzymes recognize specific DNA sequences called recognition sites or restriction sites. These recognition sites are usually palindromic, meaning they read the same forward and backward on complementary DNA strands. For example, the recognition site for the restriction enzyme EcoRI is 5'-GAATTC-3', which is palindromic.
Cutting the DNA:
Once the restriction enzyme recognizes its specific recognition site, it binds to the DNA at that site and makes a double-stranded cut. The cut can be blunt or staggered, depending on the type of restriction enzyme. Some enzymes create overhangs known as sticky ends, while others create blunt ends.
Applications:
Restriction enzymes are widely used in molecular biology and biotechnology. Their ability to cut DNA at specific sequences allows scientists to manipulate and study DNA in various ways. Some applications of restriction enzymes include:
1. DNA Fragmentation: Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA into smaller fragments, which can be further analyzed or used in other experiments.
2. DNA Cloning: Restriction enzymes are used to generate compatible ends on DNA fragments and vectors, allowing them to be ligated together during the cloning process.
3. Genetic Engineering: Restriction enzymes are used to insert or remove specific DNA sequences during the process of genetic engineering.
4. DNA Fingerprinting: Restriction enzymes are used in DNA fingerprinting techniques to generate unique DNA fragment patterns for identification purposes.
In summary, the term "molecular scissors" refers to restriction enzymes because they have the ability to recognize specific DNA sequences and cleave the DNA at those sequences. These enzymes play a crucial role in DNA manipulation and various applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
A correct pair of characteristics of molecular probe is
A. Very long molecule
B. Double stranded
C. Single stranded DNA or RNA
D. Complementary to part of desired gene- a)A and B
- b)B and C
- c)C and D
- d)A and D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A correct pair of characteristics of molecular probe is
A. Very long molecule
B. Double stranded
C. Single stranded DNA or RNA
D. Complementary to part of desired gene
A. Very long molecule
B. Double stranded
C. Single stranded DNA or RNA
D. Complementary to part of desired gene
a)
A and B
b)
B and C
c)
C and D
d)
A and D
|
|
Nandini Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Molecular Probes
Molecular probes are essential tools used in genetics and molecular biology for detecting specific sequences of DNA or RNA. The characteristics of these probes are crucial for their effective application.
Characteristics of Molecular Probes
- Single Stranded DNA or RNA (Option C)
- Molecular probes are typically designed as single-stranded nucleic acids. This structure allows them to hybridize specifically with complementary sequences in the target DNA or RNA.
- Single-stranded probes can bind to their targets more efficiently, enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of detection methods.
- Complementary to Part of Desired Gene (Option D)
- A critical feature of molecular probes is that they must be complementary to the specific sequence of the gene of interest. This complementarity ensures that the probe will only bind to its intended target, minimizing cross-reactivity and false positives.
- The design of these probes is crucial for applications like PCR, in situ hybridization, and various other diagnostic techniques.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
- Very Long Molecule (Option A)
- Probes are not necessarily very long. In fact, shorter probes (typically 15-30 nucleotides) can be more effective as they allow for quicker hybridization and easier handling.
- Double Stranded (Option B)
- While double-stranded nucleic acids are stable, molecular probes must be single-stranded to hybridize with their target. Double-stranded probes would not be able to effectively bind to the complementary sequences.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option C - Single Stranded DNA or RNA and Complementary to part of the desired gene, as these characteristics enhance the functionality and specificity of molecular probes in various applications.
Molecular probes are essential tools used in genetics and molecular biology for detecting specific sequences of DNA or RNA. The characteristics of these probes are crucial for their effective application.
Characteristics of Molecular Probes
- Single Stranded DNA or RNA (Option C)
- Molecular probes are typically designed as single-stranded nucleic acids. This structure allows them to hybridize specifically with complementary sequences in the target DNA or RNA.
- Single-stranded probes can bind to their targets more efficiently, enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of detection methods.
- Complementary to Part of Desired Gene (Option D)
- A critical feature of molecular probes is that they must be complementary to the specific sequence of the gene of interest. This complementarity ensures that the probe will only bind to its intended target, minimizing cross-reactivity and false positives.
- The design of these probes is crucial for applications like PCR, in situ hybridization, and various other diagnostic techniques.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
- Very Long Molecule (Option A)
- Probes are not necessarily very long. In fact, shorter probes (typically 15-30 nucleotides) can be more effective as they allow for quicker hybridization and easier handling.
- Double Stranded (Option B)
- While double-stranded nucleic acids are stable, molecular probes must be single-stranded to hybridize with their target. Double-stranded probes would not be able to effectively bind to the complementary sequences.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option C - Single Stranded DNA or RNA and Complementary to part of the desired gene, as these characteristics enhance the functionality and specificity of molecular probes in various applications.
An advantage of using yeasts rather than bacteria as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes is that yeasts can __________.- a)Produce restriction enzymes
- b)Excise introns from the RNA transcript
- c)Remove methyl groups
- d)Reproduce more rapidly
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An advantage of using yeasts rather than bacteria as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes is that yeasts can __________.
a)
Produce restriction enzymes
b)
Excise introns from the RNA transcript
c)
Remove methyl groups
d)
Reproduce more rapidly
|
|
Sinjini Das answered |
Advantages of using yeasts rather than bacteria as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes:
There are several advantages to using yeasts as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes, as compared to bacteria. One of the main advantages is that yeasts can excise introns from the RNA transcript.
1. Yeasts can excise introns from the RNA transcript:
- In eukaryotes, genes contain non-coding regions called introns, which need to be removed from the RNA transcript before translation into proteins.
- Bacteria lack the necessary machinery to remove introns, making them unsuitable for processing eukaryotic genes.
- On the other hand, yeasts, being eukaryotic organisms themselves, possess the necessary enzymes and machinery to accurately excise introns from RNA transcripts.
- This ability allows yeasts to properly process and express eukaryotic genes, making them ideal recipient cells for recombinant DNA work involving eukaryotic genes.
2. Other advantages:
- Yeasts are also advantageous because they can carry out post-translational modifications that bacteria cannot perform. These modifications include proper protein folding, glycosylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, and more.
- Yeasts are capable of performing complex cellular processes similar to those found in higher eukaryotes, making them more suitable for expressing and producing eukaryotic proteins.
- Yeasts are more similar to higher eukaryotes in terms of gene regulation and expression, making them a better model system for studying eukaryotic gene function and regulation.
- Yeasts have a longer lifespan and can undergo multiple rounds of cell division, allowing for the production of larger quantities of recombinant proteins compared to bacteria, which have a shorter lifespan and slower reproduction rate.
- Yeasts can also be easily cultured in large-scale fermentation systems, making them suitable for industrial production of recombinant proteins.
In conclusion, yeasts are advantageous over bacteria as recipient cells for recombinant DNA of eukaryotes due to their ability to accurately excise introns from RNA transcripts, perform post-translational modifications, resemble higher eukaryotes in terms of gene regulation, and produce larger quantities of recombinant proteins.
There are several advantages to using yeasts as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes, as compared to bacteria. One of the main advantages is that yeasts can excise introns from the RNA transcript.
1. Yeasts can excise introns from the RNA transcript:
- In eukaryotes, genes contain non-coding regions called introns, which need to be removed from the RNA transcript before translation into proteins.
- Bacteria lack the necessary machinery to remove introns, making them unsuitable for processing eukaryotic genes.
- On the other hand, yeasts, being eukaryotic organisms themselves, possess the necessary enzymes and machinery to accurately excise introns from RNA transcripts.
- This ability allows yeasts to properly process and express eukaryotic genes, making them ideal recipient cells for recombinant DNA work involving eukaryotic genes.
2. Other advantages:
- Yeasts are also advantageous because they can carry out post-translational modifications that bacteria cannot perform. These modifications include proper protein folding, glycosylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, and more.
- Yeasts are capable of performing complex cellular processes similar to those found in higher eukaryotes, making them more suitable for expressing and producing eukaryotic proteins.
- Yeasts are more similar to higher eukaryotes in terms of gene regulation and expression, making them a better model system for studying eukaryotic gene function and regulation.
- Yeasts have a longer lifespan and can undergo multiple rounds of cell division, allowing for the production of larger quantities of recombinant proteins compared to bacteria, which have a shorter lifespan and slower reproduction rate.
- Yeasts can also be easily cultured in large-scale fermentation systems, making them suitable for industrial production of recombinant proteins.
In conclusion, yeasts are advantageous over bacteria as recipient cells for recombinant DNA of eukaryotes due to their ability to accurately excise introns from RNA transcripts, perform post-translational modifications, resemble higher eukaryotes in terms of gene regulation, and produce larger quantities of recombinant proteins.
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge
(ii) Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast
(iii) It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule
(iv) In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge
(ii) Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast
(iii) It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule
(iv) In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13
(i) Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge
(ii) Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast
(iii) It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule
(iv) In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
- Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge.
- Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast.
- It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule.
- In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13.
Genetic engineering is possible, because- a)We can cut DNA at specific sites by endonucleases
- b)Restriction endonucleases purified from bacteria can be used in vitro
- c)The phenomenon of transduction in bacteria is well understood
- d)We can see DNA by electron microscope
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic engineering is possible, because
a)
We can cut DNA at specific sites by endonucleases
b)
Restriction endonucleases purified from bacteria can be used in vitro
c)
The phenomenon of transduction in bacteria is well understood
d)
We can see DNA by electron microscope
|
|
Shraddha Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Genetic engineering is possible primarily due to the ability to cut DNA at specific sites by endonucleases. Endonucleases are enzymes that can recognize specific sequences in DNA and cleave the phosphodiester bonds within the DNA backbone at those sites. This allows for precise manipulation of DNA sequences, enabling scientists to insert or remove specific genes.
Endonucleases:
- Endonucleases can be used to create precise cuts in DNA, allowing for the insertion of new genetic material.
- These enzymes have been extensively studied and characterized, making them valuable tools in genetic engineering.
Restriction Endonucleases:
- Restriction endonucleases, which are purified from bacteria, are commonly used in genetic engineering.
- These enzymes have specific recognition sites within DNA and can be used to cut DNA at those sites.
Transduction:
- While the phenomenon of transduction in bacteria is important in molecular biology, it is not directly related to the ability to genetically engineer organisms.
- Transduction involves the transfer of genetic material between bacteria through bacteriophages.
Visualization of DNA:
- While electron microscopes can be used to visualize DNA, this ability alone does not enable genetic engineering.
- The key factor in genetic engineering is the ability to manipulate DNA sequences using enzymes like endonucleases.
In conclusion, genetic engineering is made possible by the precise cutting of DNA at specific sites by endonucleases, allowing for the manipulation of genetic material in a controlled manner.
What is the effect if pBR322, a cloning vector does not carry 'ori site'?- a)sticky ends will not produce
- b)the transformation will not take place
- c)the cell will transfer into a tumor cell
- d)replication will not take place
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the effect if pBR322, a cloning vector does not carry 'ori site'?
a)
sticky ends will not produce
b)
the transformation will not take place
c)
the cell will transfer into a tumor cell
d)
replication will not take place
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
For the multiplication of any alien piece of DNA in an organism, it needs to be a part of a chromosome which has a specific sequence known as 'origin of replication' (ori). If ori is not present in a cloning vector, replication will not be initiated.
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding EcoRI restriction endonuclease enzyme?- a)It is isolated from Escherichia coli RY13
- b)Its recognition sequence is 5'-GAATTC-3' - 3'-CTTAAG-5'
- c)It produces complementary blunt ends
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding EcoRI restriction endonuclease enzyme?
a)
It is isolated from Escherichia coli RY13
b)
Its recognition sequence is 5'-GAATTC-3' - 3'-CTTAAG-5'
c)
It produces complementary blunt ends
d)
None of these
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI was isolated from bacterium Escherichia coli RY13. It recognises the base sequence GAATTC in DNA duplex and cuts its strands between G and A as shown below:
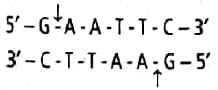
It results in complementary sticky ends.
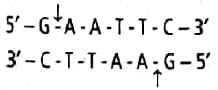
It results in complementary sticky ends.
The sticky ends of a fragmented DNA molecule are made of- a)Calcium salts
- b)Endonuclease enzyme
- c)Unpaired bases
- d)Methyl groups
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sticky ends of a fragmented DNA molecule are made of
a)
Calcium salts
b)
Endonuclease enzyme
c)
Unpaired bases
d)
Methyl groups
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The single-stranded free ends that project from each fragment of DNA duplex are unpaired bases and are known as "sticky ends". Sticky ends can join with similar complementary ends of DNA fragment from some other sources.
In addition to the Taq polymerase enzyme, which other thermostable DNA polymerases have been isolated to be used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?- a)Pfu polymerase isolated from Pyrococcus furiosus
- b)Tli polymerase (vent polymerase) isolated from Thermococcus litoralis
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In addition to the Taq polymerase enzyme, which other thermostable DNA polymerases have been isolated to be used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
a)
Pfu polymerase isolated from Pyrococcus furiosus
b)
Tli polymerase (vent polymerase) isolated from Thermococcus litoralis
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In addition to Tag DNA polymerase, Pfu polymerase and Tli polymerase have been isolated which are also thermostable. Pfu polymerase is isolated from Pyrococcus furiosus. Tli (vent) polymerase is isolated from Thermococcus litoralis.
How many fragments will be generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA?- a)5
- b)7
- c)6
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many fragments will be generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA?
a)
5
b)
7
c)
6
d)
9
|
|
Raghav Pillai answered |
To determine the number of fragments generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule, we need to consider the number of recognition sites for the restriction enzyme on the DNA.
Given that the restriction enzyme has six recognition sites on the DNA molecule, we can assume that each recognition site will be cleaved by the enzyme, resulting in the formation of two fragments.
Let's analyze the possible scenarios:
1. No overlapping recognition sites:
- In this case, each recognition site will be cleaved, resulting in the formation of two fragments.
- Since there are six recognition sites, the total number of fragments will be 6 x 2 = 12.
2. Overlapping recognition sites:
- If the recognition sites overlap, some of the fragments generated may be the same.
- Let's assume that there are overlapping recognition sites, resulting in the formation of fewer fragments.
- Since there are six recognition sites, the minimum number of fragments that can be generated is 6 x 2 = 12.
- However, since some of the fragments may be the same, the actual number of fragments will be less than 12.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 6 fragments.
In conclusion, the number of fragments generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA is 6.
Given that the restriction enzyme has six recognition sites on the DNA molecule, we can assume that each recognition site will be cleaved by the enzyme, resulting in the formation of two fragments.
Let's analyze the possible scenarios:
1. No overlapping recognition sites:
- In this case, each recognition site will be cleaved, resulting in the formation of two fragments.
- Since there are six recognition sites, the total number of fragments will be 6 x 2 = 12.
2. Overlapping recognition sites:
- If the recognition sites overlap, some of the fragments generated may be the same.
- Let's assume that there are overlapping recognition sites, resulting in the formation of fewer fragments.
- Since there are six recognition sites, the minimum number of fragments that can be generated is 6 x 2 = 12.
- However, since some of the fragments may be the same, the actual number of fragments will be less than 12.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 6 fragments.
In conclusion, the number of fragments generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA is 6.
Stirred-tank bioreactors have advantages over shake flasks because they ___________.- a)Provide high temperature and pH
- b)Provide better aeration and mixing properties
- c)Do not allow the entry of CO2
- d)Are easy to operate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Stirred-tank bioreactors have advantages over shake flasks because they ___________.
a)
Provide high temperature and pH
b)
Provide better aeration and mixing properties
c)
Do not allow the entry of CO2
d)
Are easy to operate
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Stirred-tank bioreactor is used for processing large volumes of culture. It is a cylindrical tank with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor.
Eukaryotic genes do not function properly when cloned into a bacterial cell because
- a)of the inability to excise introns and destruction by bacterial restriction enzymes
- b)of high pH present in bacterial cells
- c)of inappropriate insertion of genes
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Eukaryotic genes do not function properly when cloned into a bacterial cell because
a)
of the inability to excise introns and destruction by bacterial restriction enzymes
b)
of high pH present in bacterial cells
c)
of inappropriate insertion of genes
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Eukaryotic genes do not function properly When transferred into bacterial cell because introns are present eukaryotic cells but are absent in prokaryotic cells. Hence, when bacterial cell is transformed with recombinant DNA is genrated human gene, it could not process it. As a result no desired protien will be produced.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The tumour inducing plasmid (Ti plasmid) acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology.
Statements 2: The Ti plasmid which is used in the mechanisms of delivering genes to a cell remains pathogenic.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The tumour inducing plasmid (Ti plasmid) acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology.
Statements 2: The Ti plasmid which is used in the mechanisms of delivering genes to a cell remains pathogenic.
Statement 1: The tumour inducing plasmid (Ti plasmid) acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology.
Statements 2: The Ti plasmid which is used in the mechanisms of delivering genes to a cell remains pathogenic.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been modified into a cloning vector which is not pathogenic to the plants, However, it is still able to use its mechanism to deliver genes of our interest into various plants.
Who is the father of genetic engineering?- a)Steward Linn
- b)Stanley Cohen
- c)Paul Berg
- d)Kary Mullis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is the father of genetic engineering?
a)
Steward Linn
b)
Stanley Cohen
c)
Paul Berg
d)
Kary Mullis
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
In 1972, genetic engineering was started by Paul Berg. He was able to introduce a gene of the SV-40 virus into a bacterium with the help of lambda phage. Berg is often considered as "Father of genetic engineering". He was awarded Nobel Prize in 1980.
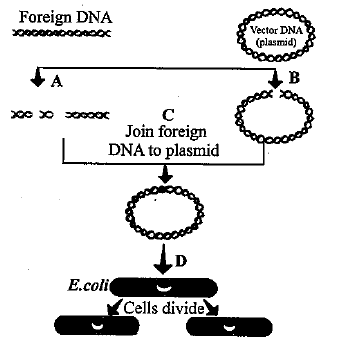
The flow chart given below represents the process of recombinant DNA technology. Identify A, B, C and D
- a)A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-Hydrolase, D-Transduction
- b)A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-DNA ligase, D-Transformation
- c)A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-Hydrolase, D-Transformation
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The flow chart given below represents the process of recombinant DNA technology. Identify A, B, C and D
a)
A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-Hydrolase, D-Transduction
b)
A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-DNA ligase, D-Transformation
c)
A-Restriction endonuclease, B-Restriction endonuclease, C-Hydrolase, D-Transformation
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A and B are restriction endonucleases because same restrction enzyme cuts both foreign DNA and vector DNA at specific Point. C is DNA ligase which joins foreign DNA to vector DNA The newly formed recombinant DNA is transformed in bacteria and tha bacterial cells are allowed to divide.
In the process of insertional inactivation
- a)A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of enzyme -galactosidase, resulting in inactivation of the enzyme
- b)A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid
- c)A recombinat DNA is inserted within the recongnition site for EcoRl
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the process of insertional inactivation
a)
A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of enzyme -galactosidase, resulting in inactivation of the enzyme
b)
A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid
c)
A recombinat DNA is inserted within the recongnition site for EcoRl
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of enzyme -galactosidase, resulting in inactivation of the enzyme
Alternative selectable markers have been developed which differentiate recombinants from the non-recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. In this, a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme, galactosidase. This results into inactivation of the enzyme, which is referred to as insertional inactivation. The presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert. Presence of insert results into insertional inactivation of the -galactosidase gene and the colonies do not produce any colour, these are identified as recombinant colonies.
Alternative selectable markers have been developed which differentiate recombinants from the non-recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. In this, a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme, galactosidase. This results into inactivation of the enzyme, which is referred to as insertional inactivation. The presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert. Presence of insert results into insertional inactivation of the -galactosidase gene and the colonies do not produce any colour, these are identified as recombinant colonies.
The different steps of recombinant DNA technology are given below randomly.
(i) Isolation of the DNA fragments or genes to be cloned
(ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation)
(iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment
(v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vectorWhich of the following represents the correct sequence of steps?- a)(i), (iii), (ii), (iv), (v)
- b)(iii), (ii), (i), (v), (iv)
- c)(i), (v), (ii), (iv), (iii)
- d)(v), (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The different steps of recombinant DNA technology are given below randomly.
(i) Isolation of the DNA fragments or genes to be cloned
(ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation)
(iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment
(v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
(i) Isolation of the DNA fragments or genes to be cloned
(ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation)
(iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment
(v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of steps?
a)
(i), (iii), (ii), (iv), (v)
b)
(iii), (ii), (i), (v), (iv)
c)
(i), (v), (ii), (iv), (iii)
d)
(v), (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
|
|
Pallavi Pillai answered |
Understanding Recombinant DNA Technology Steps
Recombinant DNA technology involves several crucial steps to successfully clone and express a gene of interest. The correct sequence of these steps is pivotal for achieving the desired outcome.
1. Isolation of the DNA Fragments
- This is the first step where the specific DNA fragments or genes that need to be cloned are isolated from the source organism.
2. Insertion into a Suitable Plasmid Vector
- The isolated gene is then inserted into a suitable plasmid vector. This vector is essential as it carries the gene into the host cell.
3. Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Host Cells
- The next step involves the introduction of the recombinant DNA (plasmid containing the gene) into a host cell, typically E. coli. This process is known as transformation.
4. Selection of Transformed Host Cells
- After transformation, it is crucial to select the host cells that have successfully taken up the recombinant DNA. Identification techniques are used to isolate those clones containing the desired gene.
5. Multiplication/Expression of the Introduced Gene
- Finally, the transformed cells multiply and express the introduced gene, producing the desired protein or product.
Correct Sequence Summary
- The correct sequence of steps is:
- (i) Isolation of the DNA fragments
- (v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
- (ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (transformation)
- (iv) Selection of the transformed host cells
- (iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene
This systematic approach ensures that the recombinant DNA technology is executed effectively, leading to successful gene cloning and expression.
Recombinant DNA technology involves several crucial steps to successfully clone and express a gene of interest. The correct sequence of these steps is pivotal for achieving the desired outcome.
1. Isolation of the DNA Fragments
- This is the first step where the specific DNA fragments or genes that need to be cloned are isolated from the source organism.
2. Insertion into a Suitable Plasmid Vector
- The isolated gene is then inserted into a suitable plasmid vector. This vector is essential as it carries the gene into the host cell.
3. Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Host Cells
- The next step involves the introduction of the recombinant DNA (plasmid containing the gene) into a host cell, typically E. coli. This process is known as transformation.
4. Selection of Transformed Host Cells
- After transformation, it is crucial to select the host cells that have successfully taken up the recombinant DNA. Identification techniques are used to isolate those clones containing the desired gene.
5. Multiplication/Expression of the Introduced Gene
- Finally, the transformed cells multiply and express the introduced gene, producing the desired protein or product.
Correct Sequence Summary
- The correct sequence of steps is:
- (i) Isolation of the DNA fragments
- (v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
- (ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (transformation)
- (iv) Selection of the transformed host cells
- (iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene
This systematic approach ensures that the recombinant DNA technology is executed effectively, leading to successful gene cloning and expression.
Match the terms given in column I with their definitions in column II and select the correct answer from codes given below.

- a)A−(iv), B−(i), C−(ii), D−(iii)
- b)A−(iii), B−(i), C−(ii), D−(iv)
- c)A−(i), B−(ii), C−(iii), D−(iv)
- d)A−(ii), B−(iii), C−(iv), D−(i)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the terms given in column I with their definitions in column II and select the correct answer from codes given below.

a)
A−(iv), B−(i), C−(ii), D−(iii)
b)
A−(iii), B−(i), C−(ii), D−(iv)
c)
A−(i), B−(ii), C−(iii), D−(iv)
d)
A−(ii), B−(iii), C−(iv), D−(i)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Transformation is the process of genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through cell membrane.
Recognition site or restriction sites are locations on a DNA molecule containing specific sequences of nucleotides which are recognised by restriction enzymes.
Gel electrophoresis is a process used to separate DNA fragments according to their size and charge.
Recombinant DNA are the DNA molecules from the different species that are inserted into a host to produce new genetic combinations.
Recognition site or restriction sites are locations on a DNA molecule containing specific sequences of nucleotides which are recognised by restriction enzymes.
Gel electrophoresis is a process used to separate DNA fragments according to their size and charge.
Recombinant DNA are the DNA molecules from the different species that are inserted into a host to produce new genetic combinations.
So, the correct answer is A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3.
If you want to recover many copies of the target DNA, you will choose a vector- a)Which does not have the origin of replication
- b)Which has antibiotic resistance gene
- c)Whose origin supports high copy number
- d)Which has only one restriction site
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If you want to recover many copies of the target DNA, you will choose a vector
a)
Which does not have the origin of replication
b)
Which has antibiotic resistance gene
c)
Whose origin supports high copy number
d)
Which has only one restriction site
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Vectors that have high number per cell will have high copy number of their genome within the bacterial cell. If we link an alien piece of DNA with vectorm we can multiply its number equal to the copy number of the vector. Any piece of DNA when linked to the 'ori' sequence, can be made to replicate within the host cells. This property of 'ori' is used to make a number of copies of the linked DNA. If we want to obtain many copies of the target DNA, then it should be cloned in such a vector whose 'ori' supports high copy number.
Which of the following statements is correct for molecular probes?- a)Used to detect the complementary sequence in nucleic acid samples
- b)Used to introduce recombinant DNA Into an animal cell
- c)Used to cut DNA at random positions
- d)Facilitate the multiplication of DNA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct for molecular probes?
a)
Used to detect the complementary sequence in nucleic acid samples
b)
Used to introduce recombinant DNA Into an animal cell
c)
Used to cut DNA at random positions
d)
Facilitate the multiplication of DNA
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Molecular probes are small DNA or RNA segments that are used to detect the presence of complementary sequences in nucleic acid samples. These are usually formed of 200-500 nucleotide sequences but may have up to 500 nucleotides. These segments or probes are labelled either with radioactive or with nonradioactive compound. Single stranded DNA probes, denatured double stranded DNA probes and RNA probes are used for identification and isolation of DNA and RNA.
Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure of E. coli cloning vector pBR322 and select the correct option
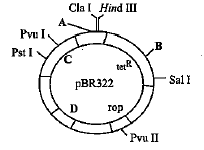
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure of E. coli cloning vector pBR322 and select the correct option


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
pBR322 was the first artificial cloning vector constructed in 1977 by Boliver and Rodriguez. It is widely used in gene cloning experiments. In pBR322 plasmid vector, p - denotes that it is a plasmid; BR - stands for Boliver and Rodriguez who constructed this plasmid; 322 - Is a number given to distinguish this plasmid from others developed in the same laboratory. E coli cloning vector pBR 322 has restriction sites {Hind III, Eco R I, Bam H l, SaI I, PvuI I, Pst I, Cla I), ori(origin of replication) and antibiotic resistance genes (ampR and tetR). rop codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Identify the palindromic sequence in the following.- a)
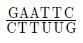
- b)

- c)
- d)
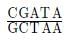
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the palindromic sequence in the following.
a)
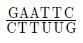
b)

c)
d)
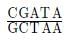
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The palindromes in DNA are base pair sequences that are the same when read forward (left to right) or backward (right to left) from a central axis of symmetry. Thus,  is a palindromic sequence.
is a palindromic sequence.
 is a palindromic sequence.
is a palindromic sequence.In pBR322, tetracycline resistance gene (tetR) has recognition site for which of the following restriction endonuclease?- a)Hind III
- b)Bam H l
- c)Eco R I
- d)Pst l
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In pBR322, tetracycline resistance gene (tetR) has recognition site for which of the following restriction endonuclease?
a)
Hind III
b)
Bam H l
c)
Eco R I
d)
Pst l
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In plasmid vector pBR322, two unique restriction sites Pst I arid Pvu I are located within the ampR gene and Bam H l, SaI I, etc., are located within the tetR gene. The presence of restriction sites within the marker genes tetR and ampR permits an easy selection for cells transformed with the I recombinant pBR322. When restriction enzyme Bam H l or SaI I is used, the DNA insert is placed within the gene tetR making it nonfunctional.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









