All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes for NEET Exam
The sequence of the 5’ and 3’ primers for the following DNA sequence will be:
5’ AATGCGGCAATCGAGTC3’
3’ TTACGCCGTTAGCTCCAG5’- a)5’ TTACG 3’, 5’ CTGAG 3’
- b)5’ AATGC 3’, 5’ TTACG 3’
- c)5’ AATGC 3’, 5’ GACTC 3’
- d)5’ AGTC 3’ , 5’ TCAG 3’
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence of the 5’ and 3’ primers for the following DNA sequence will be:
5’ AATGCGGCAATCGAGTC3’
3’ TTACGCCGTTAGCTCCAG5’
5’ AATGCGGCAATCGAGTC3’
3’ TTACGCCGTTAGCTCCAG5’
a)
5’ TTACG 3’, 5’ CTGAG 3’
b)
5’ AATGC 3’, 5’ TTACG 3’
c)
5’ AATGC 3’, 5’ GACTC 3’
d)
5’ AGTC 3’ , 5’ TCAG 3’

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
The sequence of the 5’ and 3’ primers for the given DNA sequence will be 5’ AATGC 3’, 5’ GACTC 3’.
Which one is called molecular scissors?a) Endocrine
b) Ribonucleasec) Restriction enzymesd) ExonucleaseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Restriction enzymes are also called 'molecular scissors' as they cleave DNA at or near specific recognition sequences known as restriction sites. These enzymes make one incision on each of the two strands of DNA and are also called restriction endonucleases.
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non recombinant bacteria because of :
[NEET 2013]
- a)Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
- b)Non-recombinant bacteria containing β-galactosidease
- c)Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non recombinant bacteria because of :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Insertional inactivation of α-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
b)
Non-recombinant bacteria containing β-galactosidease
c)
Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
d)
None of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The blue-white screen is a screening technique that allows for the rapid and convenient detection of recombinant bacteria . This technique is based on the insertional inactivation of the β-galactosidase gene.
Cells transformed with vector containing the recombinant DNA contain an inactive form of the β-galactosidase gene and hence produce white colonies.
cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmid i.e. only the vector, have an active β-galactosidase gene and thus produce blue colonies.
Cells transformed with vector containing the recombinant DNA contain an inactive form of the β-galactosidase gene and hence produce white colonies.
cells transformed with non-recombinant plasmid i.e. only the vector, have an active β-galactosidase gene and thus produce blue colonies.
During agarose gel, electrophoresis DNA fragments move towards the anode. This is because _________.
- a)Anode is negatively charged.
- b)DNA moves in random direction.
- c)DNA is negatively charged molecules.
- d)DNA is positively charged molecules.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During agarose gel, electrophoresis DNA fragments move towards the anode. This is because _________.
a)
Anode is negatively charged.
b)
DNA moves in random direction.
c)
DNA is negatively charged molecules.
d)
DNA is positively charged molecules.

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
- In gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules moves towards positively charged anode because DNA is negatively charged molecules.
- The molecules separate out due to difference in molecular weight.
The group of letters that form same words when read both forward and backward are called?- a)Palindrome
- b)Puzzle
- c)Endonucleases
- d)Sticky ends
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The group of letters that form same words when read both forward and backward are called?
a)
Palindrome
b)
Puzzle
c)
Endonucleases
d)
Sticky ends

|
Pooja Saha answered |
The groups of letters that form same words when read both forward and backward are called Palindrome. For example MALYALAM which read same from both side.
Insertional inactivation helps in- a)X-gal breakdown
- b)Identification of recombinant clones
- c)Ampicillin resistance
- d)Functioning of B-galactosidase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Insertional inactivation helps in
a)
X-gal breakdown
b)
Identification of recombinant clones
c)
Ampicillin resistance
d)
Functioning of B-galactosidase
|
|
Bhargavi Choudhary answered |
Insertional inactivation is a technique used in molecular biology to identify recombinant clones. It involves the insertion of a foreign DNA fragment into a plasmid vector, which disrupts the function of a selectable marker gene. This results in the loss of the ability of the host cell to grow on a selective medium containing the corresponding antibiotic.
Mechanism
The mechanism of insertional inactivation involves the insertion of a foreign DNA fragment into a plasmid vector, which disrupts the function of a selectable marker gene. The selectable marker gene is usually a gene that confers resistance to an antibiotic, such as ampicillin. The disruption of this gene results in the loss of the ability of the host cell to grow on a selective medium containing the corresponding antibiotic. This allows for the identification of recombinant clones that have taken up the plasmid vector with the foreign DNA fragment.
Applications
Insertional inactivation is commonly used in molecular biology to identify recombinant clones. It is particularly useful in the construction of cDNA libraries and the screening of genomic DNA libraries for specific genes. It can also be used to study gene expression and regulation, as well as for the production of recombinant proteins.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insertional inactivation is a useful technique in molecular biology for identifying recombinant clones. It involves the insertion of a foreign DNA fragment into a plasmid vector, which disrupts the function of a selectable marker gene. This results in the loss of the ability of the host cell to grow on a selective medium containing the corresponding antibiotic, allowing for the identification of recombinant clones that have taken up the plasmid vector with the foreign DNA fragment.
Mechanism
The mechanism of insertional inactivation involves the insertion of a foreign DNA fragment into a plasmid vector, which disrupts the function of a selectable marker gene. The selectable marker gene is usually a gene that confers resistance to an antibiotic, such as ampicillin. The disruption of this gene results in the loss of the ability of the host cell to grow on a selective medium containing the corresponding antibiotic. This allows for the identification of recombinant clones that have taken up the plasmid vector with the foreign DNA fragment.
Applications
Insertional inactivation is commonly used in molecular biology to identify recombinant clones. It is particularly useful in the construction of cDNA libraries and the screening of genomic DNA libraries for specific genes. It can also be used to study gene expression and regulation, as well as for the production of recombinant proteins.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insertional inactivation is a useful technique in molecular biology for identifying recombinant clones. It involves the insertion of a foreign DNA fragment into a plasmid vector, which disrupts the function of a selectable marker gene. This results in the loss of the ability of the host cell to grow on a selective medium containing the corresponding antibiotic, allowing for the identification of recombinant clones that have taken up the plasmid vector with the foreign DNA fragment.
Having two antibiotic resistant genes in the same plasmid- a)two antibiotics add to the effect for selection
- b)helps in identifying transformants
- c)one antibiotic does not gives the sufficient result
- d)one antibiotic may not be functional
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Having two antibiotic resistant genes in the same plasmid
a)
two antibiotics add to the effect for selection
b)
helps in identifying transformants
c)
one antibiotic does not gives the sufficient result
d)
one antibiotic may not be functional

|
Ved Patidar answered |
In general genes that confer resistance to various antibiotics are used as selective marker in cloning vectors.
Enzymes used to join foreign DNA to plasmid is______.- a)Nucleases
- b)Ligases
- c)Endonucleases
- d)Pectinases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes used to join foreign DNA to plasmid is______.
a)
Nucleases
b)
Ligases
c)
Endonucleases
d)
Pectinases

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The Enzymes used to join foreign DNA to plasmid is ligases. The plasmid of bacteria replicate this DNA strands along with other which can be further transferred to target cells.
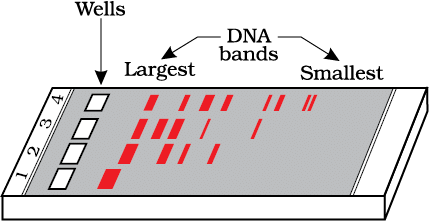
The smallest bands in the agarose gel will be towards- a)Wells
- b)Middle of the gel
- c)Cathode
- d)Anode
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The smallest bands in the agarose gel will be towards
a)
Wells
b)
Middle of the gel
c)
Cathode
d)
Anode

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
Gel electrophoresis technique involves separation of different segments of DNA according to their size. The smallest bands in the agarose gel will be towards positively charged anode.
Biolistics (gene-gun) is suitable for[2012M]a)DNA finger printing.b)Disarming pathogen vectors.c)Constructing recombinant DNA by joining with vectors.d)Transformation of plant cells.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A gene gun or a biolistic particle delivery system, originally designed for plant transformation, is a device for delivering exogenous DNA (transgenes) to cells. The payload is an elemental particle of a heavy metal coated with DNA (typically plasmid DNA). This technique is often simply referred to as biolistics.
The particles used to coat with DNA in Biolistic gun is of- a)Tungsten
- b)Zinc
- c)Helium
- d)Quartz
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The particles used to coat with DNA in Biolistic gun is of
a)
Tungsten
b)
Zinc
c)
Helium
d)
Quartz

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
DNA is coated with tungsten before used in biolistic gun for inserting the DNA directly into target cells for obtaining particular protein.
Rop genes in pBR322 codes for______.- a)Tetracycline resistance
- b)Antibiotic resistance
- c)Proteins involved in replication of plasmid
- d)Ampicillin resistance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rop genes in pBR322 codes for______.
a)
Tetracycline resistance
b)
Antibiotic resistance
c)
Proteins involved in replication of plasmid
d)
Ampicillin resistance

|
Yash Saha answered |
Rop genes in pBR322 codes for protein involved in replication of plasmid. Plasmid are able to take the foreign gene and to be transferred to target cells.
Origin of replication is the specific DNA sequence on chromosome that which is responsible for- a)Initiating replication
- b)Synthesis of polymerase enzyme
- c)Terminating replication
- d)All of the these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Origin of replication is the specific DNA sequence on chromosome that which is responsible for
a)
Initiating replication
b)
Synthesis of polymerase enzyme
c)
Terminating replication
d)
All of the these

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
For replication of DNA their is specific seq. like TATA BOX
A bioreactor is:- a)Culture for synthesis of new chemicals
- b)Hybridoma
- c)Culture containing radioactive isotopes
- d)Fermentation tank
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bioreactor is:
a)
Culture for synthesis of new chemicals
b)
Hybridoma
c)
Culture containing radioactive isotopes
d)
Fermentation tank
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Fermentation is defined more from the point of view of engineers. They see fermentation as the cultivation of high amount of microorganisms and biotransformation being carried out in special vessels called fermenter or bioreactors.
The nuclease will act on______.- a)DNA only
- b)Proteins
- c)RNA only
- d)DNA and RNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The nuclease will act on______.
a)
DNA only
b)
Proteins
c)
RNA only
d)
DNA and RNA

|
Arya Khanna answered |
The enzyme nuclease acts on nucleic acid DNA and RNA. This enzyme is used to hydrolyze nucleic acid.
‘R’ in EcoRI restriction endonuclease denotes- a)Strain RY13
- b)Sequence of isolation of the enzyme
- c)Species
- d)Genus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
‘R’ in EcoRI restriction endonuclease denotes
a)
Strain RY13
b)
Sequence of isolation of the enzyme
c)
Species
d)
Genus

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
EcoRI comes from Escherichia coli RY 13. In EcoRI, the letter ‘R’ is derived from the name of strain.
Polyethylene glycol method is used for[2009]- a)biodiesel production
- b)seedless fruit production
- c)energy production from sewage
- d)gene transfer without a vector
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Polyethylene glycol method is used for
[2009]
a)
biodiesel production
b)
seedless fruit production
c)
energy production from sewage
d)
gene transfer without a vector

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Direct gene transfer is the transfer of naked. DNA into plant cells but the presence of rigid plant cell wall acts as a barrier to uptake. Therefore protoplasts are the favoured target for direct gene transfer. Polyethylene glycol mediated DNA uptake is a direct gene transfer method that utilizes the interaction between polyethylene glycol, naked DNA, salts and the protoplast membrane to effect transport of the DNA into the cytoplasm.
In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used[2012M]- a)as selectable markers.
- b)to select healthy vectors.
- c)to keep the cultures free of infection.
- d)as sequences from where replication starts.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
[2012M]
a)
as selectable markers.
b)
to select healthy vectors.
c)
to keep the cultures free of infection.
d)
as sequences from where replication starts.

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Antibiotics are powerful medicines that fight bacterial infections. They either kill bacteria or keep them from reproducing. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used as selectable markers.
The technique used to produce large number of genetically identical offspring is called as______.- a)PCR
- b)Southern Blotting
- c)Northern Blotting
- d)Cloning
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The technique used to produce large number of genetically identical offspring is called as______.
a)
PCR
b)
Southern Blotting
c)
Northern Blotting
d)
Cloning

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Cloning is the technique of producing large number of genetically identical offspring.
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR[2012]- a)It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cell
- b)It serves as a selectable marker
- c)It is isolated from a virus
- d)It remains active at high temperature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR
[2012]
a)
It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cell
b)
It serves as a selectable marker
c)
It is isolated from a virus
d)
It remains active at high temperature

|
Rohan Unni answered |
The name of this DNA polymerase is Taq polymerase extracted from a thermophilic bacterial.
The figure below is the diagrammatic representation of the E.Coli vector pBR 322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component (s) ?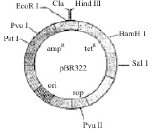 [2012]
[2012] - a)ori - original restriction enzyme
- b)rop-reduced osmotic pressure
- c)Hind III, EcoRI - selectable markers
- d)ampR, tetR - antibiotic resistance genes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure below is the diagrammatic representation of the E.Coli vector pBR 322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component (s) ?

[2012]
a)
ori - original restriction enzyme
b)
rop-reduced osmotic pressure
c)
Hind III, EcoRI - selectable markers
d)
ampR, tetR - antibiotic resistance genes

|
Palak Khanna answered |
In pBR 322
ori - represents site of originor replication rop-represents those proteins that take part in replication of plasmid. Hind III, EcoRI- Recoginition sites of Restriction endonucleases ampR and tetR - They are antibiotic resistant gene part
DNA can be isolated from fungi using chitinase as_______.- a)Its cell wall is made up of chitin
- b)It makes DNA soluble in the aqueous solution
- c)It carries out isolation fast
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA can be isolated from fungi using chitinase as_______.
a)
Its cell wall is made up of chitin
b)
It makes DNA soluble in the aqueous solution
c)
It carries out isolation fast
d)
None of the above

|
Aman Sharma answered |
The cell of fungi is made of chitin. Chitinase enzyme can hydrolyses this and DNA can be isolated from fungi.
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for :[2012]- a)Study of enzymes
- b)Genetic transformation
- c)DNA sequencing
- d)Genetic Fingerprinting
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for :
[2012]
a)
Study of enzymes
b)
Genetic transformation
c)
DNA sequencing
d)
Genetic Fingerprinting
|
|
Avantika Roy answered |
PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) are the methods used for Genetic Fingerprinting.
Genetic Fingerprinting:
Genetic Fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on differences in their DNA sequences. It is also known as DNA fingerprinting, DNA profiling or DNA typing. Genetic fingerprinting is used in forensic investigations, paternity testing, and studying genetic relationships between individuals.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It is a three-step process that involves denaturation, annealing, and extension. PCR is used to create a large amount of DNA from a small amount of starting material, such as a single hair or a drop of blood.
RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
RFLP is a technique used to analyze differences in DNA sequences. It involves cutting DNA with a restriction enzyme and separating the resulting fragments by gel electrophoresis. RFLP is used to identify genetic variations between individuals.
PCR and RFLP are used together in genetic fingerprinting to create a unique DNA profile for an individual. PCR is used to amplify specific regions of DNA, and RFLP is used to analyze the resulting fragments to identify differences between individuals. These differences are then used to create a DNA profile that can be used for identification purposes.
Genetic Fingerprinting:
Genetic Fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on differences in their DNA sequences. It is also known as DNA fingerprinting, DNA profiling or DNA typing. Genetic fingerprinting is used in forensic investigations, paternity testing, and studying genetic relationships between individuals.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It is a three-step process that involves denaturation, annealing, and extension. PCR is used to create a large amount of DNA from a small amount of starting material, such as a single hair or a drop of blood.
RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism):
RFLP is a technique used to analyze differences in DNA sequences. It involves cutting DNA with a restriction enzyme and separating the resulting fragments by gel electrophoresis. RFLP is used to identify genetic variations between individuals.
PCR and RFLP are used together in genetic fingerprinting to create a unique DNA profile for an individual. PCR is used to amplify specific regions of DNA, and RFLP is used to analyze the resulting fragments to identify differences between individuals. These differences are then used to create a DNA profile that can be used for identification purposes.
Phage is a______.- a)Fungi
- b)Virion
- c)Viroids
- d)Virus that infects bacteria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phage is a______.
a)
Fungi
b)
Virion
c)
Viroids
d)
Virus that infects bacteria

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
Phage is a virus that infects bacteria. Such viruses transfer their genetic materials into host bacteria and using the bacterial machinery increase in number and multiply rapidly to kill host cells.
In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their:- a)Charge only
- b)Charge to size ratio
- c)both a and b
- d)Size only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their:
a)
Charge only
b)
Charge to size ratio
c)
both a and b
d)
Size only
|
|
Sruthi Kadambala answered |
The smaller the size the farther it moves hence depend only on the size
Study the following statements regarding recombinant DNA technology and select the incorrect ones
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction- a)(i), (iii) and (vi)
- b)(i), (iii) and (v)
- c)(ii), (iii) and (v)
- d)(i), (iv) and (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements regarding recombinant DNA technology and select the incorrect ones
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction
a)
(i), (iii) and (vi)
b)
(i), (iii) and (v)
c)
(ii), (iii) and (v)
d)
(i), (iv) and (v)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Antibiotic resistance genes are selectable markers. Desirable genes are the ones which are introduced in the vector for getting desired protein product. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments are separated according to their charge and size. After the formation of the product in a bioreactors, it undergoes through some processes before a finished product is ready for marketing. The processes include separation and purification of products which are collectively called as downstream processing.
There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does .co. part in it stand for ?[2011]- a)colon
- b)coelom
- c)coenzyme
- d)coli
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does .co. part in it stand for ?
[2011]
a)
colon
b)
coelom
c)
coenzyme
d)
coli

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
EcoRI is an endonuclease enzyme isolated from strains of E.coli and a part of restriction modified system. So co part stands for coli.
Genes of interest can be selected from a genomic library by using[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Restriction enzymes
- b)Cloning vectors
- c)DNA probes
- d)Gene targets
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Genes of interest can be selected from a genomic library by using
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Restriction enzymes
b)
Cloning vectors
c)
DNA probes
d)
Gene targets

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
A hybridization probe is a fragment of DNA of variable length which is used in DNA samples to detect the presence of nucleotide sequence (the DNA target) that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. The probe hybridize to single–stranded DNA whose base sequence allow probe target base-pairing due to complementary between the probe and target.
Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are- a)Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- b)Vibrio cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
- c)Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
- d)Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are
a)
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
b)
Vibrio cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
c)
Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
d)
Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens are the microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering.
E. coli is a motile, gram negative, rod shaped bacterium which is a normal inhabitant of human colon. It is most extensively used in bacterial genetics and molecular biology.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium. It has Ti plasmid (Tumour inducing plasmid) and it can be used for the transfer of a desired gene in dicot plants.
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by :[NEET 2013]- a)Polymerase chain reaction
- b)Electrophoresis
- c)Restriction mapping
- d)Centrifugation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Polymerase chain reaction
b)
Electrophoresis
c)
Restriction mapping
d)
Centrifugation

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
DNA fragments generated by restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by gel electrophoresis. Since DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix. The DNA fragments separate according to their size through sieving effect provided by matrix.
Read the following text and answer the following question on the basis of the same:The term biotechnology refers to the use of living organisms or their products to modify human health and their human environment. For example, ‘testtube’ programme, synthesis of a gene or correcting a defective gene are all part of biotechnology. The basis of modern biotechnology is genetic engineering and maintenance of sterile conditions. Genetic engineering is the technique that alter the chemistry of genetic material i.e. DNA and RNA, then this genetic material is introduced into host organisms, which alter the phenotype of the host organism.Q. The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of :- a)Ligases
- b)Restriction enzymes
- c)Probes
- d)Selectable markers.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following text and answer the following question on the basis of the same:
The term biotechnology refers to the use of living organisms or their products to modify human health and their human environment. For example, ‘testtube’ programme, synthesis of a gene or correcting a defective gene are all part of biotechnology. The basis of modern biotechnology is genetic engineering and maintenance of sterile conditions. Genetic engineering is the technique that alter the chemistry of genetic material i.e. DNA and RNA, then this genetic material is introduced into host organisms, which alter the phenotype of the host organism.
Q. The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of :
a)
Ligases
b)
Restriction enzymes
c)
Probes
d)
Selectable markers.
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Restriction enzymes are the molecular scissors that cut the DNA from a specific recognition site.
After completion of the biosynthetic stage in the bioreactors, the product undergoes separation and purification processes, collectively termed as __________.- a)Transformation
- b)Electrophoresis
- c)Downstream processing
- d)Upstream processing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
After completion of the biosynthetic stage in the bioreactors, the product undergoes separation and purification processes, collectively termed as __________.
a)
Transformation
b)
Electrophoresis
c)
Downstream processing
d)
Upstream processing
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
After the formation of the product in bioreactors, it undergoes through some processes before a finished product is ready for marketing. The processes include separation and purification of products which is collectively called as downstream processing.
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :Assertion (A) : E. coli having pBR322 with DNA insert at BamHI site cannot grow in medium containing tetracycline.Reason(R) : Recognition site for BamH I is present in TetR region of pBR322.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
Assertion (A) : E. coli having pBR322 with DNA insert at BamHI site cannot grow in medium containing tetracycline.
Reason(R) : Recognition site for BamH I is present in TetR region of pBR322.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
PBR322 carries recognition sites for a number of commonly used restriction enzymes. Recognition site for BamHl is present in the tetr region i.e., the region responsible for tetracycline resistance. When an insert is added at the BamHl recognition site the gene for tetracycline resistance becomes non-functional and the recombinant bacteria with plasmid pBR322 that has DNA inserted at BamHl lose tetracycline resistance.
Which of the following is correct sequence of process of recombinant DNA technology-
i. Isolation of DNA
ii. Isolation of desired DNA fragment.
iii. Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonuclease.
iv. Transferring of into host
v. Ligation of DNA fragment into vector
vi. Culturing in host cell to get desired product.- a)Step v, vi, iv, iii, ii and i
- b)Step i, ii, iii, iv, v and vi
- c)Step i, iii, ii, v, iv and vi
- d)Step i, iv, iii, ii, v and vi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct sequence of process of recombinant DNA technology-
i. Isolation of DNA
ii. Isolation of desired DNA fragment.
iii. Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonuclease.
iv. Transferring of into host
v. Ligation of DNA fragment into vector
vi. Culturing in host cell to get desired product.
i. Isolation of DNA
ii. Isolation of desired DNA fragment.
iii. Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonuclease.
iv. Transferring of into host
v. Ligation of DNA fragment into vector
vi. Culturing in host cell to get desired product.
a)
Step v, vi, iv, iii, ii and i
b)
Step i, ii, iii, iv, v and vi
c)
Step i, iii, ii, v, iv and vi
d)
Step i, iv, iii, ii, v and vi

|
Arya Khanna answered |
The correct sequences of process of recombinant DNA technology are Isolation of DNA, fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonuclease, isolation of desired DNA fragment, ligation of DNA fragment into vector, transferring of into host and culturing in host cell to get desired product.
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :- a)Silver or Platinum
- b)Gold or Tungsten
- c)Silicon or Platinum
- d)Platinum or Zinc
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :
a)
Silver or Platinum
b)
Gold or Tungsten
c)
Silicon or Platinum
d)
Platinum or Zinc
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
For gene transfer into the host cell without using vector microparticles made of tungsten and gold coated with foregin DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. This method is called biolistics or gene gun which is suitable for plants.So the correct option is 'gold or tungsten'.
Plasmid used to construct the first recombinant DNA was isolated from which bacterium species?- a)Escherichia coli
- b)Salmonella typhimurium
- c)Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- d)Thermus aquaticus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmid used to construct the first recombinant DNA was isolated from which bacterium species?
a)
Escherichia coli
b)
Salmonella typhimurium
c)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
d)
Thermus aquaticus
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The first recombinant DNA was constructed by Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer in 1972. They cut the piece of DNA from a plasmid carrying antibiotic resistance gene in the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium and linked it to the plasmid of Escherichia coil.
Introduction of food plants developed by genetic engineering is not desirable because[2002]- a)economy of developing countries may suffer
- b)these products are less tasty as compared to the already existing products
- c)this method is costly
- d)there is danger of entry of viruses and toxins with introduced crop
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Introduction of food plants developed by genetic engineering is not desirable because
[2002]
a)
economy of developing countries may suffer
b)
these products are less tasty as compared to the already existing products
c)
this method is costly
d)
there is danger of entry of viruses and toxins with introduced crop

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Plants developed by genetic engineering are called transgenic plants or genetically modified crops from which genetically modified food is produced. For their production micro-organisms (bacteria, virus) are used. So, by consuming them there is a danger of entry of viruses and toxins causing differ types of allergies and other health hazards to human beings.
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:- a)Identification of a person
- b)Paternity dispute
- c)Maternity dispute
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:
a)
Identification of a person
b)
Paternity dispute
c)
Maternity dispute
d)
All of above
|
|
Athul Chakraborty answered |
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:
Identification of a person:
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles.
- Every person's DNA is unique, except for identical twins, making DNA fingerprinting a highly accurate method for identification.
- By comparing DNA samples from a crime scene, for example, with the DNA profiles of suspects, forensic scientists can determine the identity of the perpetrator.
Paternity dispute:
- DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve paternity disputes.
- By analyzing the DNA profiles of a child and potential fathers, it is possible to determine the biological father.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential fathers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential father that are not present in the other potential fathers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological father.
Maternity dispute:
- Similarly, DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve maternity disputes.
- By analyzing DNA profiles of a child and potential mothers, it is possible to determine the biological mother.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential mothers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential mother that are not present in the other potential mothers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological mother.
All of the above:
- DNA fingerprinting can resolve all the mentioned scenarios: identification of a person, paternity disputes, and maternity disputes.
- This technique has revolutionized forensic science, allowing accurate identification of individuals involved in criminal activities.
- It has also played a crucial role in resolving legal disputes regarding parentage, ensuring the correct determination of biological relationships.
In conclusion, DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool that can be used to resolve various scenarios, including the identification of individuals, determination of paternity, and resolution of maternity disputes. Its accuracy and reliability make it an indispensable technique in forensic science and legal proceedings.
Identification of a person:
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles.
- Every person's DNA is unique, except for identical twins, making DNA fingerprinting a highly accurate method for identification.
- By comparing DNA samples from a crime scene, for example, with the DNA profiles of suspects, forensic scientists can determine the identity of the perpetrator.
Paternity dispute:
- DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve paternity disputes.
- By analyzing the DNA profiles of a child and potential fathers, it is possible to determine the biological father.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential fathers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential father that are not present in the other potential fathers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological father.
Maternity dispute:
- Similarly, DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve maternity disputes.
- By analyzing DNA profiles of a child and potential mothers, it is possible to determine the biological mother.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential mothers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential mother that are not present in the other potential mothers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological mother.
All of the above:
- DNA fingerprinting can resolve all the mentioned scenarios: identification of a person, paternity disputes, and maternity disputes.
- This technique has revolutionized forensic science, allowing accurate identification of individuals involved in criminal activities.
- It has also played a crucial role in resolving legal disputes regarding parentage, ensuring the correct determination of biological relationships.
In conclusion, DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool that can be used to resolve various scenarios, including the identification of individuals, determination of paternity, and resolution of maternity disputes. Its accuracy and reliability make it an indispensable technique in forensic science and legal proceedings.
Which of the given statements is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis?- a)Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light
- b)DNA can be seen without staining in visible light
- c)Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen in visible light
- d)DNA can be seen in visible light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the given statements is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis?
a)
Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light
b)
DNA can be seen without staining in visible light
c)
Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen in visible light
d)
DNA can be seen in visible light
|
|
Vaishnavi Sen answered |
Visualizing DNA Molecules Separated by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique to separate DNA molecules based on their size. The separated DNA fragments can be visualized using different methods.
Ethidium Bromide Staining and UV Light
Ethidium bromide is a commonly used fluorescent dye that intercalates into the DNA double helix and emits fluorescence under UV light. When DNA is stained with ethidium bromide and exposed to UV light, the dye binds to the DNA and fluoresces, allowing the DNA bands to be visualized.
Correct Statement
Option 'A' is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light. The other options are incorrect because DNA cannot be seen without staining in visible light, and ethidium bromide stained DNA cannot be seen in visible light. However, DNA can be seen in visible light if it is stained with other dyes such as SYBR Green.
Significance
Visualization of DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis is important in various molecular biology applications, including genomic DNA analysis, PCR product analysis, and DNA sequencing. Ethidium bromide staining and UV light visualization are the most commonly used methods due to their simplicity, sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness. However, the use of ethidium bromide has some safety concerns due to its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Therefore, alternative DNA stains such as SYBR Green and GelRed have been developed, which are safer and more environmentally friendly.
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique to separate DNA molecules based on their size. The separated DNA fragments can be visualized using different methods.
Ethidium Bromide Staining and UV Light
Ethidium bromide is a commonly used fluorescent dye that intercalates into the DNA double helix and emits fluorescence under UV light. When DNA is stained with ethidium bromide and exposed to UV light, the dye binds to the DNA and fluoresces, allowing the DNA bands to be visualized.
Correct Statement
Option 'A' is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Ethidium bromide stained DNA can be seen under exposure to UV light. The other options are incorrect because DNA cannot be seen without staining in visible light, and ethidium bromide stained DNA cannot be seen in visible light. However, DNA can be seen in visible light if it is stained with other dyes such as SYBR Green.
Significance
Visualization of DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis is important in various molecular biology applications, including genomic DNA analysis, PCR product analysis, and DNA sequencing. Ethidium bromide staining and UV light visualization are the most commonly used methods due to their simplicity, sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness. However, the use of ethidium bromide has some safety concerns due to its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Therefore, alternative DNA stains such as SYBR Green and GelRed have been developed, which are safer and more environmentally friendly.
DNA strands on a gel stained with ethidium bromide when viewed under UV radiation, appear as: [NEET 2021]- a)Dark red bands
- b)Bright blue bands
- c)Yellow bands
- d)Bright orange bands
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA strands on a gel stained with ethidium bromide when viewed under UV radiation, appear as: [NEET 2021]
a)
Dark red bands
b)
Bright blue bands
c)
Yellow bands
d)
Bright orange bands
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The separated DNA fragments can be visualised only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation (you cannot see pure DNA fragments in the visible light and without staining). You can see bright orange coloured bands of DNA in a ethidium bromide stained gel exposed to UV light.

If a plasmid vector is digested with EcoRI at a single site, then- a)One sticky ends will be produced
- b)Two sticky ends will be produced
- c)Four sticky ends will be produced
- d)Six sticky ends will be produced
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a plasmid vector is digested with EcoRI at a single site, then
a)
One sticky ends will be produced
b)
Two sticky ends will be produced
c)
Four sticky ends will be produced
d)
Six sticky ends will be produced
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Plasmid is a circular DNA, if it is digested at a single site, one fragment will be produced with two sticky ends.
Read statements (i)-(iv). Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.- a)(ii) and (iii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (ii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read statements (i)-(iv). Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.
(i) First transgenic buffalo Rosie produced milk which was human alpha-lactalbumin enriched.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used in isolation of DNA from other macromolecules.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.
a)
(ii) and (iii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (ii)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In 1997, Rosie, the tirst transgenic cow was engineered to produce milk enriched with a human protein called alpha-lactalbumin, making it nutritionally more balanced. Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sites.
Assertion: The separated DNA fragments can be visualized only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Reason: We can see bright red coloured bands of DNA in an ethidium bromide-stained gel exposed to UV light.- a)Both assertion and reason are correct.
- b)Assertion is correct but reason does not explain the assertion
- c)Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
- d)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The separated DNA fragments can be visualized only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Reason: We can see bright red coloured bands of DNA in an ethidium bromide-stained gel exposed to UV light.
Reason: We can see bright red coloured bands of DNA in an ethidium bromide-stained gel exposed to UV light.
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct.
b)
Assertion is correct but reason does not explain the assertion
c)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
d)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The separated DNA fragments can be visualized only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation. We can see bright orange coloured bands of DNA in aethidium bromide stained gel exposed to UV light.
Topic in NCERT: Separation and isolation of DNA fragments
Line in NCERT: "The separated DNA fragments can be visualised only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation (you cannot see pure DNA fragments in the visible light and without staining). You can see bright orange coloured bands of DNA in an ethidium bromide stained gel exposed to UV light."
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :Assertion (A) : Thermus aquaticus, is used in PCR technique.Reason (R) : It is a heat-stable DNA polymerase.- a)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- b)Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
Assertion (A) : Thermus aquaticus, is used in PCR technique.
Reason (R) : It is a heat-stable DNA polymerase.
a)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
b)
Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Thermus aquaticus is the source of DNA polymerase because it is a heat-stable DNA polymerase.
Which of the following is not a desirable feature of a cloning vector?- a)Presence of origin of replication
- b)Presence of a marker gene
- c)Presence of single restriction enzyme site
- d)Presence of two or more recognition sites
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a desirable feature of a cloning vector?
a)
Presence of origin of replication
b)
Presence of a marker gene
c)
Presence of single restriction enzyme site
d)
Presence of two or more recognition sites

|
Top Rankers answered |
Option (d) is the correct answer. Cloning vectors are the carriers of the desired gene in the host cell. The features desirable in a cloning vector are :-
- Presence of origin of replication
- Presence of marker genes
- Presence of very few, preferably single recognition site for the commonly used restriction enzymes
Primers are______.- a)Nucleases
- b)Fragments of RNA
- c)Palindromic sequences
- d)Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Primers are______.
a)
Nucleases
b)
Fragments of RNA
c)
Palindromic sequences
d)
Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Primers are chemically synthesized oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA and the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Restriction endonuclease- a)Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
- b)Synthesizes DNA
- c)Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
- d)Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Restriction endonuclease
a)
Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
b)
Synthesizes DNA
c)
Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
d)
Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
Restriction endonuclease is a type of enzyme that can cleave molecules of DNA at a particular site called restriction site having polindromic sequence. These enzymes are produced by many bacteria and protect the cell by cleaving and destroying the DNA of invading viruses. Now a days, restriction enzymes are widely used in the techniques of genetic engineering.Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______- a)ligase
- b)lipase
- c)DNase
- d)RNase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______
a)
ligase
b)
lipase
c)
DNase
d)
RNase
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is DNase. It catalyzes the breakdown of phosphodiester linkages of DNA. It is a type of endonuclease. Ligases are the enzymes used in the joining of two strands.
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?- a)To release DNA from cells
- b)To remove proteins
- c)To isolate RNA
- d)To precipitate DNA with ethanol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?
a)
To release DNA from cells
b)
To remove proteins
c)
To isolate RNA
d)
To precipitate DNA with ethanol

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, and chitinase are used to break down cell walls and release DNA from cells.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









